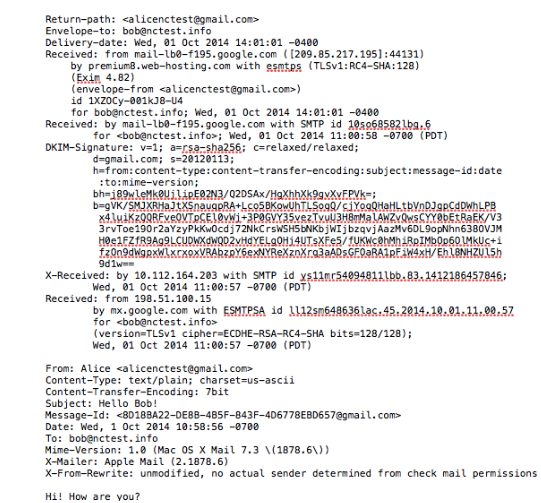
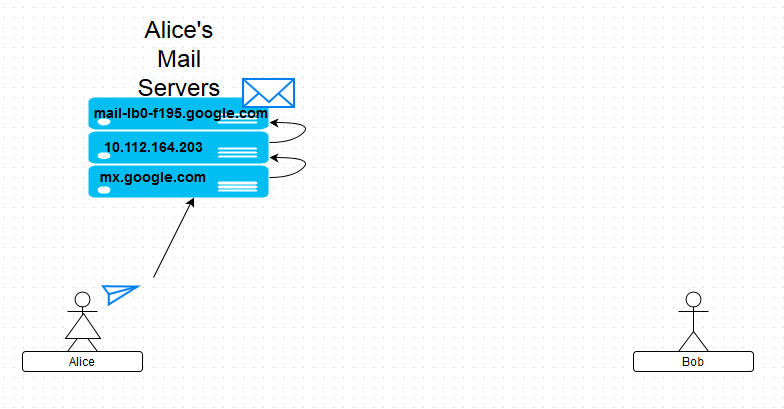
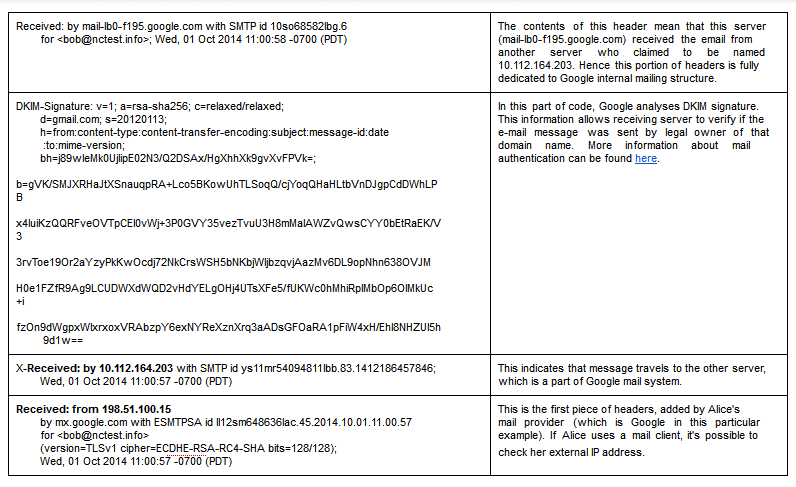
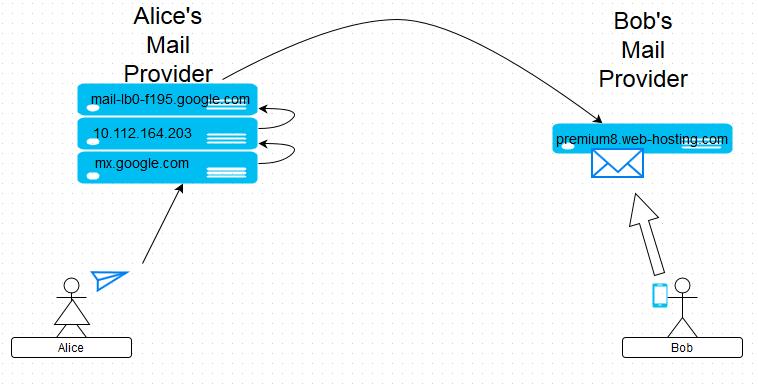
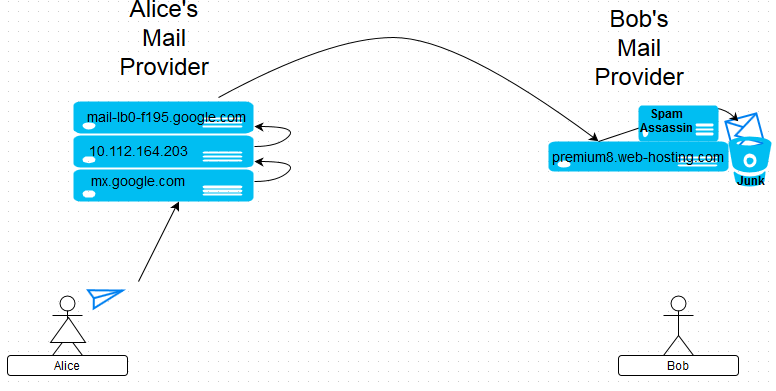
{"/api/v1/ncpl/simplekb/getarticle:\"{\\\"articleId\\\":9429,\\\"categoryId\\\":31}\"":{"body":{"Id":9429,"FriendlyId":"","ArticleTypeId":2,"Title":"User-friendly guide to email headers","ArticleName":"User-friendly guide to email headers","ArticleSummary":null,"PreponedSummary":false,"Approved":true,"Body":"CQlXaXRoIHRoaXMgZ3VpZGUsIHlvdeKAmWxsIGxlYXJuIGhvdyB0byBhbmFseXplIGVtYWlsIGhlYWRlcnMuDQoNCjxiciAvPjxiciAvPjxiPldoYXQgYXJlIGVtYWlsIGhlYWRlcnM/PGJyIC8+PC9iPjxiciAvPkZ1bGwgZW1haWwgaGVhZGVycyAob3IgZW1haWwgbWVzc2FnZSBzb3VyY2UsIEludGVybmV0IGhlYWRlcnMsIGV0YykgYXJlIHJhdyBhbmQgdW5lZGl0ZWQgcmVjb3JkcyBvZiBhbiBlbWFpbCBtZXNzYWdlIHdlIGFsbCBhcmUgYWNjdXN0b21lZCB0bywgYnV0IHdoaWNoIHdlcmUgbm90IHlldCBlbmNvZGVkIGJ5IHRoZSBzZXJ2ZXIuDQoNCjxiciAvPjxiciAvPjxiPldoeSBkbyB3ZSBuZWVkIHRoZW0/DQo8YnIgLz48YnIgLz48L2I+SGVhZGVycyBjb250YWluIGluZm9ybWF0aW9uIGFib3V0IHRoZSBwbGFjZSwgdGltZSBhbmQgd2F5IHRoZSBtZXNzYWdlIGlzIHNlbnQgYW5kIHRyYW5zbWl0dGVkIHRvIHRoZSByZWNpcGllbnTigJlzIHNpZGUuIFlvdSBjYW4gdXNlIGl0IHRvIGZpbmQgb3V0IHdoeSBhbmQgd2hlcmUgdGhlIGltcG9ydGFudCBtZXNzYWdlIHdhcyBkZWxheWVkIG9yIHJlamVjdGVkLCBvciBob3cgdW53YW50ZWQgbWVzc2FnZSBmb3VuZCBpdHMgd2F5IHRvIHlvdXIgaW5ib3guDQoNCjxiciAvPjxiciAvPjxiPkhvdyBkbyB0aGV5IGxvb2sgbGlrZT88YnIgLz48L2I+wqA8YnIgLz5UaGlzIGlzIGhvdyBhbiBvcmRpbmFyeSBtZXNzYWdlIGxvb2tzIGluIGVtYWlsIGNsaWVudDoNCg0KPGJyIC8+PGJyIC8+PGltZyBjbGFzcz0ia2ItaW1hZ2UiIHNyYz0iaHR0cHM6Ly9OYW1lY2hlYXAuc2ltcGxla2IuY29tL1NpdGVDb250ZW50cy8yLTdDMjJENTIzNkE0NTQzRUI4MjdGM0JEODkzNkUxNTNFL21lZGlhL2hlYWRlcnMxLnBuZyIgd2lkdGg9IjYzOCIgaGVpZ2h0PSI5NCIgYm9yZGVyPSIwIiAvPjxiciAvPjxiciAvPkFuZCB0aGlzIGlzIGhvdyBpdHMgZnVsbCBoZWFkZXJzIGxvb2sgbGlrZTo8YnIgLz48YnIgLz48aW1nIGNsYXNzPSJrYi1pbWFnZSIgc3JjPSJodHRwczovL05hbWVjaGVhcC5zaW1wbGVrYi5jb20vU2l0ZUNvbnRlbnRzLzItN0MyMkQ1MjM2QTQ1NDNFQjgyN0YzQkQ4OTM2RTE1M0UvbWVkaWEvaGVhZGVyczIucG5nIiAvPjxiciAvPjxiciAvPllvdSBjYW4gY2hlY2sgPGEgaHJlZj0iaHR0cHM6Ly93d3cubmFtZWNoZWFwLmNvbS9zdXBwb3J0L2tub3dsZWRnZWJhc2UvYXJ0aWNsZS5hc3B4Lzg1OCI+dGhpcyBndWlkZTwvYT4gb24gaG93IHRvIGdldCBlbWFpbCBoZWFkZXJzIGluIGRpZmZlcmVudCBpbnRlcmZhY2VzLiANCg0KDQo8YnIgLz48YnIgLz48Yj5Tbywgd2hhdCBzaG91bGQgdGhleSB0ZWxsIG1lPzwvYj48YnIgLz48YnIgLz5JbiBvcmRlciB0byB1bmRlcnN0YW5kIGhlYWRlcnMgaXTigJlzIG5lY2Vzc2FyeSB0byBjb21wcmVoZW5kIHRoZSB3YXkgbWFpbCB0cmF2ZWxzIGZyb20gdGhlIHNlbmRlciB0byB0aGUgcmVjaXBpZW50LiBIZWFkZXJzIGFyZSBiZWluZyBhdHRhY2hlZCB0byB0aGUgbWVzc2FnZSBzZXZlcmFsIHRpbWVzLCBlYWNoIHRpbWUgaXQgcGFzc2VzIHRocm91Z2ggY2VydGFpbiBtYWlsIGhvc3QuIEhlYWRlcnMgYXJlIGJlaW5nIGF0dGFjaGVkIHRvIHRoZSB0b3Agb2YgdGhlIG1lc3NhZ2UsIHdoaWNoIG1lYW5zIHRoYXQgaXTigJlzIG5lY2Vzc2FyeSB0byBjaGVjayB0aGVtIHN0YXJ0aW5nIGZyb20gdGhlIGVuZCBpbiBvcmRlciB0byB0cmFjZSBpdHMgZmxvdyB0aHJvdWdoIHRoZSBtYWlsIHN5c3RlbS4NCg0KPGJyIC8+PGJyIC8+V2Ugd2lsbCB1c2UgYSBkaWFncmFtIHRvIGlsbHVzdHJhdGUgZWFjaCBwYXJ0IG9mIHRoZSBzeXN0ZW0gYW5kIGNvcnJlc3BvbmRpbmcgaGVhZGVycy4gDQpVc2VyIEEgKHNlbmRlcikgYW5kIHVzZXIgQiAocmVjaXBpZW50KSBhcmUgbmFtZWQgYXMgQWxpY2UgYW5kIEJvYiBmb3IgeW91ciBjb252ZW5pZW5jZToNCg0KPGJyIC8+PGJyIC8+PGltZyBjbGFzcz0ia2ItaW1hZ2UiIHNyYz0iaHR0cHM6Ly9OYW1lY2hlYXAuc2ltcGxla2IuY29tL1NpdGVDb250ZW50cy8yLTdDMjJENTIzNkE0NTQzRUI4MjdGM0JEODkzNkUxNTNFL21lZGlhL2hlYWRlcnMzLnBuZyIgd2lkdGg9IjUzMiIgaGVpZ2h0PSIxNDEiIGJvcmRlcj0iMCIgLz48YnIgLz48YnIgLz5PbmNlIEFsaWNlIGNvbXBvc2VzIGFuZCBzZW5kcyB0aGUgbWVzc2FnZSwgaGVyIG1haWxpbmcgcHJvZ3JhbSBhdHRhY2hlcyB0aGUgZmlyc3QgcG9ydGlvbiBvZiBoZWFkZXJzLiBUaGVzZSBhcmUgbG9jYXRlZCBhdCB0aGUgYm90dG9tIHBhcnQgb2YgdGhlIGZ1bGwgaGVhZGVycyBvdXRwdXQuIEhlcmUgaXMgYW4gZXhwbGFuYXRpb24gb2Ygd2hhdCBoYXBwZW5zIGF0IHRoaXMgc3RhZ2U6DQo8YnIgLz48YnIgLz48aW1nIGNsYXNzPSJrYi1pbWFnZSIgc3JjPSJodHRwczovL05hbWVjaGVhcC5zaW1wbGVrYi5jb20vU2l0ZUNvbnRlbnRzLzItN0MyMkQ1MjM2QTQ1NDNFQjgyN0YzQkQ4OTM2RTE1M0UvbWVkaWEvaGVhZGVyczMuMS5wbmciIC8+PGJyIC8+PGJyIC8+PGI+U3RhZ2UgMjwvYj4gIC0gIEFsaWNlJ3MgbWVzc2FnZSBjb21lcyB0byBHb29nbGUgbWFpbCBzeXN0ZW0gYW5kIHRyYXZlbHMgdGhyb3VnaCBpdC4NCkNvcnJlc3BvbmRpbmcgaGVhZGVycyBhcmUgYXR0YWNoZWQgYnkgZWFjaCBNVEEgKE1haWwgVHJhbnNmZXIgQWdlbnQpOg0KDQo8YnIgLz48YnIgLz48aW1nIGNsYXNzPSJrYi1pbWFnZSIgc3JjPSJodHRwczovL05hbWVjaGVhcC5zaW1wbGVrYi5jb20vU2l0ZUNvbnRlbnRzLzItN0MyMkQ1MjM2QTQ1NDNFQjgyN0YzQkQ4OTM2RTE1M0UvbWVkaWEvaGVhZGVyczQucG5nIiB3aWR0aD0iNTc5IiBoZWlnaHQ9IjI5MSIgYm9yZGVyPSIwIiAvPjxiciAvPjxiciAvPjxpbWcgY2xhc3M9ImtiLWltYWdlIiBzcmM9Imh0dHBzOi8vTmFtZWNoZWFwLnNpbXBsZWtiLmNvbS9TaXRlQ29udGVudHMvMi03QzIyRDUyMzZBNDU0M0VCODI3RjNCRDg5MzZFMTUzRS9tZWRpYS9oZWFkZXJzNC4xLnBuZyIgLz48YnIgLz48YnIgLz48Yj5TdGFnZSAzIDwvYj4tIEFsaWNl4oCZcyBtZXNzYWdlIGlzIGJlaW5nIHNlbnQgZnJvbSBHb29nbGUgbWFpbCBzZXJ2ZXJzIHRvIEJvYuKAmXMgbWFpbCBzZXJ2ZXJzLiBTbywgbWFpbCBpcyBkZWxpdmVyZWQgdG8gQm9i4oCZcyBtYWlsIGFjY291bnQuIEl04oCZcyB1cCB0byBoaW0gaG93IGFuZCB3aGVuIHRvIGNvbm5lY3QgdG8gaXQgYW5kIGNoZWNrIGZvciBuZXcgbWFpbDo8YnIgLz48YnIgLz48YnIgLz48aW1nIGNsYXNzPSJrYi1pbWFnZSIgc3JjPSJodHRwczovL05hbWVjaGVhcC5zaW1wbGVrYi5jb20vU2l0ZUNvbnRlbnRzLzItN0MyMkQ1MjM2QTQ1NDNFQjgyN0YzQkQ4OTM2RTE1M0UvbWVkaWEvaGVhZGVyczUucG5nIiB3aWR0aD0iNTEyIiBoZWlnaHQ9IjI2OSIgYm9yZGVyPSIwIiAvPjxiciAvPjxiciAvPkFsbCBvZiB0aGVzZSBoZWFkZXJzIGFyZSBhZGRlZCBieSBCb2LigJlzIG1haWwgc2VydmVyLCBwcmVtaXVtOC53ZWItaG9zdGluZy5jb206IDxiciAvPjxiciAvPjxpbWcgY2xhc3M9ImtiLWltYWdlIiBzcmM9Imh0dHBzOi8vTmFtZWNoZWFwLnNpbXBsZWtiLmNvbS9TaXRlQ29udGVudHMvMi03QzIyRDUyMzZBNDU0M0VCODI3RjNCRDg5MzZFMTUzRS9tZWRpYS9oZWFkZXJzNS4xLnBuZyIgLz48YnIgLz48ZGl2PjxiPldoYXQgaWYgSSBzZWUgaGVhZGVyIGZpZWxkcyB0aGF0IGFyZW7igJl0IGV4cGxhaW5lZCBhYm92ZT88L2I+PGJyIC8+PGJyIC8+RnJvbSB0aW1lIHRvIHRpbWUgeW91IG1heSBzZWUgYWRkaXRpb25hbCBoZWFkZXIgZmllbGRzIGluIGFuIGVtYWlsLiBUaGlzIGRvZXNu4oCZdCBtZWFuIGFueXRoaW5nIGlzIHdyb25nLiBFbWFpbCBzZXJ2aWNlIHByb3ZpZGVycyBjYW4gYWRkIGN1c3RvbSBoZWFkZXIgZmllbGRzIHRvIG1haWxzIHRoYXQgcGFzcyB0aHJvdWdoIHRoZWlyIHNlcnZlcnMuIDxiciAvPjxiciAvPldoeSBhcmUgdGhleSBuZWNlc3Nhcnk/IFRoZXNlIGZpZWxkcyBhZGQgZXh0cmEgZGV0YWlscyBpbiBhZGRpdGlvbiB0byByb3V0aW5nIGluZm9ybWF0aW9uLCBhcyBzdWNoLCB0aGV5IGVuaGFuY2UgdGhlIHF1YWxpdHkgb2YgbWFpbCBwcm9jZXNzaW5nIGFuZCBpbXByb3ZlIG1haWwgdHJhY2tpbmcuIDxiciAvPjxiciAvPlJlY2VudGx5IHdlIGhhdmUgYWRkZWQgWC1OQ0pGLVJlc3VsdCBhbmQgWC1OQ0pGLVZlcnNpb24gY3VzdG9tIGZpZWxkcy4gVGhleSBtaWdodCBzb3VuZCB3ZWlyZCBmb3IgdGhlIHVuaW5pdGlhdGVkLiBIb3dldmVyLCB0aGVzZSBoZWFkZXJzIHdpdGggZW5jcnlwdGVkIHRlY2huaWNhbCBkYXRhIGhlbHAgb3VyIGN1c3RvbWVyIHN1cHBvcnQgZ2l2ZSB1cGRhdGVzIHNob3J0bHkgYW5kIE5hbWVjaGVhcCB1c2VzIHRoZW0gZm9yIGludGVybmFsIHNwYW0gZmlsdGVyaW5nIHBvbGljaWVzLiBObyBwZXJzb25hbCBkZXRhaWxzIGFyZSBoaWRkZW4gaW5zaWRlIHRoZXNlIG5ldyBjdXN0b20gZmllbGRzLCBhbmQgdGhlc2UgZGV0YWlscyBhcmUgdXNlZCBzb2xlbHkgYnkgb3VyIGNvbXBhbnkgYW5kIG5vdCB0cmFuc21pdHRlZCB0byB0aGlyZCBwYXJ0aWVzLiA8YnIgLz48YnIgLz5FbWFpbCBzZXJ2aWNlIHByb3ZpZGVycyBvZnRlbiB1c2UgY3VzdG9tIGZpZWxkcywgYWx0aG91Z2ggdGhlaXIgdGl0bGVzIGFuZCBwdXJwb3NlIGNhbiB2YXJ5LiBOZXZlcnRoZWxlc3MsIGlmIGFueSBsaW5lIG9mIHlvdXIgZW1haWwgaGVhZGVyIHNlZW1zIHRvIGJlIGV4dHJlbWVseSBzdXNwaWNpb3VzIGFuZCB5b3UgZG8gbm90IHVuZGVyc3RhbmQgaXRzIG1lYW5pbmcsIGZlZWwgZnJlZSB0byBjb250YWN0IHVzIGZvciBhc3Npc3RhbmNlLjxiciAvPjxiciAvPjwvZGl2PjxkaXY+PGJyIC8+PC9kaXY+PGI+SG93IGNhbiBJIHVzZSBtYWlsIGhlYWRlcnMgdG8gZmlnaHQgc3BhbT88YnIgLz48YnIgLz48L2I+SWYgQm9iIGhhcyBTcGFtIHByb3RlY3Rpb24gc29mdHdhcmUgZW5hYmxlZCBvbiBoaXMgbWFpbCBzZXJ2ZXIsIHRoYW4gYSBzcGFtIHJlcG9ydCBpcyBhdHRhY2hlZCB0byBtYWlsIGhlYWRlcnMgKHlvdSBjYW4gY2hlY2sgdGhpcyA8YSBocmVmPSJodHRwczovL3d3dy5uYW1lY2hlYXAuY29tL3N1cHBvcnQva25vd2xlZGdlYmFzZS9hcnRpY2xlLmFzcHgvODU4LzMxL2hvdy10by1nZXQtZW1haWwtaGVhZGVycyI+Z3VpZGU8L2E+IHRvIGxlYXJuIGhvdyB0byBlbmFibGUgc3BhbSBwcm90ZWN0aW9uIC0gU3BhbUFzc2Fzc2luIGluIHlvdXIgY1BhbmVsLiBGb3IgUHJpdmF0ZSBFbWFpbCB1c2VycyBpdCBpcyBlbmFibGVkICBieSBkZWZhdWx0KS4NCg0KU28sIEFsaWNlIHNlbmRzIGEgbWVzc2FnZSBpbmNsdWRpbmcgZmV3IHdvcmRzIHRoYXQgZHJhd3Mgc3BhbSBwcm90ZWN0aW9uIHNvZnR3YXJlIGF0dGVudGlvbjoNCiA8YnIgLz48YnIgLz48aW1nIGNsYXNzPSJrYi1pbWFnZSIgc3JjPSJodHRwczovL05hbWVjaGVhcC5zaW1wbGVrYi5jb20vU2l0ZUNvbnRlbnRzLzItN0MyMkQ1MjM2QTQ1NDNFQjgyN0YzQkQ4OTM2RTE1M0UvbWVkaWEvaGVhZGVyczYucG5nIiB3aWR0aD0iNjA5IiBoZWlnaHQ9IjI4MiIgYm9yZGVyPSIwIiAvPjxiciAvPjxiciAvPldlIGFyZSBpbnRlcmVzdGVkIGluICB0aGlzIHBhcnRpY3VsYXIgcGFydC4gTGV04oCZcyBhbmFseXplIGl0IHN0ZXAgYnkgc3RlcDoNCg0KPGJyIC8+PGJyIC8+PGltZyBjbGFzcz0ia2ItaW1hZ2UiIHNyYz0iaHR0cHM6Ly9OYW1lY2hlYXAuc2ltcGxla2IuY29tL1NpdGVDb250ZW50cy8yLTdDMjJENTIzNkE0NTQzRUI4MjdGM0JEODkzNkUxNTNFL21lZGlhL2hlYWRlcnM3LnBuZyIgLz48YnIgLz48YnIgLz4gSW4gb3VyIGV4YW1wbGUsIHNwYW0gdGhyZXNob2xkIHdhcyBzZXQgdG8gMiwgc28gdGhlIG1lc3NhZ2Ugd2FzIGNvbnNpZGVyZWQgdG8gYmUgc3BhbS4gDQoNCjxiciAvPjxiciAvPllvdSBjYW4gc2V0IHNwYW0gdGhyZXNob2xkIGluIFNwYW1Bc3Nhc3NpbiBzZXR0aW5ncyBpZiB5b3UgaGF2ZSB3ZWIgaG9zdGluZyBhY2NvdW50IHdpdGggdXMuIElmIHlvdSBhcmUgYSBQcml2YXRlIE1haWwgc3Vic2NyaXB0aW9uIG93bmVyLCBwbGVhc2UgY29udGFjdCBvdXIgc3VwcG9ydCB0ZWFtLCBzbyB3ZSBjYW4gYWRqdXN0IHNwYW0gZmlsdGVyaW5nIHNldHRpbmdzIGZvciB5b3VyIGFjY291bnQuIA0KDQo8YnIgLz48YnIgLz5BcyBhbiBhbHRlcm5hdGl2ZSwgeW91IGNhbiBibGFja2xpc3QgdGhlIHNlbmRlciBvciBzZW5kIGEgY29tcGxhaW50IHRvIHRoZSByZWdpc3RyYXIgb2YgaGlzIGRvbWFpbiBuYW1lIG9yIHRvIHRoZSBvd25lciBvZiB0aGUgSVAgYWRkcmVzcy4gDQoNCg0KPGJyIC8+PGJyIC8+PGJyIC8+PGI+TXkgbWVzc2FnZSBpcyBub3QgZGVsaXZlcmVkLiBXaHk/DQoNCjwvYj48YnIgLz48YnIgLz5JZiBhIG1lc3NhZ2UgaXMgbm90IGRlbGl2ZXJlZCwgaW4gbW9zdCBjYXNlcyBib3VuY2UtYmFjayBtZXNzYWdlIHNob3VsZCBiZSBleHBlY3RlZC4gQm91bmNlLWJhY2sgaXMgYW4gZW1haWwgZGVsaXZlcnkgcmVwb3J0LCBzZW50IGJ5IGEgY2VydGFpbiBtYWlsIHNlcnZlciwgd2hpY2ggd2FzIG5vdCBhYmxlIHRvIGRlbGl2ZXIgdGhlIG1lc3NhZ2UgZnVydGhlciBkdWUgdG8gYSBzcGVjaWZpYyBlcnJvci4gSnVzdCBsaWtlIGluIHJlZ3VsYXIgbWFpbCwgd2hlbiBhIGxldHRlciBpcyBiZWluZyByZXR1cm5lZCB0byBhIHNlbmRlciBpZiBhIHBvc3Qgc3RhbXAgaXMgbm90IGFwcGxpZWQuDQoNCjxiciAvPjxiciAvPkZvciBleGFtcGxlLCBBbGljZSB0cmllcyB0byBzZW5kIGEgbWVzc2FnZSB0byBib2JAbmN0ZXN0LmluZm8sIGJ1dCBtYWtlcyBhIHR5cG8gaW4gdGhlIGFkZHJlc3MgYW5kIHRoZSBtZXNzYWdlIGlzIGJlaW5nIHNlbnQgdG8gYmliQG5jdGVzdC5pbmZvIGluc3RlYWQuIEhlciBtYWlsIHByb3ZpZGVyIGNvbnRhY3RzIEJvYuKAmXMgbWFpbCBwcm92aWRlciB0byBjaGVjayB3aGV0aGVyIHRoZXkgaGF2ZSBzb21lYm9keSB3aXRoIGJpYkBuY3Rlc3QuaW5mbyBhZGRyZXNzLiBJZiB0aGVyZSBpcyBubyBzdWNoIGFkZHJlc3MsIGl0IHJlcG9ydHMgdGhhdCB0aGlzIHVzZXIgaXMgbm90IGF2YWlsYWJsZSAtIHlvdSB3aWxsIHNlZSA8Yj5ObyBtYWlsYm94IGJ5IHRoYXQgbmFtZTwvYj4gb3IgPGI+Tm8gc3VjaCB1c2VyIGhlcmU8L2I+IGVycm9ycy4gQWxpY2XigJlzIG1haWwgcHJvdmlkZXIgc2VuZHMgYSBib3VuY2UtYmFjayBtZXNzYWdlIHRvIGhlciB0byBsZXQgaGVyIGtub3cgdGhhdCBpdCB3YXMgbm90IHBvc3NpYmxlIHRvIHNlbmQgdGhlIG1lc3NhZ2UgYW5kIGF0dGFjaGVzIHRoZSByZXBseSBvZiBCb2LigJlzIG1haWwgcHJvdmlkZXIgZm9yIGhlciByZWZlcmVuY2UuIDxiciAvPjxiciAvPkEgbWVzc2FnZSBpcyBiZWluZyByZWplY3RlZCB3aXRoIHN1Y2ggY29kZSBvbiB0d28gY29uZGl0aW9uczo8YnIgLz7CoDxiciAvPjEuIEEgdHlwbyBpcyBkZXRlY3RlZCBpbiB0aGUgYWRkcmVzcyAmZ3Q7IGl0IHNob3VsZCBiZSBjaGVja2VkLjxiciAvPjIuIEEgbWFpbCBzZXJ2ZXIgaXMgYmVpbmcgbG9va2VkIHVwIGluIHRoZSB3cm9uZyBwbGFjZSAmZ3Q7IE1YIHJlY29yZCBmb3IgZGVzdGluYXRpb24gYWRkcmVzcyBzaG91bGQgYmUgY2hlY2tlZC4NCjxiciAvPjxiciAvPklmIHRoZSBib3VuY2UtYmFjayBlcnJvciByZWNlaXZlZCBpcyA8Yj5NYWlsYm94IGZ1bGw8L2I+IG9yIDxiPlF1b3RhIGV4Y2VlZGVkPC9iPiBpdCBtZWFucyB0aGF0IGRlc3RpbmF0aW9uIG1haWwgc2VydmVyIChCb2LigJlzIG9uZSkgcmVmdXNlcyB0byByZWNlaXZlIHRoZSBtZXNzYWdlLCBiZWNhdXNlIHdlYnNwYWNlLCBkZWRpY2F0ZWQgdG8gc3RvcmluZyBtYWlsIGZvciB0aGlzIGFkZHJlc3MgaXMgb3ZlciB0aGUgbGltaXQuIEluIG9yZGVyIHRvIGZpeCB0aGlzIGVycm9yLCBCb2Igc2hvdWxkIGVpdGhlciBkZWxldGUgc29tZSBvZiB0aGUgbWVzc2FnZXMgaGUgaGFzIHN0b3JlZCBvbiB0aGUgc2VydmVyIG9yIHB1cmNoYXNlIGFkZGl0aW9uYWwgc3BhY2UuDQo8YnIgLz48YnIgLz5JZiB0aGUgYm91bmNlLWJhY2sgbWVzc2FnZSBzYXlzIDxiPkhvc3QgdW5rbm93bjwvYj4sIDxiPkRvbWFpbiBMb29rdXAgRmFpbGVkPC9iPiwgaXQgbWVhbnMgcmVsYXRpdmVseSB0aGUgc2FtZSBhcyBObyBzdWNoIHVzZXIgaGVyZSwgYnV0IHRoZSB0eXBvIG9jY3VycyBpbiB0aGUgZG9tYWluIHBhcnQgb2YgdGhlIGFkZHJlc3M6IGJvYkBuY3Rpc3QuaW5mbyBpbnN0ZWFkIG9mIGJvYkBuY3Rlc3QuaW5mby4gSW4gY2FzZSB0aGUgZG9tYWluIG5hbWUgaXMgZW50ZXJlZCBpbiB0aGUgY29ycmVjdCB3YXksIHNvbWV0aGluZyBtaWdodCBiZSB3cm9uZyB3aXRoIHRoZSB3YXkgaG93IGRvbWFpbiBuYW1lIHJlc29sdmVkIGluIHRoZSBETlMgc3lzdGVtLiBJdCBjYW4gZWl0aGVyIGdldCBleHBpcmVkIG9yIHNvbWV0aGluZyBtaWdodCBnbyB3cm9uZyBvbiB0aGUgc2lkZSBvZiBpdHMgbmFtZSBzZXJ2ZXIuIFN1cHBvcnQgb24gdGhlIGRlc3RpbmF0aW9uIHNpZGUgc2hvdWxkIGJlIGNvbnRhY3RlZCBpbiBzdWNoIGEgY2FzZS4NCjxiciAvPjxiciAvPkFub3RoZXIgZ3JvdXAgb2YgYm91bmNlLWJhY2sgZXJyb3IgbWVzc2FnZXMgaXMgc3BhbS1yZWxhdGVkIG1lc3NhZ2VzLCA8Yj5JUCBCbGFja2xpc3RlZCAvIExpc3RlZCBpbiBTcGFtIHJlcG9ydCBsaXN0PC9iPiBvciBzZW5kaW5nIGZhaWxlZCBkdWUgdG8gPGI+UG9vciBNVEEgcmVwdXRhdGlvbjwvYj4uIFRoZSBlcnJvciBpbmRpY2F0ZXMgdGhhdCB0aGUgSVAgYWRkcmVzcyBvZiB0aGUgbWFpbCBzZXJ2ZXIgaGFzIGJlZW4gY29tcHJvbWlzZWQgYnkgc3BhbW1lcnMsIGhhY2tlcnMsIG9yIHZpcnVzIHByb3BhZ2F0b3JzLg0KPGJyIC8+PGJyIC8+SWYgeW91IGhhdmUgcHJpdmF0ZSBlbWFpbCBzdWJzY3JpcHRpb24gb3Igc2hhcmVkL3Jlc2VsbGVyIGhvc3RpbmcgYWNjb3VudCB3aXRoIHVzLCBwbGVhc2UgY3JlYXRlIGFuIDxhIGhyZWY9Imh0dHBzOi8vd3d3Lm5hbWVjaGVhcC5jb20vc3VwcG9ydC9rbm93bGVkZ2ViYXNlL2FydGljbGUuYXNweC8yMjcvNS9ob3ctY2FuLWktcmVxdWVzdC1zdXBwb3J0LXZpYS1lbWFpbC8iPmVtYWlsPC9hPiB0byBhIGNvcnJlc3BvbmRpbmcgZGVwYXJ0bWVudCBhbmQgYXR0YWNoIHRoZSBib3VuY2UtYmFjayBtZXNzYWdlIHRvIGl0LiBDb3JyZXNwb25kaW5nIGFjdGlvbnMgd2lsbCBiZSB0YWtlbiBieSB1cyB0byByZXNvbHZlIHRoZSBpc3N1ZS4gSWYgeW91IGhhdmUgVXNlci1SZXNwb25zaWJsZSBWUFMgb3IgRGVkaWNhdGVkIHNlcnZlciB3aXRoIHVzLCB5b3Ugd2lsbCBuZWVkIHRvIGRlbGlzdCB5b3VyIElQIGFkZHJlc3NlcyB3aXRoIHRoZSBjb3JyZXNwb25kaW5nIG9yZ2FuaXphdGlvbnMgb24geW91ciBvd24uDQoNCjxiciAvPjxiciAvPlNvIGVtYWlsIGhlYWRlcnMgYXJlIHZlcnkgaW1wb3J0YW50IHBhcnQgb2YgdGhlIG1haWwgc3lzdGVtIGFuZCB0aGV5IGFyZSBlc3NlbnRpYWwgZm9yIHRoZSBtYWlsIGlzc3VlcyBkaWFnbm9zdGljcy4gVGhleSBoZWxwIHRvIHF1aWNrbHkgaWRlbnRpZnkgdGhlIHNlcnZlcnMgdGhhdCByZXBvcnQgdGhlIGVycm9yIGluIHRoZSBjaGFpbiBhbmQgdGh1cyBmaXggdGhlIGlzc3VlcyBlZmZlY3RpdmVseS4NCjxiciAvPjxkaXY+PGJyIC8+PC9kaXY+PGRpdj48YnIgLz48L2Rpdj4NCsKgwqDCoMKgwqDCoMKgwqDCoMKgwqDCoMKgwqAgPGJyIC8+PGRpdiBhbGlnbj0iY2VudGVyIj5OZWVkIGFueSBoZWxwPyBDb250YWN0IG91ciA8YSBocmVmPSJodHRwczovL3d3dy5uYW1lY2hlYXAuY29tL2hlbHAtY2VudGVyLyI+SGVscERlc2s8L2E+PGJyIC8+PC9kaXY+PGJyIC8+","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"2025-02-07T13:24:16.0000000","LiveDateTime":"1754-02-02T00:00:00.0000000","CreatedDateTime":"2014-11-19T09:20:46.0000000","ApprovalDatetime":"2014-11-19T10:54:38.0000000","RequestCount":44602,"MarkedAsNew":false,"MarkedAsFeatured":false,"RatingValue":3,"CategoryPaths":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryPathDto","Level":1,"CategoryId":93,"CategoryName":"Email service"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryPathDto","Level":2,"CategoryId":31,"CategoryName":"cPanel Email FAQs"}],"AssociatedCategories":[{"CategoryId":31,"CategoryName":"cPanel Email FAQs","CategoryDisplayName":"Email servicecPanel Email FAQs"}],"AssociatedTags":[{"TagId":51,"Tag":"email"},{"TagId":1466,"Tag":" mail"},{"TagId":17622,"Tag":" hosting"},{"TagId":20097,"Tag":" .htaccess"},{"TagId":20195,"Tag":" user"},{"TagId":82698,"Tag":" headers"},{"TagId":82699,"Tag":" guide"}],"RelatedArticles":[{"ArticleId":858,"PreferedCategoryId":2194,"ArticleTypeId":3,"ArticleName":"How to get email headers","ArticleTypeName":"How_To","Title":"How to get email headers","LiveDateTime":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"06/12/2025","MarkedAsNew":false,"MarkedAsFeatured":false}],"AssociatedMedias":[],"PreferredCategoryId":0,"RootParentCategoryName":"","RootParentCategoryId":0},"status":200,"statusText":"OK"},"/api/v1/ncpl/simplekb/getcategorybycategoryid:\"{\\\"categoryId\\\":31}\"":{"body":{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"Parent_Category_Name":"Email service","FriendlyId":null,"ApprovedYN":true,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"CreatedDateTime":"07/21/2008 16:06:06","CurrentCategoryPaths":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryPathDto","Level":1,"CategoryId":93,"CategoryName":"Email service"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryPathDto","Level":2,"CategoryId":31,"CategoryName":"cPanel Email FAQs"}],"RelatedCategories":[],"AssociatedArticles":[{"ArticleId":10038,"Title":"How to configure a Contact Form with us","ArticleName":"How to configure a Contact Form with us","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"04/16/2025"},{"ArticleId":10317,"Title":"How to access cPanel Webmail","ArticleName":"How to access cPanel Webmail","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"04/30/2025"},{"ArticleId":10565,"Title":"How to change password for your cPanel email account","ArticleName":"How to change password for your cPanel email account","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"09/25/2024"},{"ArticleId":9751,"Title":"How to configure PHP mail()/SMTP authentication for different CMS","ArticleName":"How to configure PHP mail()/SMTP authentication for different CMS","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"04/30/2024"},{"ArticleId":110,"Title":"How to Create An Email Account in cPanel","ArticleName":"How to Create An Email Account in cPanel","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"09/25/2024"},{"ArticleId":9205,"Title":"How