{"/api/v1/ncpl/simplekb/getarticle:\"{\\\"articleId\\\":9642,\\\"categoryId\\\":2290}\"":{"body":{"Id":9642,"FriendlyId":"","ArticleTypeId":0,"Title":"Difference between bare domain/www in the CSR","ArticleName":"Difference between bare domain/www in the CSR","ArticleSummary":null,"PreponedSummary":false,"Approved":true,"Body":"DQoJCTxwPldoZW4gYSBuZXcgPGEgaHJlZj0iaHR0cHM6Ly93d3cubmFtZWNoZWFwLmNvbS9zZWN1cml0eS9zc2wtY2VydGlmaWNhdGVzLyI+U1NMIGNlcnRpZmljYXRlPC9hPiBpcyBhY3RpdmF0ZWQsIHF1aXRlIG9mdGVuIGEgcXVlc3Rpb24gYXJpc2VzOiDigJxIb3cgdG8gcHV0IHRoZSBkb21haW4gaW4gdGhlIENTUj8gV2l0aCBvciB3aXRob3V0IHd3dz/igJ0uIE5vdyB3ZSB3aWxsIGNsYXJpZnkgdGhpcyBmb3IgeW91LjwvcD4NCgkJPHA+RXZlbiBpZiB0aGUgd3d3LmV4YW1wbGUuY29tIHN1YmRvbWFpbiBpcyBjb25zaWRlcmVkIGp1c3QgYSBjb3B5IG9mIHRoZSBiYXJlIGRvbWFpbiB3ZWJzaXRlLCBpdCBpcyBzdGlsbCBhIGRpZmZlcmVudCBuYW1lIGZvciBTU0wgY2VydGlmaWNhdGVzLiBTb21lIGNlcnRpZmljYXRlcyBkbyBpbmNsdWRlIGl0IGFzIGEgZnJlZSBTdWJqZWN0IEFsdGVybmF0aXZlIE5hbWUsIHNvbWUgb2YgdGhlbSBkbyBub3QuIFRoaXMgZmVhdHVyZSBkZXBlbmRzIG9uIHRoZSBjZXJ0aWZpY2F0ZSB0eXBlLCBhbmQgdGhlIHJ1bGVzIG9mIHRoZSBBdXRob3JpdHkgdGhpcyBjZXJ0aWZpY2F0ZSBpcyBpc3N1ZWQgYnkuIExldCB1cyBsb29rIHRocm91Z2ggdGhpcyBxdWVzdGlvbiBpbiBhIGRldGFpbGVkIHdheS48L3A+DQoJCTxoND5TaW5nbGUtZG9tYWluIGNlcnRpZmljYXRlczwvaDQ+DQoJCTxwPlNpbmdsZS1kb21haW4gPGEgaHJlZj0iaHR0cHM6Ly93d3cubmFtZWNoZWFwLmNvbS9zZWN1cml0eS9zc2wtY2VydGlmaWNhdGVzL2NvbW9kby5hc3B4IiB0YXJnZXQ9Il9ibGFuayI+Q29tb2RvIChub3cgU2VjdGlnbykgY2VydGlmaWNhdGVzPC9hPiB3aWxsIHNlY3VyZSBib3RoIC0geW91ciBiYXJlIGRvbWFpbiBhbmQgaXRzIHd3dyB2ZXJzaW9uIC0gYnkgZGVmYXVsdC4gRm9yIHRoZXNlIGNlcnRpZmljYXRlcywgaXQgZG9lcyBub3QgbWF0dGVyIHdoZXRoZXIgeW91IHNwZWNpZnkgdGhlIENvbW1vbiBOYW1lIHdpdGggb3Igd2l0aG91dCB3d3cgaW4geW91ciBDU1IuPC9wPg0KCQk8cD5UaGlzIGZlYXR1cmUgaXMgY29tcGxldGVseSBkaWZmZXJlbnQgZm9yIENvbW9kbyAobm93IFNlY3RpZ28pIDxhIGhyZWY9Imh0dHBzOi8vd3d3Lm5hbWVjaGVhcC5jb20vc2VjdXJpdHkvc3NsLWNlcnRpZmljYXRlcy9tdWx0aS1kb21haW4uYXNweCI+TXVsdGktZG9tYWluIGNlcnRpZmljYXRlczwvYT4uIEV2ZXJ5IGRvbWFpbiBvciBzdWJkb21haW4gaW4gc3VjaCBhIGNlcnRpZmljYXRlIHdpbGwgZ28gdG8gYSBzZXBhcmF0ZSBTdWJqZWN0IEFsdGVybmF0aXZlIE5hbWUgc2xvdC4gU28sIGlmIHlvdSBuZWVkIHRvIHNlY3VyZSBib3RoLCB0aGUgYmFyZSBhbmQgd3d3IHZlcnNpb25zIG9mIHlvdXIgZG9tYWlucywgaXQgd2lsbCBiZSBuZWNlc3NhcnkgdG8gZmlsbCB0aGVtIGluIHNlcGFyYXRlbHkgLSBvbmUgYXMgYSBDb21tb24gTmFtZSBhbmQgb25lIGFzIGEgU0FOIC0gbGlrZSBvbiB0aGUgc2NyZWVuc2hvdCBiZWxvdzo8L3A+DQoJCTxwPg0KCQkJCTxpbWcgY2xhc3M9ImtiLWltYWdlIiBzcmM9Imh0dHBzOi8vTmFtZWNoZWFwLnNpbXBsZWtiLmNvbS9TaXRlQ29udGVudHMvMi03QzIyRDUyMzZBNDU0M0VCODI3RjNCRDg5MzZFMTUzRS9tZWRpYS9kaWZmMS5qcGciIGFsdD0iZGlmZjEiIHdpZHRoPSI2MzYiIGhlaWdodD0iNjc1IiBib3JkZXI9IjAiIC8+DQoJCTwvcD4NCgkJPHA+VGhlcmUgaXMgbm8gZGlmZmVyZW5jZSBhdCBhbGwgd2hpY2ggb2YgdGhlbSB3aWxsIGdvIHRvIHRoZSBDb21tb24gbmFtZSBpbiB0aGUgQ1NSLCBhbmQgd2hpY2ggd2lsbCBiZSBzcGVjaWZpZWQgYXMgRG9tYWluIDIgZHVyaW5nIGFjdGl2YXRpb24uPC9wPg0KCQk8aDQ+V2lsZGNhcmQgY2VydGlmaWNhdGVzPC9oND4NCgkJPHA+VGhlIGZlYXR1cmUgb2YgPGEgaHJlZj0iaHR0cHM6Ly93d3cubmFtZWNoZWFwLmNvbS9zZWN1cml0eS9zc2wtY2VydGlmaWNhdGVzL3dpbGRjYXJkLmFzcHgiPldpbGRDYXJkIFNTTHM8L2E+IGlzIG11bHRpcGxlIHN1YmRvbWFpbnMgc2VjdXJpdHkuIElmIHRoZSBDb21tb24gTmFtZSBpbiBhIFdpbGRjYXJkIGNlcnRpZmljYXRlIGlzIHNwZWNpZmllZCBhcyAqLnd3dy5leGFtcGxlLmNvbSwgbm8gb3RoZXIgZmlyc3QtbGV2ZWwgc3ViZG9tYWlucyB3aWxsIGJlIHNlY3VyZWQgKGUuZy4gPGk+c3ViMS5leGFtcGxlLmNvbSwgc3ViMi5leGFtcGxlLmNvbTwvaT4gZXRjLikuIFlvdSB3aWxsIG9ubHkgYmUgYWJsZSB0byBzZWN1cmUgdGhlIHNlY29uZC1sZXZlbCBzdWJkb21haW5zICg8aT5zdWIxLnd3dy5leGFtcGxlLmNvbSwgc3ViMi53d3cuZXhhbXBsZS5jb208L2k+IGFuZCBzbyBvbikuIDwvcD4NCgkJPHA+U28sIGluIHRoZXNlIGNlcnRzLCB0aGUgY29tbW9uIG5hbWUgc2hvdWxkIGJlIHVzZWQgPGI+d2l0aG91dDwvYj4gd3d3LCB1bmxlc3MgaXQgaXMgZG9uZSBpbnRlbnRpb25hbGx5IGFuZCB5b3UgbmVlZCB0byBzZWN1cmUgc3ViMS53d3cuZXhhbXBsZS5jb20sIHN1YjIud3d3LmV4YW1wbGUuY29tIGV0Yy48L3A+DQoJCTxwPkJlbG93IHlvdSBjYW4gZmluZCBhIHRhYmxlIHdpdGggYWxsIHRoZSBjZXJ0aWZpY2F0ZXMgd2Ugb2ZmZXIgYW5kIGhhdmUgYSBxdWljayBjaGVjayB3aGV0aGVyIHRoZXJlIGlzIGEgZGlmZmVyZW5jZSBpbiB3aGF0IENvbW1vbiBOYW1lIHRvIHVzZS4gSWYgdGhlIGFuc3dlciBpcyDigJxZZXPigJ0sIGZpbmQgdGhlIGRldGFpbGVkIGRlc2NyaXB0aW9uIGluIHRoZSBhYm92ZSBhcnRpY2xlLjwvcD4NCgkJPGg0PlNpbmdsZSBkb21haW48L2g0Pg0KCQk8dGFibGUgc3R5bGU9InRleHQtYWxpZ246IGNlbnRlcjsgdmVydGljYWwtYWxpZ246IHRvcDsiIGJvcmRlcj0iMnB4Ij4NCgkJCQk8dGJvZHk+DQoJCQkJCQk8dHI+DQoJCQkJCQkJCTx0ZD4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQk8cD5TU0wgY2VydGlmaWNhdGUgbmFtZSA8L3A+DQoJCQkJCQkJCTwvdGQ+DQoJCQkJCQkJCTx0ZD4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQk8cD5Db21tb24gbmFtZTwvcD4NCgkJCQkJCQkJPC90ZD4NCgkJCQkJCQkJPHRkPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCTxwPkFyZSBib3RoIHd3dyA8YnIgLz48L3A+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJPHA+YW5kIG5vbi13d3cgY292ZXJlZD88L3A+DQoJCQkJCQkJCTwvdGQ+DQoJCQkJCQk8L3RyPg0KCQkJCQkJPHRyPg0KCQkJCQkJCQk8dGQ+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJPHA+UG9zaXRpdmVTU0w8L3A+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJPHA+RXNzZW50aWFsU1NMPC9wPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCTxwPkluc3RhbnRTU0w8L3A+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJPHA+SW5zdGFudFNTTCBQcm88L3A+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJPHA+UHJlbWl1bVNTTDwvcD4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQk8cD5Db21vZG8gRVYgU1NMPC9wPg0KCQkJCQkJCQk8L3RkPg0KCQkJCQkJCQk8dGQ+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJPHA+d3d3LmV4YW1wbGUuY29tPC9wPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCTxwPm9yPC9wPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCTxwPmV4YW1wbGUuY29tPC9wPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCTxiciAvPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCTxiciAvPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCTxwPnd3dy5zdWIuZXhhbXBsZS5jb208L3A+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJPHA+b3I8L3A+DQoJCQkJCQkJCTwvdGQ+DQoJCQkJCQkJCTx0ZD4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQk8cD5ZZXM8L3A+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJPGJyIC8+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJPGJyIC8+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJPGJyIC8+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJPGJyIC8+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJPHA+WWVzPC9wPg0KCQkJCQkJCQk8L3RkPg0KCQkJCQkJPC90cj4NCgkJCQk8L3Rib2R5Pg0KCQk8L3RhYmxlPg0KCQk8aDQ+V2lsZGNhcmQ8L2g0Pg0KCQk8dGFibGUgc3R5bGU9InRleHQtYWxpZ246IGNlbnRlcjsgdmVydGljYWwtYWxpZ246IHRvcDsiIGJvcmRlcj0iMnB4Ij4NCgkJCQk8dGJvZHk+DQoJCQkJCQk8dHI+DQoJCQkJCQkJCTx0ZD4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQk8cD5TU0wgY2VydGlmaWNhdGUgbmFtZSA8L3A+DQoJCQkJCQkJCTwvdGQ+DQoJCQkJCQkJCTx0ZD4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQk8cD5Db21tb24gbmFtZTwvcD4NCgkJCQkJCQkJPC90ZD4NCgkJCQkJCQkJPHRkPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCTxwPuKAnHd3d+KAnSBjb3ZlcmVkIDxiciAvPjwvcD4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQk8cD5ieSB0aGUgYXN0ZXJpc2sgKOKAnCrigJ0pPC9wPg0KCQkJCQkJCQk8L3RkPg0KCQkJCQkJCQk8dGQ+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJPHA+QmFyZSBkb21haW4gY292ZXJhZ2UgPGJyIC8+PC9wPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCTxwPihleGFtcGxlLmNvbSk8L3A+DQoJCQkJCQkJCTwvdGQ+DQoJCQkJCQk8L3RyPg0KCQkJCQkJPHRyPg0KCQkJCQkJCQk8dGQ+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJPHA+UG9zaXRpdmVTU0wgV2lsZGNhcmQ8L3A+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJPHA+RXNzZW50aWFsU1NMICBXaWxkY2FyZDwvcD4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQk8cD5QcmVtaXVtU1NMIFdpbGRjYXJkPC9wPg0KCQkJCQkJCQk8L3RkPg0KCQkJCQkJCQk8dGQ+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJPHA+Ki5leGFtcGxlLmNvbTwvcD4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQk8YnIgLz4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQk8YnIgLz4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQk8cD4qLnN1Yi5leGFtcGxlLmNvbTwvcD4NCgkJCQkJCQkJPC90ZD4NCgkJCQkJCQkJPHRkPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCTxwPlllczwvcD4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQk8YnIgLz4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQk8YnIgLz4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQk8cD5ZZXM8L3A+DQoJCQkJCQkJCTwvdGQ+DQoJCQkJCQkJCTx0ZD4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQk8cD5ZZXM8L3A+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJPGJyIC8+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJPGJyIC8+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJPHA+Tm88L3A+DQoJCQkJCQkJCTwvdGQ+DQoJCQkJCQk8L3RyPg0KCQkJCTwvdGJvZHk+DQoJCTwvdGFibGU+DQoJCTxoND5NdWx0aS1Eb21haW48L2g0Pg0KCQk8dGFibGUgc3R5bGU9InRleHQtYWxpZ246IGNlbnRlcjsgdmVydGljYWwtYWxpZ246IHRvcDsiIGJvcmRlcj0iMnB4Ij4NCgkJCQk8dGJvZHk+DQoJCQkJCQk8dHI+DQoJCQkJCQkJCTx0ZD4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQk8cD5TU0wgY2VydGlmaWNhdGUgbmFtZTwvcD4NCgkJCQkJCQkJPC90ZD4NCgkJCQkJCQkJPHRkPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCTxwPlByaW1hcnkgZG9tYWluPC9wPg0KCQkJCQkJCQk8L3RkPg0KCQkJCQkJCQk8dGQ+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJPHA+IEFyZSBib3RoIHd3dyA8YnIgLz48L3A+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJPHA+YW5kIG5vbi13d3cgY292ZXJlZD88L3A+DQoJCQkJCQkJCTwvdGQ+DQoJCQkJCQkJCTx0ZD4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQk8cD4gQWRkaXRpb25hbCBkb21haW4gKFNBTik8L3A+DQoJCQkJCQkJCTwvdGQ+DQoJCQkJCQkJCTx0ZD4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQk8cD5BcmUgYm90aCB3d3cgPGJyIC8+PC9wPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCTxwPmFuZCBub24td3d3IGNvdmVyZWQ/PC9wPg0KCQkJCQkJCQk8L3RkPg0KCQkJCQkJPC90cj4NCgkJCQkJCTx0cj4NCgkJCQkJCQkJPHRkPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCTxwPlBvc2l0aXZlU1NMIE11bHRpLURvbWFpbjwvcD4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQk8cD5NdWx0aS1Eb21haW4gU1NMPC9wPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCTxwPlVuaWZpZWQgQ29tbXVuaWNhdGlvbnM8L3A+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJPHA+RVYgTXVsdGktRG9tYWluIFNTTDwvcD4NCgkJCQkJCQkJPC90ZD4NCgkJCQkJCQkJPHRkPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCTxwPnd3dy5leGFtcGxlLmNvbTwvcD4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQk8cD4gb3I8L3A+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJPHA+IGV4YW1wbGUuY29tPC9wPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCTxwPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJPGJyIC8+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJPC9wPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCTxwPiB3d3cuc3ViLmV4YW1wbGUuY29tPC9wPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCTxwPiBvcjwvcD4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQk8cD4gc3ViLmV4YW1wbGUuY29tPC9wPg0KCQkJCQkJCQk8L3RkPg0KCQkJCQkJCQk8dGQ+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJPHA+Tm88L3A+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJPGJyIC8+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJPGJyIC8+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJPGJyIC8+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJPHA+IE5vPC9wPg0KCQkJCQkJCQk8L3RkPg0KCQkJCQkJCQk8dGQ+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJPHA+d3d3LmV4YW1wbGUuY29tPC9wPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCTxwPiBvcjwvcD4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQk8cD4gZXhhbXBsZS5jb208L3A+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJPHA+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQk8YnIgLz4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQk8L3A+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJPHA+IHd3dy5zdWIuZXhhbXBsZS5jb208L3A+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJPHA+IG9yPC9wPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCTxwPiBzdWIuZXhhbXBsZS5jb208L3A+DQoJCQkJCQkJCTwvdGQ+DQoJCQkJCQkJCTx0ZD4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQk8cD5ObzwvcD4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQk8YnIgLz4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQk8YnIgLz4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQk8YnIgLz4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQk8YnIgLz4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQk8YnIgLz4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQk8cD4gTm88L3A+DQoJCQkJCQkJCTwvdGQ+DQoJCQkJCQk8L3RyPg0KCQkJCTwvdGJvZHk+DQoJCTwvdGFibGU+DQo=","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"2019-09-17T13:34:11.0000000","LiveDateTime":"1754-02-02T00:00:00.0000000","CreatedDateTime":"2015-10-11T02:36:11.0000000","ApprovalDatetime":"2015-10-11T02:36:18.0000000","RequestCount":52310,"MarkedAsNew":false,"MarkedAsFeatured":false,"RatingValue":2,"CategoryPaths":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryPathDto","Level":1,"CategoryId":14,"CategoryName":"SSL Certificates"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryPathDto","Level":2,"CategoryId":2290,"CategoryName":"CSR code"}],"AssociatedCategories":[{"CategoryId":2290,"CategoryName":"CSR code","CategoryDisplayName":"SSL CertificatesCSR code"}],"AssociatedTags":[],"RelatedArticles":[],"AssociatedMedias":[],"PreferredCategoryId":0,"RootParentCategoryName":"","RootParentCategoryId":0},"status":200,"statusText":"OK"},"/api/v1/ncpl/simplekb/getcategorybycategoryid:\"{\\\"categoryId\\\":2290}\"":{"body":{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"Parent_Category_Name":"SSL