{"/api/v1/ncpl/simplekb/getarticle:\"{\\\"articleId\\\":544,\\\"categoryId\\\":51}\"":{"body":{"Id":544,"FriendlyId":"","ArticleTypeId":3,"Title":"How do I set up host records for a domain when I use FreeDNS?","ArticleName":"How do I set up host records for a domain when I use FreeDNS?","ArticleSummary":null,"PreponedSummary":false,"Approved":true,"Body":"DQoJCTxwPlRvIHNldCB1cCB5b3VyIGhvc3QgcmVjb3JkcyBmb3IgYSBkb21haW4gdGhhdCB1c2VzIDxhIGhyZWY9Imh0dHBzOi8vd3d3Lm5hbWVjaGVhcC5jb20vZG9tYWlucy9mcmVlZG5zLyI+RnJlZUROUzwvYT4sIGZvbGxvdyB0aGUgaW5zdHJ1Y3Rpb25zIGdpdmVuIGJlbG93Og0KDQogDQo8YnIgLz48YnIgLz4xLiBTaWduIGludG8geW91ciA8Yj5OYW1lY2hlYXAgYWNjb3VudDwvYj4gKFRoZSBTaWduIEluIG9wdGlvbiBpcyBhdmFpbGFibGUgaW4gdGhlIGhlYWRlciBvZiB0aGUgcGFnZSkuPGJyIC8+PC9wPg0KCQk8cD4yLiBNb3VzZSBvdmVyIHRoZSA8Yj5BY2NvdW50PC9iPiBvcHRpb24gaW4gdGhlIHVwcGVyIHJpZ2h0IGNvcm5lciBvZiB0aGUgcGFnZSBhbmQgY2hvb3NlIDxiPkRvbWFpbiBMaXN0IDwvYj5vciBjaG9vc2U8Yj4gRG9tYWluIExpc3Q8L2I+IGZyb20gdGhlIGxlZnQgc2lkZWJhcjo8YnIgLz48YnIgLz48aW1nIHNyYz0iaHR0cHM6Ly9OYW1lY2hlYXAuc2ltcGxla2IuY29tL1NpdGVDb250ZW50cy8yLTdDMjJENTIzNkE0NTQzRUI4MjdGM0JEODkzNkUxNTNFL21lZGlhL2ZyZWVkbnNob3N0cmVjMS5wbmciIHdpZHRoPSIxNjMiIGhlaWdodD0iMjMxIiAvPjxpbWcgc3JjPSJodHRwczovL05hbWVjaGVhcC5zaW1wbGVrYi5jb20vU2l0ZUNvbnRlbnRzLzItN0MyMkQ1MjM2QTQ1NDNFQjgyN0YzQkQ4OTM2RTE1M0UvbWVkaWEvZnJlZWRuc2hvc3RyZWMyLnBuZyIgd2lkdGg9IjM1NSIgaGVpZ2h0PSIyMjQiIC8+PGJyIC8+PC9wPg0KCQk8cD4NCgkJCQkzLiAgU2VsZWN0IDxiPkFsbCBQcm9kdWN0czwvYj4gZnJvbSB0aGUgbGlzdCBhdCB0aGUgcmlnaHQgc2lkZSBvZiB0aGUgcGFnZTo8YnIgLz48YnIgLz48aW1nIGNsYXNzPSJrYi1pbWFnZSIgc3JjPSJodHRwczovL05hbWVjaGVhcC5zaW1wbGVrYi5jb20vU2l0ZUNvbnRlbnRzLzItN0MyMkQ1MjM2QTQ1NDNFQjgyN0YzQkQ4OTM2RTE1M0UvbWVkaWEvYWxscHJvZHVjdHNfZG9tYWlubGlzdC5wbmciIC8+PGJyIC8+PC9wPg0KCQk8cD40LiBDbGljayBvbiB0aGUgPGI+TWFuYWdlPC9iPiBvcHRpb24gaW4gZnJvbnQgb2YgdGhlIGRvbWFpbiBuYW1lOg0KDQoNCjxiciAvPjxiciAvPjxpbWcgc3JjPSJodHRwczovL05hbWVjaGVhcC5zaW1wbGVrYi5jb20vU2l0ZUNvbnRlbnRzLzItN0MyMkQ1MjM2QTQ1NDNFQjgyN0YzQkQ4OTM2RTE1M0UvbWVkaWEvZmRuc19tYW5hZ2UucG5nIiB3aWR0aD0iNzcyIiBoZWlnaHQ9IjEzMCIgLz48YnIgLz48L3A+DQoJCTxwPg0KCQkJCTxiciAvPjUuIFNlbGVjdCA8Yj5BZHZhbmNlZCBETlMgPC9iPmF0IHRoZSB0b3Agb2YgdGhlIHBhZ2UuIEhlcmUgeW91IGNhbiBhZGQgZG9tYWluJ3MgaG9zdCByZWNvcmRzIChpbmNsdWRpbmcgQSwgQ05BTUUsIFRYVCwgU1JWLCBldGMuKSwgc2V0IHVwIG1haWwgc2V0dGluZ3Mgb3IgZW5hYmxlL2Rpc2FibGUgdGhlIER5bmFtaWMgRE5TIGZlYXR1cmU6DQoNCjxiciAvPjxiciAvPjxpbWcgc3JjPSJodHRwczovL05hbWVjaGVhcC5zaW1wbGVrYi5jb20vU2l0ZUNvbnRlbnRzLzItN0MyMkQ1MjM2QTQ1NDNFQjgyN0YzQkQ4OTM2RTE1M0UvbWVkaWEvZmRuc19hZGRfbmV3MS5wbmciIHdpZHRoPSI3NzgiIGhlaWdodD0iMjc3IiAvPjxiciAvPjxpbWcgc3JjPSJodHRwczovL05hbWVjaGVhcC5zaW1wbGVrYi5jb20vU2l0ZUNvbnRlbnRzLzItN0MyMkQ1MjM2QTQ1NDNFQjgyN0YzQkQ4OTM2RTE1M0UvbWVkaWEvZm5kc19tYWlsX2RkbnMucG5nIiB3aWR0aD0iNzc4IiBoZWlnaHQ9IjExMiIgLz48L3A+DQoJCTxwPg0KCQkJCTxiciAvPg0KCQk8L3A+DQoJCTxwPkhlcmUgaXMgYSBicmllZiBkZXNjcmlwdGlvbiBvZiBhbGwgcmVjb3JkIHR5cGVzIHRoYXQgY2FuIGJlIGFkZGVkIG9uIG91ciA8YSBocmVmPSJodHRwczovL3d3dy5uYW1lY2hlYXAuY29tL2Rucy93aGF0LWlzLWRucy1kb21haW4tbmFtZS1zeXN0ZW0tZGVmaW5pdGlvbi8iPkROUzwvYT4gc2VydmVyczoNCg0KDQo8YnIgLz48YnIgLz48L3A+DQoJCTx0YWJsZSBjbGFzcz0iTXNvTm9ybWFsVGFibGUiIHN0eWxlPSJib3JkZXItY29sbGFwc2U6IGNvbGxhcHNlOyIgd2lkdGg9IjU2NSIgaGVpZ2h0PSIxNDY1IiBjZWxsc3BhY2luZz0iMCIgY2VsbHBhZGRpbmc9IjAiIGJvcmRlcj0iMCI+DQoJCQkJPHRib2R5Pg0KCQkJCQkJPHRyPg0KCQkJCQkJCQk8dGQgc3R5bGU9ImJvcmRlcjogMXB0IHNvbGlkIHdpbmRvd3RleHQ7IHBhZGRpbmc6IDBpbiA1LjRwdDsgYmFja2dyb3VuZDogcmdiKDIyMywgMjIzLCAyNDUpIG5vbmUgcmVwZWF0IHNjcm9sbCAwJSA1MCU7IHdpZHRoOiAyMjEuNHB0OyAtbW96LWJhY2tncm91bmQtY2xpcDogLW1vei1pbml0aWFsOyAtbW96LWJhY2tncm91bmQtb3JpZ2luOiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IC1tb3otYmFja2dyb3VuZC1pbmxpbmUtcG9saWN5OiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IiB3aWR0aD0iMjk1IiB2YWxpZ249InRvcCI+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJPHAgc3R5bGU9InRleHQtYWxpZ246IGNlbnRlcjsiIGFsaWduPSJjZW50ZXIiPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJPGI+QWRkcmVzcyBSZWNvcmQgVHlwZTwvYj4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCTxiciAvPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCTwvcD4NCgkJCQkJCQkJPC90ZD4NCgkJCQkJCQkJPHRkIHN0eWxlPSJib3JkZXItc3R5bGU6IHNvbGlkIHNvbGlkIHNvbGlkIG5vbmU7IGJvcmRlci1jb2xvcjogd2luZG93dGV4dCB3aW5kb3d0ZXh0IHdpbmRvd3RleHQgLW1vei11c2UtdGV4dC1jb2xvcjsgYm9yZGVyLXdpZHRoOiAxcHQgMXB0IDFwdCBtZWRpdW07IHBhZGRpbmc6IDBpbiA1LjRwdDsgYmFja2dyb3VuZDogcmdiKDIyMywgMjIzLCAyNDUpIG5vbmUgcmVwZWF0IHNjcm9sbCAwJSA1MCU7IHdpZHRoOiAyMjEuNHB0OyAtbW96LWJhY2tncm91bmQtY2xpcDogLW1vei1pbml0aWFsOyAtbW96LWJhY2tncm91bmQtb3JpZ2luOiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IC1tb3otYmFja2dyb3VuZC1pbmxpbmUtcG9saWN5OiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IiB3aWR0aD0iMjk1IiB2YWxpZ249InRvcCI+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJPHAgc3R5bGU9InRleHQtYWxpZ246IGNlbnRlcjsiIGFsaWduPSJjZW50ZXIiPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJPGI+RGVzY3JpcHRpb248L2I+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJPC9wPg0KCQkJCQkJCQk8L3RkPg0KCQkJCQkJPC90cj4NCgkJCQkJCTx0cj4NCgkJCQkJCQkJPHRkIHN0eWxlPSJib3JkZXItc3R5bGU6IG5vbmUgc29saWQgc29saWQ7IGJvcmRlci1jb2xvcjogLW1vei11c2UtdGV4dC1jb2xvcjsgYm9yZGVyLXdpZHRoOiBtZWRpdW0gMXB0IDFwdDsgcGFkZGluZzogMGluIDUuNHB0OyBiYWNrZ3JvdW5kOiByZ2IoMjQ2LCAyNDYsIDI1Mikgbm9uZSByZXBlYXQgc2Nyb2xsIDAlIDUwJTsgd2lkdGg6IDIyMS40cHQ7IC1tb3otYmFja2dyb3VuZC1jbGlwOiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IC1tb3otYmFja2dyb3VuZC1vcmlnaW46IC1tb3otaW5pdGlhbDsgLW1vei1iYWNrZ3JvdW5kLWlubGluZS1wb2xpY3k6IC1tb3otaW5pdGlhbDsiIHdpZHRoPSIyOTUiIHZhbGlnbj0idG9wIj4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQk8cD4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCTxzcGFuIHN0eWxlPSJmb250LXNpemU6IDExcHQ7Ij4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJPGEgaHJlZj0iaHR0cHM6Ly93d3cubmFtZWNoZWFwLmNvbS9zdXBwb3J0L2tub3dsZWRnZWJhc2UvYXJ0aWNsZS5hc3B4LzMxOS8yMjM3L2hvdy1jYW4taS1zZXQtdXAtYW4tYS1hZGRyZXNzLXJlY29yZC1mb3ItbXktZG9tYWluIiBsaW5rdGV4dD0iQSAoQWRkcmVzcykiIGxpbmt0eXBlPSJDdXN0b20iIHRhcmdldD0iX2JsYW5rIj5BIChBZGRyZXNzKTwvYT4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCTwvc3Bhbj4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQk8L3A+DQoJCQkJCQkJCTwvdGQ+DQoJCQkJCQkJCTx0ZCBzdHlsZT0iYm9yZGVyLXN0eWxlOiBub25lIHNvbGlkIHNvbGlkIG5vbmU7IGJvcmRlci1jb2xvcjogLW1vei11c2UtdGV4dC1jb2xvcjsgYm9yZGVyLXdpZHRoOiBtZWRpdW0gMXB0IDFwdCBtZWRpdW07IHBhZGRpbmc6IDBpbiA1LjRwdDsgYmFja2dyb3VuZDogcmdiKDI0NiwgMjQ2LCAyNTIpIG5vbmUgcmVwZWF0IHNjcm9sbCAwJSA1MCU7IHdpZHRoOiAyMjEuNHB0OyAtbW96LWJhY2tncm91bmQtY2xpcDogLW1vei1pbml0aWFsOyAtbW96LWJhY2tncm91bmQtb3JpZ2luOiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IC1tb3otYmFja2dyb3VuZC1pbmxpbmUtcG9saWN5OiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IiB3aWR0aD0iMjk1IiB2YWxpZ249InRvcCI+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJPHA+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQk8c3BhbiBzdHlsZT0iZm9udC1zaXplOiAxMXB0OyI+QWxsb3dzIHlvdSB0byBhc3NvY2lhdGUgYSBob3N0IHdpdGggYW4gSVB2NCBhZGRyZXNzLiBUaGUgSVAgYWRkcmVzcyB0aGF0IHlvdSB1c2UgZG9lcyBub3QgaGF2ZSB0byBiZSBvbiB5b3VyIG5ldHdvcmsuIDwvc3Bhbj4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQk8L3A+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJPHA+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQk8c3BhbiBzdHlsZT0iZm9udC1zaXplOiAxMXB0OyI+Rm9yIGV4YW1wbGU6PC9zcGFuPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJPHNwYW4gc3R5bGU9ImZvbnQtc2l6ZTogMTFwdDsiPllvdSBjYW4gaGF2ZSB0aGUgaG9zdCByZWNvcmQgZm9yIHd3dyBwb2ludGVkIHRvIDIwNy40Ni4xMzAuMTQgKE1pY3Jvc29mdCB3ZWJzaXRlJ3MgYWRkcmVzcykuIDwvc3Bhbj4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQk8L3A+DQoJCQkJCQkJCTwvdGQ+DQoJCQkJCQk8L3RyPg0KCQkJCQkJPHRyPg0KCQkJCQkJCQk8dGQgc3R5bGU9ImJvcmRlci1zdHlsZTogbm9uZSBzb2xpZCBzb2xpZDsgYm9yZGVyLWNvbG9yOiAtbW96LXVzZS10ZXh0LWNvbG9yOyBib3JkZXItd2lkdGg6IG1lZGl1bSAxcHQgMXB0OyBwYWRkaW5nOiAwaW4gNS40cHQ7IGJhY2tncm91bmQ6IHJnYigyMjMsIDIyMywgMjQ1KSBub25lIHJlcGVhdCBzY3JvbGwgMCUgNTAlOyB3aWR0aDogMjIxLjRwdDsgLW1vei1iYWNrZ3JvdW5kLWNsaXA6IC1tb3otaW5pdGlhbDsgLW1vei1iYWNrZ3JvdW5kLW9yaWdpbjogLW1vei1pbml0aWFsOyAtbW96LWJhY2tncm91bmQtaW5saW5lLXBvbGljeTogLW1vei1pbml0aWFsOyIgd2lkdGg9IjI5NSIgdmFsaWduPSJ0b3AiPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCTxwPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJPHNwYW4gc3R5bGU9ImZvbnQtc2l6ZTogMTFwdDsiPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQk8YSBocmVmPSJodHRwczovL3d3dy5uYW1lY2hlYXAuY29tL3N1cHBvcnQva25vd2xlZGdlYmFzZS9hcnRpY2xlLmFzcHgvMzE5LzIyMzcvaG93LWNhbi1pLXNldC11cC1hbi1hLWFkZHJlc3MtcmVjb3JkLWZvci1teS1kb21haW4iIGxpbmt0ZXh0PSJBQUFBIChJUHY2KSIgbGlua3R5cGU9IkN1c3RvbSIgdGFyZ2V0PSJfYmxhbmsiPkFBQUEgKElQdjYpPC9hPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQk8YnIgLz4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCTwvc3Bhbj4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQk8L3A+DQoJCQkJCQkJCTwvdGQ+DQoJCQkJCQkJCTx0ZCBzdHlsZT0iYm9yZGVyLXN0eWxlOiBub25lIHNvbGlkIHNvbGlkIG5vbmU7IGJvcmRlci1jb2xvcjogLW1vei11c2UtdGV4dC1jb2xvcjsgYm9yZGVyLXdpZHRoOiBtZWRpdW0gMXB0IDFwdCBtZWRpdW07IHBhZGRpbmc6IDBpbiA1LjRwdDsgYmFja2dyb3VuZDogcmdiKDIyMywgMjIzLCAyNDUpIG5vbmUgcmVwZWF0IHNjcm9sbCAwJSA1MCU7IHdpZHRoOiAyMjEuNHB0OyAtbW96LWJhY2tncm91bmQtY2xpcDogLW1vei1pbml0aWFsOyAtbW96LWJhY2tncm91bmQtb3JpZ2luOiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IC1tb3otYmFja2dyb3VuZC1pbmxpbmUtcG9saWN5OiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IiB3aWR0aD0iMjk1IiB2YWxpZ249InRvcCI+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJPHA+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQk8c3BhbiBzdHlsZT0iZm9udC1zaXplOiAxMXB0OyI+QWxsb3dzIHlvdSB0byBhc3NvY2lhdGUgYSBob3N0IHdpdGggYW4gSVB2NiBhZGRyZXNzLiBUaGUgSVAgYWRkcmVzcyB0aGF0IHlvdSB1c2UgZG9lcyBub3QgaGF2ZSB0byBiZSBvbiB5b3VyIG5ldHdvcmsuIDwvc3Bhbj4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQk8L3A+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJPHA+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQk8c3BhbiBzdHlsZT0iZm9udC1zaXplOiAxMXB0OyI+Rm9yIGV4YW1wbGU6PC9zcGFuPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJPHNwYW4gc3R5bGU9ImZvbnQtc2l6ZTogMTFwdDsiPiBZb3UgY2FuIGhhdmUgdGhlIGhvc3QgcmVjb3JkIGZvciB3d3cgcG9pbnRlZCB0byAyMDAxOjBkYjg6MTFhMzowOWQ3OjFmMzQ6OGEyZTowN2EwOjc2NWQ8YnIgLz48L3NwYW4+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJPC9wPg0KCQkJCQkJCQk8L3RkPg0KCQkJCQkJPC90cj4NCgkJCQkJCTx0cj4NCgkJCQkJCQkJPHRkIHN0eWxlPSJib3JkZXItc3R5bGU6IG5vbmUgc29saWQgc29saWQ7IGJvcmRlci1jb2xvcjogLW1vei11c2UtdGV4dC1jb2xvcjsgYm9yZGVyLXdpZHRoOiBtZWRpdW0gMXB0IDFwdDsgcGFkZGluZzogMGluIDUuNHB0OyBiYWNrZ3JvdW5kOiByZ2IoMjQ2LCAyNDYsIDI1Mikgbm9uZSByZXBlYXQgc2Nyb2xsIDAlIDUwJTsgd2lkdGg6IDIyMS40cHQ7IC1tb3otYmFja2dyb3VuZC1jbGlwOiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IC1tb3otYmFja2dyb3VuZC1vcmlnaW46IC1tb3otaW5pdGlhbDsgLW1vei1iYWNrZ3JvdW5kLWlubGluZS1wb2xpY3k6IC1tb3otaW5pdGlhbDsiIHdpZHRoPSIyOTUiIHZhbGlnbj0idG9wIj4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQk8cD4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCTxzdHJvbmc+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCTxzcGFuIHN0eWxlPSJmb250LXdlaWdodDogbm9ybWFsOyBmb250LXNpemU6IDExcHQ7Ij4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQk8YSBocmVmPSJodHRwczovL3d3dy5uYW1lY2hlYXAuY29tL3N1cHBvcnQva25vd2xlZGdlYmFzZS9hcnRpY2xlLmFzcHgvMzIyLzIyMzcvaG93LWNhbi1pLXNldC11cC1teC1yZWNvcmRzLXJlcXVpcmVkLWZvci1tYWlsLXNlcnZpY2UiIGxpbmt0ZXh0PSJNWEUgKE1haWwgRWFzeSkiIGxpbmt0eXBlPSJDdXN0b20iIHRhcmdldD0iX2JsYW5rIj5NWEUgKE1haWwgRWFzeSk8L2E+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCTwvc3Bhbj4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCTwvc3Ryb25nPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJPHN0cm9uZz4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJPHNwYW4gc3R5bGU9ImZvbnQtc2l6ZTogMTFwdDsiPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQk8L3NwYW4+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQk8L3N0cm9uZz4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCTxzcGFuIHN0eWxlPSJmb250LXNpemU6IDExcHQ7Ij4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCTwvc3Bhbj4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQk8L3A+DQoJCQkJCQkJCTwvdGQ+DQoJCQkJCQkJCTx0ZCBzdHlsZT0iYm9yZGVyLXN0eWxlOiBub25lIHNvbGlkIHNvbGlkIG5vbmU7IGJvcmRlci1jb2xvcjogLW1vei11c2UtdGV4dC1jb2xvcjsgYm9yZGVyLXdpZHRoOiBtZWRpdW0gMXB0IDFwdCBtZWRpdW07IHBhZGRpbmc6IDBpbiA1LjRwdDsgYmFja2dyb3VuZDogcmdiKDI0NiwgMjQ2LCAyNTIpIG5vbmUgcmVwZWF0IHNjcm9sbCAwJSA1MCU7IHdpZHRoOiAyMjEuNHB0OyAtbW96LWJhY2tncm91bmQtY2xpcDogLW1vei1pbml0aWFsOyAtbW96LWJhY2tncm91bmQtb3JpZ2luOiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IC1tb3otYmFja2dyb3VuZC1pbmxpbmUtcG9saWN5OiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IiB3aWR0aD0iMjk1IiB2YWxpZ249InRvcCI+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJPHA+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQk8c3BhbiBzdHlsZT0iZm9udC1zaXplOiAxMXB0OyI+QWxsb3dzIHlvdSB0byBzcGVjaWZ5IHRoZSBhZGRyZXNzIG9mIHlvdXIgbWFpbCBzZXJ2ZXIuIFdoZW4geW91IHVzZSBhIG1haWwgcmVjb3JkLCB5b3UgbXVzdCB1c2UgYW4gSVAgYWRkcmVzcyBpbiB0aGUgYWRkcmVzcyBmaWVsZC4gPC9zcGFuPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCTwvcD4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQk8cD4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCTxzcGFuIHN0eWxlPSJmb250LXNpemU6IDExcHQ7Ij5Ob3RlIHRvIHByb2Zlc3Npb25hbCB1c2Vyczo8L3NwYW4+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQk8c3BhbiBzdHlsZT0iZm9udC1zaXplOiAxMXB0OyI+Q3JlYXRpbmcgYSBtYWlsIHJlY29yZCBjcmVhdGVzIGJvdGggdGhlIE1YIGFuZCBBIHJlY29yZHMgaW4gRE5TLiBBbHNvLCB3aGVuIHVzaW5nIG11bHRpcGxlIG1haWwgc2VydmVycywgYSBwcmVmZXJlbmNlIHZhbHVlIG9mIDEwIGlzIHVzZWQgb24gYWxsIGVudHJpZXMuIDwvc3Bhbj4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQk8L3A+DQoJCQkJCQkJCTwvdGQ+DQoJCQkJCQk8L3RyPg0KCQkJCQkJPHRyPg0KCQkJCQkJCQk8dGQgc3R5bGU9ImJvcmRlci1zdHlsZTogbm9uZSBzb2xpZCBzb2xpZDsgYm9yZGVyLWNvbG9yOiAtbW96LXVzZS10ZXh0LWNvbG9yOyBib3JkZXItd2lkdGg6IG1lZGl1bSAxcHQgMXB0OyBwYWRkaW5nOiAwaW4gNS40cHQ7IGJhY2tncm91bmQ6IHJnYigyMjMsIDIyMywgMjQ1KSBub25lIHJlcGVhdCBzY3JvbGwgMCUgNTAlOyB3aWR0aDogMjIxLjRwdDsgLW1vei1iYWNrZ3JvdW5kLWNsaXA6IC1tb3otaW5pdGlhbDsgLW1vei1iYWNrZ3JvdW5kLW9yaWdpbjogLW1vei1pbml0aWFsOyAtbW96LWJhY2tncm91bmQtaW5saW5lLXBvbGljeTogLW1vei1pbml0aWFsOyIgd2lkdGg9IjI5NSIgdmFsaWduPSJ0b3AiPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCTxwPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJPHN0cm9uZz4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJPHNwYW4gc3R5bGU9ImZvbnQtd2VpZ2h0OiBub3JtYWw7IGZvbnQtc2l6ZTogMTFwdDsiPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCTxhIGhyZWY9Imh0dHBzOi8vd3d3Lm5hbWVjaGVhcC5jb20vc3VwcG9ydC9rbm93bGVkZ2ViYXNlL2FydGljbGUuYXNweC8zMjIvMjIzNy9ob3ctY2FuLWktc2V0LXVwLW14LXJlY29yZHMtcmVxdWlyZWQtZm9yLW1haWwtc2VydmljZSIgbGlua3RleHQ9Ik1YIChNYWlsKSIgbGlua3R5cGU9IkN1c3RvbSIgdGFyZ2V0PSJfYmxhbmsiPk1YIChNYWlsKTwvYT4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJPC9zcGFuPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJPC9zdHJvbmc+