to set up email forwarding in cPanel","ArticleName":"How to set up email forwarding in cPanel","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"07/06/2023"},{"ArticleId":9609,"Title":"How to set up and manage mail filters in cPanel","ArticleName":"How to set up and manage mail filters in cPanel","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"11/25/2024"},{"ArticleId":912,"Title":"How to create a catch-all email address in cPanel","ArticleName":"How to create a catch-all email address in cPanel","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"07/12/2023"},{"ArticleId":1157,"Title":"How to create auto-responder in cPanel","ArticleName":"How to create auto-responder in cPanel","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"07/12/2023"},{"ArticleId":9258,"Title":"How to change MX records and Email Routing in cPanel","ArticleName":"How to change MX records and Email Routing in cPanel","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"09/25/2024"},{"ArticleId":9713,"Title":"How to set up cPanel webmail to go directly to Roundcube","ArticleName":"How to set up cPanel webmail to go directly to Roundcube","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"07/06/2023"},{"ArticleId":9967,"Title":"How to set up DNS records for Namecheap email service with Cloudflare (cPanel and Private Email)","ArticleName":"How to set up DNS records for Namecheap email service with Cloudflare (cPanel and Private Email)","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"01/18/2024"},{"ArticleId":9515,"Title":"How to import/export contacts via cPanel Webmail","ArticleName":"How to import/export contacts via cPanel Webmail","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"12/28/2020"},{"ArticleId":9676,"Title":"How to set up email signature in cPanel webmail","ArticleName":"How to set up email signature in cPanel webmail","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"12/07/2023"},{"ArticleId":9570,"Title":"Dealing with excessive Gmail and Outlook security","ArticleName":"Dealing with excessive Gmail and Outlook security","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"10/05/2022"},{"ArticleId":133,"Title":"Do you have any restrictions on sending out emails?","ArticleName":"Do you have any restrictions on sending out emails?","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"12/22/2025"},{"ArticleId":9214,"Title":"cPanel Email Deliverability Tool – SPF, DKIM, and DMARC Records","ArticleName":"cPanel Email Deliverability Tool – SPF, DKIM, and DMARC Records","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"10/27/2025"},{"ArticleId":9193,"Title":"Differences between Namecheap Private Email and cPanel email","ArticleName":"Differences between Namecheap Private Email and cPanel email","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"01/23/2025"},{"ArticleId":9429,"Title":"User-friendly guide to email headers","ArticleName":"User-friendly guide to email headers","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"02/07/2025"},{"ArticleId":9567,"Title":"Rewrite From Header - Explained","ArticleName":"Rewrite From Header - Explained","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"12/20/2021"}],"AssociatedTags":[{"TagId":8,"Tag":"web hosting"},{"TagId":77,"Tag":" email accounts"}],"CategoryId":31,"CategoryName":"cPanel Email FAQs"},"status":200,"statusText":"OK"},"/api/v1/ncpl/simplekb/getcategories:\"{\\\"parentCategoryId\\\":0,\\\"getTree\\\":true}\"":{"body":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2216,"CategoryName":"Spam Protection"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2217,"CategoryName":"Renewal"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2218,"CategoryName":"cPanel SSL Plugin"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2219,"CategoryName":"PHP Configuration"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2221,"CategoryName":"Multi-Domain SSL Certificates"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2222,"CategoryName":"Cancellation"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2223,"CategoryName":"Browser errors"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2224,"CategoryName":"Site Seal, Logo"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2225,"CategoryName":"SEO"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2226,"CategoryName":"Email Migration"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2211,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2227,"CategoryName":"SSL Resellers"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":true,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/cloud-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2228,"CategoryName":"Apps","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2228,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2251,"CategoryName":"Supersonic CDN"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2228,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2298,"CategoryName":"Site Maker"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2228,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":177,"CategoryName":"Google Workspace (formerly G Suite)"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2211,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2229,"CategoryName":"Hosting Resellers"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2232,"CategoryName":"DNSSEC"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2234,"CategoryName":"Google Workspace (formerly