Certificates","FriendlyId":null,"ApprovedYN":true,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"CreatedDateTime":"09/12/2022 10:47:13","CurrentCategoryPaths":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryPathDto","Level":1,"CategoryId":14,"CategoryName":"SSL Certificates"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryPathDto","Level":2,"CategoryId":2290,"CategoryName":"CSR code"}],"RelatedCategories":[],"AssociatedArticles":[{"ArticleId":798,"Title":"What is an RSA key used for?","ArticleName":"What is an RSA key used for?","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"11/17/2022"},{"ArticleId":9505,"Title":"What should I do if my Private Key was lost or deleted?","ArticleName":"What should I do if my Private Key was lost or deleted?","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"11/17/2022"},{"ArticleId":337,"Title":"What is a Certificate Signing Request (CSR)?","ArticleName":"What is a Certificate Signing Request (CSR)?","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"09/13/2022"},{"ArticleId":467,"Title":"How to generate CSR (Certificate Signing Request) Code","ArticleName":"How to generate CSR (Certificate Signing Request) Code","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":"01/31/2012 05:00:00","ModifiedDateTime":"01/29/2025"},{"ArticleId":9641,"Title":"How to put domain correctly in CSR?","ArticleName":"How to put domain correctly in CSR?","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"02/06/2025"},{"ArticleId":9642,"Title":"Difference between bare domain/www in the CSR","ArticleName":"Difference between bare domain/www in the CSR","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"09/17/2019"},{"ArticleId":9952,"Title":"Supported key sizes and signature algorithms in CSRs","ArticleName":"Supported key sizes and signature algorithms in CSRs","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":"12/05/2017 05:00:00","ModifiedDateTime":"07/27/2023"},{"ArticleId":9592,"Title":"Generating a CSR on Amazon Web Services (AWS)","ArticleName":"Generating a CSR on Amazon Web Services (AWS)","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"09/13/2022"},{"ArticleId":9634,"Title":"Domain & CSR code setup for Synology NAS","ArticleName":"Domain & CSR code setup for Synology NAS","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"01/31/2024"},{"ArticleId":9680,"Title":"Generating a CSR in Vesta CP","ArticleName":"Generating a CSR in Vesta CP","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"01/31/2024"},{"ArticleId":9683,"Title":"Generating a CSR on Mac OS X Server/Yosemite/El Capitan","ArticleName":"Generating a CSR on Mac OS X Server/Yosemite/El Capitan","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"09/13/2022"},{"ArticleId":9685,"Title":"Generating a CSR on Sun Java System Web Server 7.x","ArticleName":"Generating a CSR on Sun Java System Web Server 7.x","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"09/13/2022"},{"ArticleId":9703,"Title":"Generating a CSR on Webmin","ArticleName":"Generating a CSR on Webmin","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"01/31/2024"},{"ArticleId":9704,"Title":"Generating a CSR on Node.js","ArticleName":"Generating a CSR on Node.js","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"01/31/2024"},{"ArticleId":9745,"Title":"Generating CSR in Exchange 2013 EAC","ArticleName":"Generating CSR in Exchange 2013 EAC","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"10/03/2019"},{"ArticleId":9748,"Title":"Generating CSR in Exchange 2013 Shell","ArticleName":"Generating CSR in Exchange 2013 Shell","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"09/13/2022"},{"ArticleId":9753,"Title":"Generating a CSR code on IIS 8&10","ArticleName":"Generating a CSR code on IIS 8&10","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"12/17/2024"},{"ArticleId":9824,"Title":"CSR generation on a GlassFish application server","ArticleName":"CSR generation on a GlassFish application server","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"10/03/2019"},{"ArticleId":9841,"Title":"Generating a CSR on Zimbra","ArticleName":"Generating a CSR on Zimbra","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"10/03/2019"},{"ArticleId":9852,"Title":"CSR generation on Google Cloud services","ArticleName":"CSR generation on Google Cloud services","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"05/28/2020"},{"ArticleId":9854,"Title":"How to generate a CSR code on a Windows-based server without IIS Manager","ArticleName":"How to generate a CSR code on a Windows-based server without IIS Manager","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"12/17/2020"},{"ArticleId":9864,"Title":"CSR generation on Exchange 2010","ArticleName":"CSR generation on Exchange 2010","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"10/03/2019"},{"ArticleId":9918,"Title":"CSR generation on SonicWall","ArticleName":"CSR generation on SonicWall","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"02/12/2020"},{"ArticleId":9955,"Title":"Generating a CSR on Plesk Onyx","ArticleName":"Generating a CSR on Plesk Onyx","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"01/31/2024"},{"ArticleId":9957,"Title":"Generating a CSR on Citrix NetScaler VPX","ArticleName":"Generating a CSR on Citrix NetScaler VPX","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"10/03/2019"},{"ArticleId":10051,"Title":"Generating CSR in CWP 7","ArticleName":"Generating CSR in CWP 7","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"01/31/2024"},{"ArticleId":10062,"Title":"Generating a CSR code on Windows using Certeq","ArticleName":"Generating a CSR code on Windows using Certeq","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"10/03/2019"},{"ArticleId":10133,"Title":"CSR generation on Ubiquiti Unifi","ArticleName":"CSR generation on Ubiquiti Unifi","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"01/31/2024"},{"ArticleId":10153,"Title":"Generating a CSR on ISPConfig","ArticleName":"Generating a CSR on ISPConfig","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"01/31/2024"},{"ArticleId":10161,"Title":"Generating a CSR on Windows using OpenSSL","ArticleName":"Generating a CSR on Windows using OpenSSL","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"12/17/2020"},{"ArticleId":10207,"Title":"Generating a CSR on Mac OS using Keychain","ArticleName":"Generating a CSR on Mac OS using Keychain","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"09/20/2022"},{"ArticleId":9422,"Title":"Generating a CSR on