| Subtotal | $0.00 |
| Subtotal | $0.00 |
phpMyAdmin is an application for MySQL databases management. With it you can create, alter, drop, delete, import and export MySQL database tables. You can also run MySQL queries, optimize, repair and check tables, change collation.
NOTE: Make sure the database you would like to manage is already created in the MySQL Databases menu.
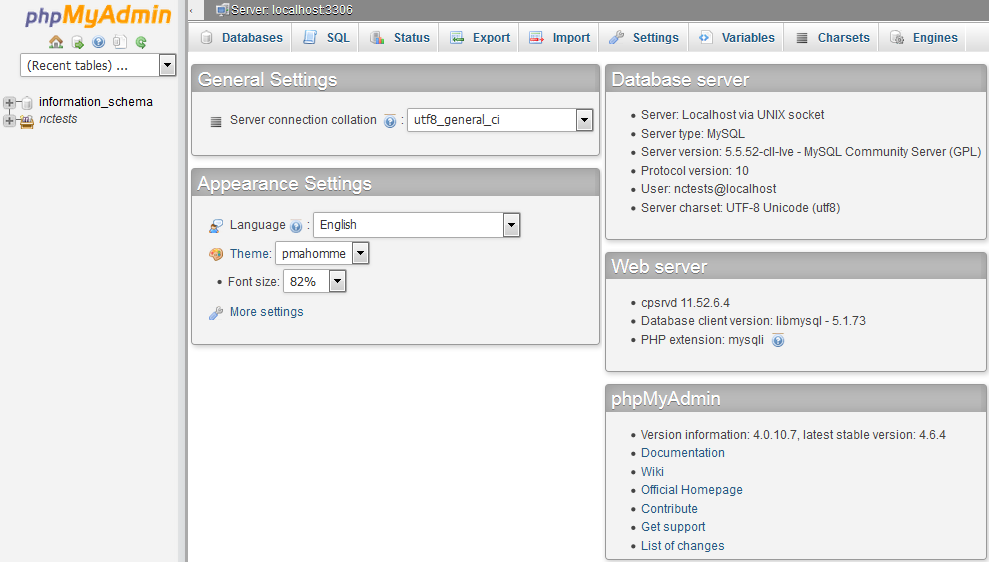
Let’s take a look at the most widely used tabs.
Databases
The Databases tab lists all the databases which can be managed through the cPanel user.
If you enable the statistics for the databases, you will see a table with the used collations, the number of the tables and rows, the size of the data and indexes, the total size and the overhead.
SQL
In this tab you can run SQL queries either by entering the entire SQL query code or manually defining the parameters of the query.
Keep in mind that this tab is context-sensitive, which means that depending on what you're looking at, the target of your SQL queries might be different, e.g., if you are on the home page of phpMyAdmin and do not have any databases selected, if you click on the SQL tab, any queries you run will apply to the overall server (or hosting account if on shared hosting).
Export
The Export tab allows you to export the database tables content in different formats – CSV, SQL, PDF, Microsoft Excel, Microsoft Word, XML, etc. You can select either all the database tables or choose specific ones.
This tab is also context-sensitive - you can either export all databases or a single database/table.
Import
The Import tab allows you to import your database tables from a file saved on your local computer.
NOTE: You can only import the databases that are under 1 GB. If you database backup is bigger than this, you will need need to import it via SSH.
Database Management
Go to the Databases tab and click on the database you would like to manage:
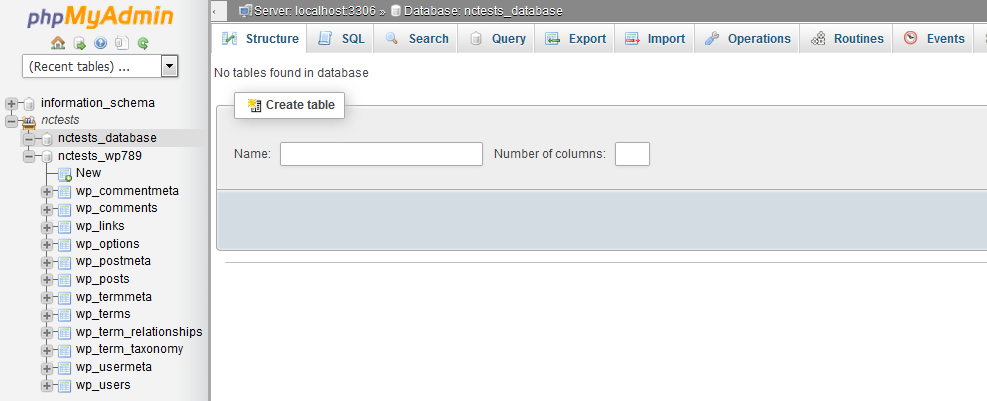
Then create a table:
1. Enter the name of your table in the field Name
2. Enter the number of columns in the field Number of Columns
3. Click on Go to proceed to the next screen
4. Define the column(s) by providing the following information:
4.1. Name
4.2. Select the Type of data for the column. Some common types include:
Need help? We're always here for you.