G Suite)"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2237,"CategoryName":"Host records setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2238,"CategoryName":"SSL installation errors"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/easywp-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2239,"CategoryName":"EasyWP","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2280,"CategoryName":"Getting Started"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2279,"CategoryName":"General Information"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2281,"CategoryName":"WordPress Migration"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2282,"CategoryName":"Plugins and Themes"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2284,"CategoryName":"WordPress Management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2285,"CategoryName":"SFTP and Database access"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2286,"CategoryName":"Domains questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2288,"CategoryName":"Billing questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2287,"CategoryName":"SSL questions"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2228,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2251,"CategoryName":"Supersonic CDN"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2252,"CategoryName":"InterWorx questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2253,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2254,"CategoryName":"Domains How-To"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2253,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2255,"CategoryName":"Hosting How-To"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2253,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2257,"CategoryName":"Sales & Payments How-To"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2253,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2258,"CategoryName":"cPanel Email How-To"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2260,"CategoryName":"Private Email Contacts and Calendars Setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2253,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2262,"CategoryName":"EasyWP How-To"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"https://download.namecheap.com/assets/img/domainvault-red@2x.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2289,"CategoryName":"Domain Vault","SubCategories":[]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2290,"CategoryName":"CSR code"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2291,"CategoryName":"Webuzo questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2292,"CategoryName":"Browser Extensions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2293,"CategoryName":"Automated SSL management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2228,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2298,"CategoryName":"Site Maker"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":27,"CategoryName":"Getting Started"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/support-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":5,"CategoryName":"General & Support","SubCategories":[]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2200,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":7,"CategoryName":"Billing FAQ"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2209,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":8,"CategoryName":"Transfer Information"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":22,"CategoryName":"Hosting Information"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":38,"CategoryName":"SSL General"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":9,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":45,"CategoryName":"Account Security"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":46,"CategoryName":"Domain Management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2211,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":63,"CategoryName":"Namecheap API"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2228,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":177,"CategoryName":"Google Workspace (formerly G Suite)"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2179,"CategoryName":"Private Email: General Information"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2274,"CategoryName":"General"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2280,"CategoryName":"Getting Started"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2279,"CategoryName":"General Information"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2215,"CategoryName":"Private Email: Mailbox Management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2211,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2196,"CategoryName":"WHMCS module for SSL"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/savings-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2200,"CategoryName":"Checkout & Billing","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2200,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":7,"CategoryName":"Billing FAQ"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2200,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2201,"CategoryName":"Domains Billing"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2200,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":21,"CategoryName":"Hosting