Tomcat using a keytool","ArticleName":"Generating a CSR on Tomcat using a keytool","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"05/24/2024"},{"ArticleId":9426,"Title":"Generating a CSR code on IIS7","ArticleName":"Generating a CSR code on IIS7","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"12/19/2024"},{"ArticleId":9436,"Title":"Generating CSR using WHM","ArticleName":"Generating CSR using WHM","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"01/31/2024"},{"ArticleId":9440,"Title":"Generating a CSR code using DirectAdmin","ArticleName":"Generating a CSR code using DirectAdmin","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"01/31/2024"},{"ArticleId":9442,"Title":"Generating a CSR in Exchange 2007 (PowerShell)","ArticleName":"Generating a CSR in Exchange 2007 (PowerShell)","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"10/04/2019"},{"ArticleId":9445,"Title":"Generating a CSR using cPanel","ArticleName":"Generating a CSR using cPanel","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"09/23/2024"},{"ArticleId":9446,"Title":"Generating CSR on Apache + OpenSSL/ModSSL/Nginx + Heroku","ArticleName":"Generating CSR on Apache + OpenSSL/ModSSL/Nginx + Heroku","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"10/21/2024"},{"ArticleId":9447,"Title":"Generating CSR in Plesk 12","ArticleName":"Generating CSR in Plesk 12","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"01/31/2024"},{"ArticleId":342,"Title":"What to do if your CSR is not accepted ('CSR invalid' errors) during certificate activation","ArticleName":"What to do if your CSR is not accepted ('CSR invalid' errors) during certificate activation","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"09/17/2019"}],"AssociatedTags":[],"CategoryId":2290,"CategoryName":"CSR code"},"status":200,"statusText":"OK"},"/api/v1/ncpl/simplekb/getcategories:\"{\\\"parentCategoryId\\\":0,\\\"getTree\\\":true}\"":{"body":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2216,"CategoryName":"Spam Protection"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2217,"CategoryName":"Renewal"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2218,"CategoryName":"cPanel SSL Plugin"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2219,"CategoryName":"PHP Configuration"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2221,"CategoryName":"Multi-Domain SSL Certificates"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2222,"CategoryName":"Cancellation"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2223,"CategoryName":"Browser errors"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2224,"CategoryName":"Site Seal, Logo"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2225,"CategoryName":"SEO"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2226,"CategoryName":"Email Migration"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2211,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2227,"CategoryName":"SSL Resellers"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":true,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/cloud-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2228,"CategoryName":"Apps","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2228,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2251,"CategoryName":"Supersonic CDN"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2228,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2298,"CategoryName":"Site Maker"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2228,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":177,"CategoryName":"Google Workspace (formerly G Suite)"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2211,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2229,"CategoryName":"Hosting Resellers"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2232,"CategoryName":"DNSSEC"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2234,"CategoryName":"Google Workspace (formerly G Suite)"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2237,"CategoryName":"Host records setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2238,"CategoryName":"SSL installation errors"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/easywp-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2239,"CategoryName":"EasyWP","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2280,"CategoryName":"Getting Started"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2279,"CategoryName":"General Information"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2281,"CategoryName":"WordPress Migration"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2282,"CategoryName":"Plugins and Themes"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2284,"CategoryName":"WordPress Management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2285,"CategoryName":"SFTP and Database access"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2286,"CategoryName":"Domains questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2288,"CategoryName":"Billing questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2287,"CategoryName":"SSL questions"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2228,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2251,"CategoryName":"Supersonic CDN"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2252,"CategoryName":"InterWorx questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2253,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2254,"CategoryName":"Domains How-To"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2253,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2255,"CategoryName":"Hosting How-To"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2253,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2257,"CategoryName":"Sales & Payments How-To"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2253,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2258,"CategoryName":"cPanel Email How-To"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2260,"CategoryName":"Private Email Contacts and Calendars Setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2253,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2262,"CategoryName":"EasyWP How-To"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"https://download.namecheap.com/assets/img/domainvault-red@2x.