| Subtotal | $0.00 |
| Subtotal | $0.00 |
When a new SSL certificate is activated, quite often a question arises: “How to put the domain in the CSR? With or without www?”. Now we will clarify this for you.
Even if the www.example.com subdomain is considered just a copy of the bare domain website, it is still a different name for SSL certificates. Some certificates do include it as a free Subject Alternative Name, some of them do not. This feature depends on the certificate type, and the rules of the Authority this certificate is issued by. Let us look through this question in a detailed way.
Single-domain Comodo (now Sectigo) certificates will secure both - your bare domain and its www version - by default. For these certificates, it does not matter whether you specify the Common Name with or without www in your CSR.
This feature is completely different for Comodo (now Sectigo) Multi-domain certificates. Every domain or subdomain in such a certificate will go to a separate Subject Alternative Name slot. So, if you need to secure both, the bare and www versions of your domains, it will be necessary to fill them in separately - one as a Common Name and one as a SAN - like on the screenshot below:
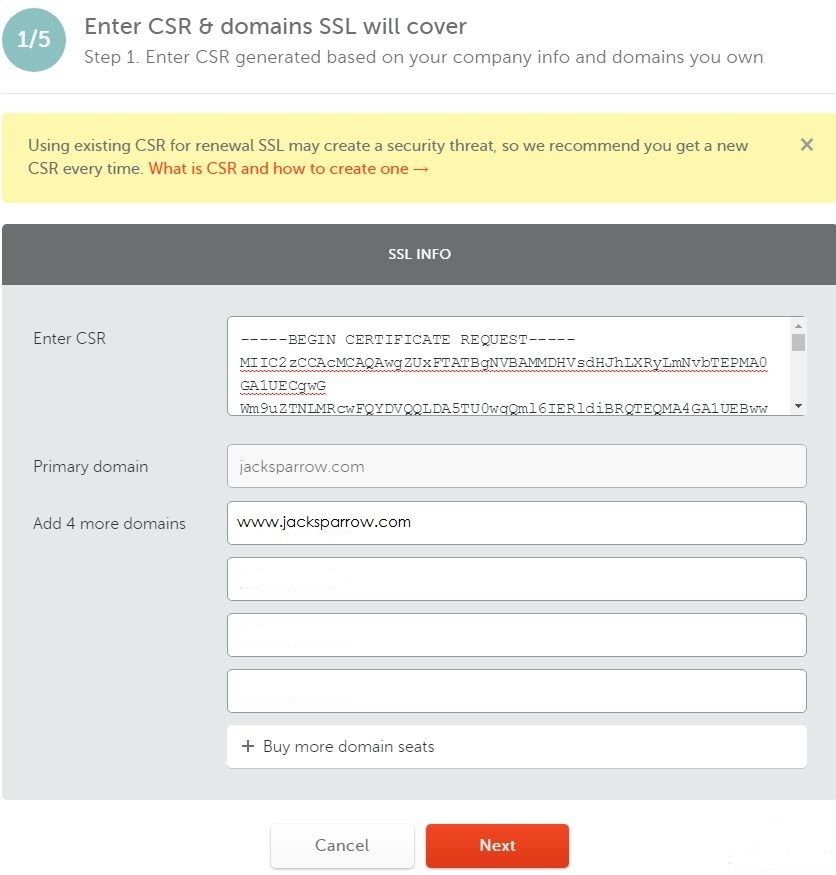
There is no difference at all which of them will go to the Common name in the CSR, and which will be specified as Domain 2 during activation.
The feature of WildCard SSLs is multiple subdomains security. If the Common Name in a Wildcard certificate is specified as *.www.example.com, no other first-level subdomains will be secured (e.g. sub1.example.com, sub2.example.com etc.). You will only be able to secure the second-level subdomains (sub1.www.example.com, sub2.www.example.com and so on).
So, in these certs, the common name should be used without www, unless it is done intentionally and you need to secure sub1.www.example.com, sub2.www.example.com etc.
Below you can find a table with all the certificates we offer and have a quick check whether there is a difference in what Common Name to use. If the answer is “Yes”, find the detailed description in the above article.
|
SSL certificate name |
Common name |
Are both www and non-www covered? |
|
PositiveSSL EssentialSSL InstantSSL InstantSSL Pro PremiumSSL Comodo EV SSL |
www.example.com or example.com www.sub.example.com or |
Yes Yes |
|
SSL certificate name |
Common name |
“www” covered by the asterisk (“*”) |
Bare domain coverage (example.com) |
|
PositiveSSL Wildcard EssentialSSL Wildcard PremiumSSL Wildcard |
*.example.com *.sub.example.com |
Yes Yes |
Yes No |
|
SSL certificate name |
Primary domain |
Are both www and non-www covered? |
Additional domain (SAN) |
Are both www and non-www covered? |
|
PositiveSSL Multi-Domain Multi-Domain SSL Unified Communications EV Multi-Domain SSL |
www.example.com or example.com
www.sub.example.com or sub.example.com |
No No |
www.example.com or example.com
www.sub.example.com or sub.example.com |
No No |
Need help? We're always here for you.