Billing"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2200,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":71,"CategoryName":"SSL Certificates Billing"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2200,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2177,"CategoryName":"Private Email"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2200,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2201,"CategoryName":"Domains Billing"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":67,"CategoryName":"Activation"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2209,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":83,"CategoryName":"Transfer to Namecheap"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":9,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":43,"CategoryName":"Profile Management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":10,"CategoryName":"DNS Questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":29,"CategoryName":"cPanel questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2200,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":21,"CategoryName":"Hosting Billing"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":11,"CategoryName":"Dynamic DNS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":9,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":44,"CategoryName":"Account Access"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2209,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":84,"CategoryName":"Transfer to another provider"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":68,"CategoryName":"Validation"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2182,"CategoryName":"cPanel: Software Management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2214,"CategoryName":"Email Forwarding"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2270,"CategoryName":"Routers"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2281,"CategoryName":"WordPress Migration"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2282,"CategoryName":"Plugins and Themes"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2272,"CategoryName":"TV"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2187,"CategoryName":"cPanel: WordPress"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2209,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":219,"CategoryName":"Canceled Transfers"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2200,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":71,"CategoryName":"SSL Certificates Billing"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2176,"CategoryName":"Private Email: DNS Settings"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":69,"CategoryName":"Installation"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/reseller-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":34,"CategoryName":"Domains","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2232,"CategoryName":"DNSSEC"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2234,"CategoryName":"Google Workspace (formerly G Suite)"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2237,"CategoryName":"Host records setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":46,"CategoryName":"Domain Management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":10,"CategoryName":"DNS Questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":11,"CategoryName":"Dynamic DNS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":35,"CategoryName":"Registrations"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2207,"CategoryName":"Renewal questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":36,"CategoryName":"Domains with extended attributes"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":51,"CategoryName":"FreeDNS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":15,"CategoryName":"Namecheap Market"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2208,"CategoryName":"3rd Party Services Setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2278,"CategoryName":"Handshake TLDs"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":35,"CategoryName":"Registrations"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":70,"CategoryName":"Reissuance"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/protection-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":37,"CategoryName":"Domain Privacy Protection","SubCategories":[]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2200,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2177,"CategoryName":"Private Email"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2178,"CategoryName":"Private Email: Webmail Features"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2207,"CategoryName":"Renewal questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2210,"CategoryName":"cPanel Add-ons"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2273,"CategoryName":"Gaming Consoles"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2284,"CategoryName":"WordPress Management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2285,"CategoryName":"SFTP and Database access"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2268,"CategoryName":"macOS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2175,"CategoryName":"Private Email: Client Setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/status-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2209,"CategoryName":"Domain Transfers","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2209,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":8,"CategoryName":"Transfer