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2289,"CategoryName":"Domain Vault","SubCategories":[]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2290,"CategoryName":"CSR code"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2291,"CategoryName":"Webuzo questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2292,"CategoryName":"Browser Extensions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2293,"CategoryName":"Automated SSL management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2228,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2298,"CategoryName":"Site Maker"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":27,"CategoryName":"Getting Started"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/support-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":5,"CategoryName":"General & Support","SubCategories":[]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2200,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":7,"CategoryName":"Billing FAQ"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2209,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":8,"CategoryName":"Transfer Information"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":22,"CategoryName":"Hosting Information"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":38,"CategoryName":"SSL General"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":9,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":45,"CategoryName":"Account Security"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":46,"CategoryName":"Domain Management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2211,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":63,"CategoryName":"Namecheap API"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2228,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":177,"CategoryName":"Google Workspace (formerly G Suite)"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2179,"CategoryName":"Private Email: General Information"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2274,"CategoryName":"General"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2280,"CategoryName":"Getting Started"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2279,"CategoryName":"General Information"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2215,"CategoryName":"Private Email: Mailbox Management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2211,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2196,"CategoryName":"WHMCS module for SSL"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/savings-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2200,"CategoryName":"Checkout & Billing","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2200,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":7,"CategoryName":"Billing FAQ"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2200,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2201,"CategoryName":"Domains Billing"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2200,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":21,"CategoryName":"Hosting Billing"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2200,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":71,"CategoryName":"SSL Certificates Billing"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2200,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2177,"CategoryName":"Private Email"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2200,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2201,"CategoryName":"Domains Billing"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":67,"CategoryName":"Activation"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2209,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":83,"CategoryName":"Transfer to Namecheap"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":9,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":43,"CategoryName":"Profile Management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":10,"CategoryName":"DNS Questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":29,"CategoryName":"cPanel questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2200,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":21,"CategoryName":"Hosting Billing"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":11,"CategoryName":"Dynamic DNS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":9,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":44,"CategoryName":"Account Access"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2209,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":84,"CategoryName":"Transfer to another provider"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":68,"CategoryName":"Validation"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2182,"CategoryName":"cPanel: Software Management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2214,"CategoryName":"Email Forwarding"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2270,"CategoryName":"Routers"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2281,"CategoryName":"WordPress Migration"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2282,"CategoryName":"Plugins and Themes"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2272,"CategoryName":"TV"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2187,"CategoryName":"cPanel: WordPress"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2209,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":219,"CategoryName":"Canceled Transfers"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2200,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":71,"CategoryName":"SSL Certificates Billing"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2176,"CategoryName":"Private Email: DNS Settings"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":69,"CategoryName":"Installation"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/reseller-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":34,"CategoryName":"Domains","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2232,"CategoryName":"DNSSEC"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2234,"CategoryName":"Google Workspace (formerly G Suite)"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2237,"CategoryName":"Host records setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":46,"CategoryName":"Domain Management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":10,"CategoryName":"DNS Questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":11,"CategoryName":"Dynamic DNS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":35,"CategoryName":"Registrations"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2207,"CategoryName":"Renewal questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":36,"CategoryName":"Domains with extended attributes"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":51,"CategoryName":"FreeDNS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":15,"CategoryName":"Namecheap Market"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2208,"CategoryName":"3rd Party Services Setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2278,"CategoryName":"Handshake TLDs"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":35,"CategoryName":"Registrations"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":70,"CategoryName":"Reissuance"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/protection-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":37,"CategoryName":"Domain Privacy Protection","SubCategories":[]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2200,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2177,"CategoryName":"Private Email"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2178,"CategoryName":"Private Email: Webmail Features"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2207,"CategoryName":"Renewal questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2210,"CategoryName":"cPanel Add-ons"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2273,"CategoryName":"Gaming Consoles"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2284,"CategoryName":"WordPress Management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2285,"CategoryName":"SFTP and Database access"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2268,"CategoryName":"macOS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2175,"CategoryName":"Private Email: Client Setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/status-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2209,"CategoryName":"Domain Transfers","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2209,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":8,"CategoryName":"Transfer Information"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2209,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":83,"CategoryName":"Transfer to Namecheap"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2209,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":84,"CategoryName":"Transfer to another provider"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2209,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":219,"CategoryName":"Canceled Transfers"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":48,"CategoryName":"VPS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":36,"CategoryName":"Domains with extended attributes"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":true,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/server-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":12,"CategoryName":"Hosting","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2219,"CategoryName":"PHP Configuration"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2225,"CategoryName":"SEO"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2252,"CategoryName":"InterWorx questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2291,"CategoryName":"Webuzo questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":27,"CategoryName":"Getting Started"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":22,"CategoryName":"Hosting Information"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":29,"CategoryName":"cPanel questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2182,"CategoryName":"cPanel: Software Management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2187,"CategoryName":"cPanel: WordPress"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2210,"CategoryName":"cPanel Add-ons"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":48,"CategoryName":"VPS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2188,"CategoryName":"Dedicated Server"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":30,"CategoryName":"WHM questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":32,"CategoryName":"DNS settings"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":103,"CategoryName":"LVE (CloudLinux)"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":89,"CategoryName":"SSH Access"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":205,"CategoryName":"FTP questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2180,"CategoryName":"MySQL questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2199,"CategoryName":"Hosting Migration"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2194,"CategoryName":"Tips & Tricks"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":239,"CategoryName":"WHMCS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":33,"CategoryName":"SSL Installation"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2171,"CategoryName":"Private Email: Active Sync (Exchange) Setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2188,"CategoryName":"Dedicated Server"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2269,"CategoryName":"iOS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2286,"CategoryName":"Domains questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2288,"CategoryName":"Billing questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2271,"CategoryName":"Linux"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":30,"CategoryName":"WHM questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":31,"CategoryName":"cPanel Email FAQs"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":51,"CategoryName":"FreeDNS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/email-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":93,"CategoryName":"Email service","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2216,"CategoryName":"Spam Protection"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2226,"CategoryName":"Email Migration"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2260,"CategoryName":"Private Email Contacts and Calendars Setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2179,"CategoryName":"Private Email: General Information"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2215,"CategoryName":"Private Email: Mailbox Management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2214,"CategoryName":"Email Forwarding"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2176,"CategoryName":"Private Email: DNS Settings"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2178,"CategoryName":"Private Email: Webmail Features"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2175,"CategoryName":"Private Email: Client Setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2171,"CategoryName":"Private Email: Active Sync (Exchange) Setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":31,"CategoryName":"cPanel Email FAQs"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2186,"CategoryName":"cPanel Email: Client Setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2204,"CategoryName":"Private Email: Video Overview"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":32,"CategoryName":"DNS settings"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":15,"CategoryName":"Namecheap Market"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2186,"CategoryName":"cPanel Email: Client Setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2266,"CategoryName":"Windows"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2287,"CategoryName":"SSL questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2267,"CategoryName":"Android"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2208,"CategoryName":"3rd Party Services Setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2204,"CategoryName":"Private Email: Video Overview"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/security-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":14,"CategoryName":"SSL Certificates","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2217,"CategoryName":"Renewal"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2218,"CategoryName":"cPanel SSL Plugin"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2221,"CategoryName":"Multi-Domain SSL Certificates"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2222,"CategoryName":"Cancellation"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2223,"CategoryName":"Browser errors"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2224,"CategoryName":"Site Seal, Logo"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2238,"CategoryName":"SSL installation errors"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2290,"CategoryName":"CSR code"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2293,"CategoryName":"Automated SSL management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":38,"CategoryName":"SSL General"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":67,"CategoryName":"Activation"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":68,"CategoryName":"Validation"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":69,"CategoryName":"Installation"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":70,"CategoryName":"Reissuance"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":true,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/performance-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":9,"CategoryName":"My Account","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":9,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":45,"CategoryName":"Account Security"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":9,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":43,"CategoryName":"Profile Management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":9,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":44,"CategoryName":"Account Access"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2278,"CategoryName":"Handshake TLDs"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":103,"CategoryName":"LVE (CloudLinux)"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/affiliates-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":55,"CategoryName":"Affiliates","SubCategories":[]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":89,"CategoryName":"SSH Access"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/tools-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2211,"CategoryName":"API & Resellers","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2211,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2227,"CategoryName":"SSL Resellers"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2211,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2229,"CategoryName":"Hosting Resellers"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2211,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":63,"CategoryName":"Namecheap API"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2211,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2196,"CategoryName":"WHMCS module for SSL"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/timer-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2212,"CategoryName":"Legacy Products","SubCategories":[]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":205,"CategoryName":"FTP questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2180,"CategoryName":"MySQL questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2199,"CategoryName":"Hosting Migration"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/premiumdns-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2231,"CategoryName":"PremiumDNS","SubCategories":[]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2194,"CategoryName":"Tips & Tricks"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"https://static.nc-img.com/live-resource/icons/knowledgebase/fastVPN_icon-150px.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2265,"CategoryName":"FastVPN","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2292,"CategoryName":"Browser Extensions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2274,"CategoryName":"General"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2270,"CategoryName":"Routers"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2272,"CategoryName":"TV"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2273,"CategoryName":"Gaming Consoles"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2268,"CategoryName":"macOS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2269,"CategoryName":"iOS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2271,"CategoryName":"Linux"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2266,"CategoryName":"Windows"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2267,"CategoryName":"Android"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":239,"CategoryName":"WHMCS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":33,"CategoryName":"SSL Installation"}],"status":200,"statusText":"OK"}}When a new SSL certificate is activated, quite often a question arises: “How to put the domain in the CSR? With or without www?”. Now we will clarify this for you.