Information"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2209,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":83,"CategoryName":"Transfer to Namecheap"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2209,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":84,"CategoryName":"Transfer to another provider"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2209,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":219,"CategoryName":"Canceled Transfers"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":48,"CategoryName":"VPS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":36,"CategoryName":"Domains with extended attributes"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":true,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/server-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":12,"CategoryName":"Hosting","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2219,"CategoryName":"PHP Configuration"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2225,"CategoryName":"SEO"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2252,"CategoryName":"InterWorx questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2291,"CategoryName":"Webuzo questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":27,"CategoryName":"Getting Started"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":22,"CategoryName":"Hosting Information"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":29,"CategoryName":"cPanel questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2182,"CategoryName":"cPanel: Software Management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2187,"CategoryName":"cPanel: WordPress"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2210,"CategoryName":"cPanel Add-ons"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":48,"CategoryName":"VPS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2188,"CategoryName":"Dedicated Server"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":30,"CategoryName":"WHM questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":32,"CategoryName":"DNS settings"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":103,"CategoryName":"LVE (CloudLinux)"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":89,"CategoryName":"SSH Access"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":205,"CategoryName":"FTP questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2180,"CategoryName":"MySQL questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2199,"CategoryName":"Hosting Migration"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2194,"CategoryName":"Tips & Tricks"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":239,"CategoryName":"WHMCS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":33,"CategoryName":"SSL Installation"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2171,"CategoryName":"Private Email: Active Sync (Exchange) Setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2188,"CategoryName":"Dedicated Server"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2269,"CategoryName":"iOS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2286,"CategoryName":"Domains questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2288,"CategoryName":"Billing questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2271,"CategoryName":"Linux"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":30,"CategoryName":"WHM questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":31,"CategoryName":"cPanel Email FAQs"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":51,"CategoryName":"FreeDNS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/email-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":93,"CategoryName":"Email service","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2216,"CategoryName":"Spam Protection"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2226,"CategoryName":"Email Migration"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2260,"CategoryName":"Private Email Contacts and Calendars Setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2179,"CategoryName":"Private Email: General Information"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2215,"CategoryName":"Private Email: Mailbox Management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2214,"CategoryName":"Email Forwarding"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2176,"CategoryName":"Private Email: DNS Settings"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2178,"CategoryName":"Private Email: Webmail Features"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2175,"CategoryName":"Private Email: Client Setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2171,"CategoryName":"Private Email: Active Sync (Exchange) Setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":31,"CategoryName":"cPanel Email FAQs"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2186,"CategoryName":"cPanel Email: Client Setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2204,"CategoryName":"Private Email: Video Overview"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":32,"CategoryName":"DNS settings"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":15,"CategoryName":"Namecheap Market"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2186,"CategoryName":"cPanel Email: Client Setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2266,"CategoryName":"Windows"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2287,"CategoryName":"SSL questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2267,"CategoryName":"Android"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2208,"CategoryName":"3rd Party Services Setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2204,"CategoryName":"Private Email: Video Overview"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/security-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":14,"CategoryName":"SSL Certificates","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2217,"CategoryName":"Renewal"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2218,"CategoryName":"cPanel SSL Plugin"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2221,"CategoryName":"Multi-Domain SSL Certificates"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2222,"CategoryName":"Cancellation"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2223,"CategoryName":"Browser errors"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2224,"CategoryName":"Site Seal, Logo"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2238,"CategoryName":"SSL installation errors"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2290,"CategoryName":"CSR code"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2293,"CategoryName":"Automated SSL management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":38,"CategoryName":"SSL General"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":67,"CategoryName":"Activation"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":68,"CategoryName":"Validation"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":69,"CategoryName":"Installation"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":70,"CategoryName":"Reissuance"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":true,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/performance-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":9,"CategoryName":"My Account","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":9,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":45,"CategoryName":"Account Security"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":9,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":43,"CategoryName":"Profile Management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":9,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":44,"CategoryName":"Account Access"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2278,"CategoryName":"Handshake TLDs"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":103,"CategoryName":"LVE (CloudLinux)"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/affiliates-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":55,"CategoryName":"Affiliates","SubCategories":[]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":89,"CategoryName":"SSH Access"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/tools-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2211,"CategoryName":"API & Resellers","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2211,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2227,"CategoryName":"SSL Resellers"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2211,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2229,"CategoryName":"Hosting Resellers"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2211,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":63,"CategoryName":"Namecheap API"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2211,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2196,"CategoryName":"WHMCS module for SSL"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/timer-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2212,"CategoryName":"Legacy Products","SubCategories":[]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":205,"CategoryName":"FTP questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2180,"CategoryName":"MySQL questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2199,"CategoryName":"Hosting Migration"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/premiumdns-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2231,"CategoryName":"PremiumDNS","SubCategories":[]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2194,"CategoryName":"Tips & Tricks"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"https://static.nc-img.com/live-resource/icons/knowledgebase/fastVPN_icon-150px.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2265,"CategoryName":"FastVPN","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2292,"CategoryName":"Browser Extensions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2274,"CategoryName":"General"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2270,"CategoryName":"Routers"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2272,"CategoryName":"TV"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2273,"CategoryName":"Gaming Consoles"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2268,"CategoryName":"macOS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2269,"CategoryName":"iOS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2271,"CategoryName":"Linux"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2266,"CategoryName":"Windows"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2267,"CategoryName":"Android"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":239,"CategoryName":"WHMCS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":33,"CategoryName":"SSL Installation"}],"status":200,"statusText":"OK"}}



Need help? We're always here for you.