Even if the www.example.com subdomain is considered just a copy of the bare domain website, it is still a different name for SSL certificates. Some certificates do include it as a free Subject Alternative Name, some of them do not. This feature depends on the certificate type, and the rules of the Authority this certificate is issued by. Let us look through this question in a detailed way.
Single-domain Comodo (now Sectigo) certificates will secure both - your bare domain and its www version - by default. For these certificates, it does not matter whether you specify the Common Name with or without www in your CSR.
This feature is completely different for Comodo (now Sectigo) Multi-domain certificates. Every domain or subdomain in such a certificate will go to a separate Subject Alternative Name slot. So, if you need to secure both, the bare and www versions of your domains, it will be necessary to fill them in separately - one as a Common Name and one as a SAN - like on the screenshot below:
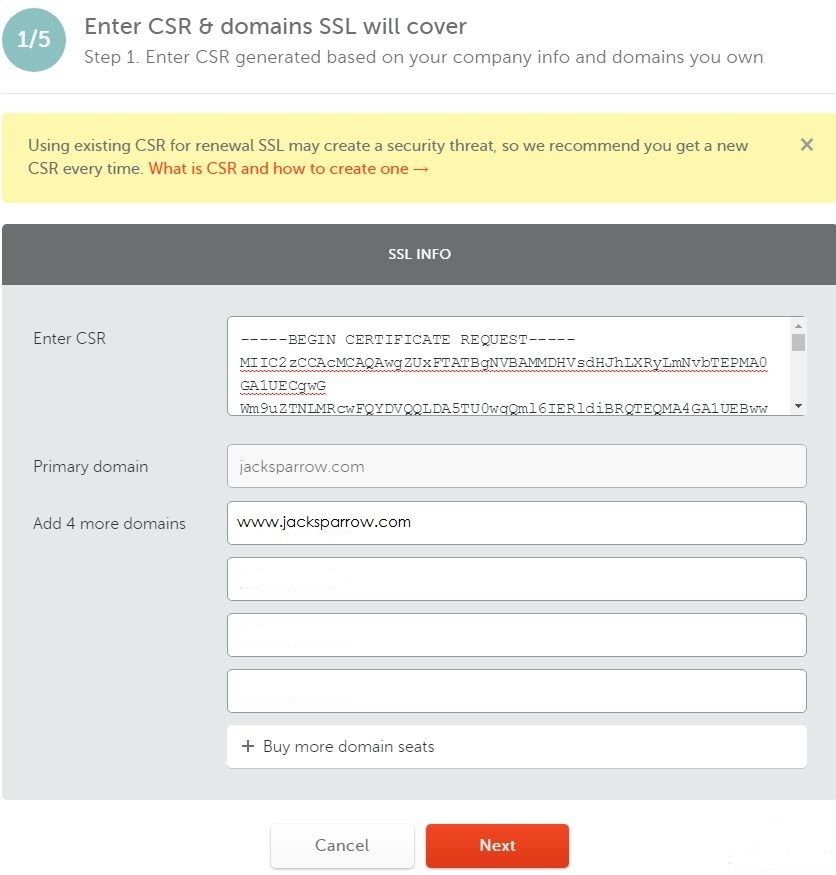
There is no difference at all which of them will go to the Common name in the CSR, and which will be specified as Domain 2 during activation.
The feature of WildCard SSLs is multiple subdomains security. If the Common Name in a Wildcard certificate is specified as *.www.example.com, no other first-level subdomains will be secured (e.g. sub1.example.com, sub2.example.com etc.). You will only be able to secure the second-level subdomains (sub1.www.example.com, sub2.www.example.com and so on).
So, in these certs, the common name should be used without www, unless it is done intentionally and you need to secure sub1.www.example.com, sub2.www.example.com etc.
Below you can find a table with all the certificates we offer and have a quick check whether there is a difference in what Common Name to use. If the answer is “Yes”, find the detailed description in the above article.
|
SSL certificate name |
Common name |
Are both www and non-www covered? |
|
PositiveSSL EssentialSSL InstantSSL InstantSSL Pro PremiumSSL Comodo EV SSL |
www.example.com or example.com www.sub.example.com or |
Yes Yes |
|
SSL certificate name |
Common name |
“www” covered by the asterisk (“*”) |
Bare domain coverage (example.com) |
|
PositiveSSL Wildcard EssentialSSL Wildcard PremiumSSL Wildcard |
*.example.com *.sub.example.com |
Yes Yes |
Yes No |
|
SSL certificate name |
Primary domain |
Are both www and non-www covered? |
Additional domain (SAN) |
Are both www and non-www covered? |
|
PositiveSSL Multi-Domain Multi-Domain SSL Unified Communications EV Multi-Domain SSL |
www.example.com or example.com
www.sub.example.com or sub.example.com |
No No |
www.example.com or example.com
www.sub.example.com or sub.example.com |
No No |
Need help? We're always here for you.