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQk8c3Ryb25nPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQk8c3BhbiBzdHlsZT0iZm9udC1zaXplOiAxMXB0OyI+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCTwvc3Bhbj4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCTwvc3Ryb25nPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJPHNwYW4gc3R5bGU9ImZvbnQtc2l6ZTogMTFwdDsiPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJPC9zcGFuPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCTwvcD4NCgkJCQkJCQkJPC90ZD4NCgkJCQkJCQkJPHRkIHN0eWxlPSJib3JkZXItc3R5bGU6IG5vbmUgc29saWQgc29saWQgbm9uZTsgYm9yZGVyLWNvbG9yOiAtbW96LXVzZS10ZXh0LWNvbG9yOyBib3JkZXItd2lkdGg6IG1lZGl1bSAxcHQgMXB0IG1lZGl1bTsgcGFkZGluZzogMGluIDUuNHB0OyBiYWNrZ3JvdW5kOiByZ2IoMjIzLCAyMjMsIDI0NSkgbm9uZSByZXBlYXQgc2Nyb2xsIDAlIDUwJTsgd2lkdGg6IDIyMS40cHQ7IC1tb3otYmFja2dyb3VuZC1jbGlwOiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IC1tb3otYmFja2dyb3VuZC1vcmlnaW46IC1tb3otaW5pdGlhbDsgLW1vei1iYWNrZ3JvdW5kLWlubGluZS1wb2xpY3k6IC1tb3otaW5pdGlhbDsiIHdpZHRoPSIyOTUiIHZhbGlnbj0idG9wIj4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQk8cD4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCTxzdHJvbmc+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQk8L3N0cm9uZz4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCTxzcGFuIHN0eWxlPSJmb250LXNpemU6IDExcHQ7Ij5DPC9zcGFuPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJPHNwYW4gc3R5bGU9ImZvbnQtc2l6ZTogMTFwdDsiPmFuIGJlIGVpdGhlciBhIGhvc3QgbmFtZSB1bmRlciB5b3VyIGRvbWFpbiBuYW1lIChmb3IgZXhhbXBsZSwgIm1haWwzIikgb3IgdGhlIG5hbWUgb2YgYSBtYWlsIHNlcnZlciAoZm9yIGV4YW1wbGUsICJtYWlsLnlhaG9vLmNvbS4iKS4gPC9zcGFuPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCTwvcD4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQk8cD4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCTxiPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQk8c3BhbiBzdHlsZT0iZm9udC1zaXplOiAxMXB0OyI+Tk9URTo8L3NwYW4+wqA8L2I+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQk8c3BhbiBzdHlsZT0iZm9udC1zaXplOiAxMXB0OyI+V2hlbiB1c2luZyBhIG1haWwgc2VydmVyIG5hbWUsIGl0IHNob3VsZCBlbmQgd2l0aCBhIHBlcmlvZCAoIi4iKS4gKElmIHlvdSBmb3JnZXQgdGhlIHBlcmlvZCBhbmQgd2UgcmVjb2duaXplIHRoZSBUTEQsIHdlIHdpbGwgYXV0b21hdGljYWxseSBpbnNlcnQgb25lKS4gPC9zcGFuPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCTwvcD4NCgkJCQkJCQkJPC90ZD4NCgkJCQkJCTwvdHI+DQoJCQkJCQk8dHI+DQoJCQkJCQkJCTx0ZCBzdHlsZT0iYm9yZGVyLXN0eWxlOiBub25lIHNvbGlkIHNvbGlkOyBib3JkZXItY29sb3I6IC1tb3otdXNlLXRleHQtY29sb3I7IGJvcmRlci13aWR0aDogbWVkaXVtIDFwdCAxcHQ7IHBhZGRpbmc6IDBpbiA1LjRwdDsgYmFja2dyb3VuZDogcmdiKDI0NiwgMjQ2LCAyNTIpIG5vbmUgcmVwZWF0IHNjcm9sbCAwJSA1MCU7IHdpZHRoOiAyMjEuNHB0OyAtbW96LWJhY2tncm91bmQtY2xpcDogLW1vei1pbml0aWFsOyAtbW96LWJhY2tncm91bmQtb3JpZ2luOiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IC1tb3otYmFja2dyb3VuZC1pbmxpbmUtcG9saWN5OiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IiB3aWR0aD0iMjk1IiB2YWxpZ249InRvcCI+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJPHA+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQk8c3Ryb25nPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQk8c3BhbiBzdHlsZT0iZm9udC13ZWlnaHQ6IG5vcm1hbDsgZm9udC1zaXplOiAxMXB0OyI+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJPGEgaHJlZj0iaHR0cHM6Ly93d3cubmFtZWNoZWFwLmNvbS9zdXBwb3J0L2tub3dsZWRnZWJhc2UvYXJ0aWNsZS5hc3B4Lzk2NDYvMjIzNy9ob3ctY2FuLWktc2V0LXVwLWEtY25hbWUtcmVjb3JkLWZvci1teS1kb21haW4iIGxpbmt0ZXh0PSJDTkFNRSAoQWxpYXMpIiBsaW5rdHlwZT0iQ3VzdG9tIiB0YXJnZXQ9Il9ibGFuayI+Q05BTUUgKEFsaWFzKTwvYT4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJPC9zcGFuPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJPC9zdHJvbmc+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQk8c3Ryb25nPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQk8c3BhbiBzdHlsZT0iZm9udC1zaXplOiAxMXB0OyI+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCTwvc3Bhbj4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCTwvc3Ryb25nPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJPHNwYW4gc3R5bGU9ImZvbnQtc2l6ZTogMTFwdDsiPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJPC9zcGFuPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCTwvcD4NCgkJCQkJCQkJPC90ZD4NCgkJCQkJCQkJPHRkIHN0eWxlPSJib3JkZXItc3R5bGU6IG5vbmUgc29saWQgc29saWQgbm9uZTsgYm9yZGVyLWNvbG9yOiAtbW96LXVzZS10ZXh0LWNvbG9yOyBib3JkZXItd2lkdGg6IG1lZGl1bSAxcHQgMXB0IG1lZGl1bTsgcGFkZGluZzogMGluIDUuNHB0OyBiYWNrZ3JvdW5kOiByZ2IoMjQ2LCAyNDYsIDI1Mikgbm9uZSByZXBlYXQgc2Nyb2xsIDAlIDUwJTsgd2lkdGg6IDIyMS40cHQ7IC1tb3otYmFja2dyb3VuZC1jbGlwOiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IC1tb3otYmFja2dyb3VuZC1vcmlnaW46IC1tb3otaW5pdGlhbDsgLW1vei1iYWNrZ3JvdW5kLWlubGluZS1wb2xpY3k6IC1tb3otaW5pdGlhbDsiIHdpZHRoPSIyOTUiIHZhbGlnbj0idG9wIj4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQk8cD4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCTxzcGFuIHN0eWxlPSJmb250LXNpemU6IDExcHQ7Ij5Bc3NvY2lhdGVzIGEgaG9zdCBuYW1lIHdpdGggYW5vdGhlciBob3N0LiBUaGUgaG9zdCB0aGF0IHlvdSB3aXNoIHRvIHBvaW50IHRvIGRvZXMgbm90IGhhdmUgdG8gYmUgb24geW91ciBuZXR3b3JrLiA8L3NwYW4+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJPC9wPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCTxwPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJPHNwYW4gc3R5bGU9ImZvbnQtc2l6ZTogMTFwdDsiPkZvciBleGFtcGxlOjwvc3Bhbj4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCTxzcGFuIHN0eWxlPSJmb250LXNpemU6IDExcHQ7Ij5Zb3UgY2FuIGhhdmUgdGhlIGhvc3QgcmVjb3JkIGZvciB3d3cgcG9pbnQgdG8gd3d3Lm1pY3Jvc29mdC5jb20uIFlvdSBjYW4gYWxzbyBzaW1wbHkgdXNlIHRoZSAiQCIgc2lnbiB0byByZXByZXNlbnQgeW91ciBkb21haW4uIDwvc3Bhbj4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQk8L3A+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJPHU+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJPC91Pg0KCQkJCQkJCQk8L3RkPg0KCQkJCQkJPC90cj4NCgkJCQkJCTx0cj4NCgkJCQkJCQkJPHRkIHN0eWxlPSJib3JkZXItc3R5bGU6IG5vbmUgc29saWQgc29saWQ7IGJvcmRlci1jb2xvcjogLW1vei11c2UtdGV4dC1jb2xvcjsgYm9yZGVyLXdpZHRoOiBtZWRpdW0gMXB0IDFwdDsgcGFkZGluZzogMGluIDUuNHB0OyBiYWNrZ3JvdW5kOiByZ2IoMjIzLCAyMjMsIDI0NSkgbm9uZSByZXBlYXQgc2Nyb2xsIDAlIDUwJTsgd2lkdGg6IDIyMS40cHQ7IC1tb3otYmFja2dyb3VuZC1jbGlwOiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IC1tb3otYmFja2dyb3VuZC1vcmlnaW46IC1tb3otaW5pdGlhbDsgLW1vei1iYWNrZ3JvdW5kLWlubGluZS1wb2xpY3k6IC1tb3otaW5pdGlhbDsiIHdpZHRoPSIyOTUiIHZhbGlnbj0idG9wIj4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQk8cD4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCTxzdHJvbmc+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCTxzcGFuIHN0eWxlPSJmb250LXdlaWdodDogbm9ybWFsOyBmb250LXNpemU6IDExcHQ7Ij5OUzwvc3Bhbj4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCTwvc3Ryb25nPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJPHN0cm9uZz4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJPHNwYW4gc3R5bGU9ImZvbnQtc2l6ZTogMTFwdDsiPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQk8L3NwYW4+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQk8L3N0cm9uZz4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCTxzcGFuIHN0eWxlPSJmb250LXNpemU6IDExcHQ7Ij4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCTwvc3Bhbj4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQk8L3A+DQoJCQkJCQkJCTwvdGQ+DQoJCQkJCQkJCTx0ZCBzdHlsZT0iYm9yZGVyLXN0eWxlOiBub25lIHNvbGlkIHNvbGlkIG5vbmU7IGJvcmRlci1jb2xvcjogLW1vei11c2UtdGV4dC1jb2xvcjsgYm9yZGVyLXdpZHRoOiBtZWRpdW0gMXB0IDFwdCBtZWRpdW07IHBhZGRpbmc6IDBpbiA1LjRwdDsgYmFja2dyb3VuZDogcmdiKDIyMywgMjIzLCAyNDUpIG5vbmUgcmVwZWF0IHNjcm9sbCAwJSA1MCU7IHdpZHRoOiAyMjEuNHB0OyAtbW96LWJhY2tncm91bmQtY2xpcDogLW1vei1pbml0aWFsOyAtbW96LWJhY2tncm91bmQtb3JpZ2luOiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IC1tb3otYmFja2dyb3VuZC1pbmxpbmUtcG9saWN5OiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IiB3aWR0aD0iMjk1IiB2YWxpZ249InRvcCI+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJPHNwYW4gc3R5bGU9ImZvbnQtc2l6ZTogMTFwdDsiPlByaW1hcmlseSB1c2VkIGlmIHlvdSB3YW50IHRvIGJyZWFrIHlvdXIgZG9tYWluIGludG8gDQpzdWJkb21haW5zLiAgICBTdWJkb21haW5zIGluZGljYXRlIHlvdSBhcmUgZGVsZWdhdGluZyBhIHBvcnRpb24gb2YgYSBkb21haW4gbmFtZSB0byBhIGRpZmZlcmVudCBncm91cCBvZiBuYW1lc2VydmVycywgdGh1cywgY3JlYXRpbmcgTlMgcmVjb3JkcyB0byBwb2ludCB0aGUgaG9zdG5hbWUgKG5hbWUgb2YgdGhlIHN1YmRvbWFpbikgdG8gZGlmZmVyZW50IG5hbWVzZXJ2ZXJzLjwvc3Bhbj4NCgkJCQkJCQkJPC90ZD4NCgkJCQkJCTwvdHI+DQoJCQkJCQk8dHI+DQoJCQkJCQkJCTx0ZCBzdHlsZT0iYm9yZGVyLXN0eWxlOiBub25lIHNvbGlkIHNvbGlkOyBib3JkZXItY29sb3I6IC1tb3otdXNlLXRleHQtY29sb3I7IGJvcmRlci13aWR0aDogbWVkaXVtIDFwdCAxcHQ7IHBhZGRpbmc6IDBpbiA1LjRwdDsgYmFja2dyb3VuZDogcmdiKDI0NiwgMjQ2LCAyNTIpIG5vbmUgcmVwZWF0IHNjcm9sbCAwJSA1MCU7IHdpZHRoOiAyMjEuNHB0OyAtbW96LWJhY2tncm91bmQtY2xpcDogLW1vei1pbml0aWFsOyAtbW96LWJhY2tncm91bmQtb3JpZ2luOiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IC1tb3otYmFja2dyb3VuZC1pbmxpbmUtcG9saWN5OiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IiB3aWR0aD0iMjk1IiB2YWxpZ249InRvcCI+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJPHA+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQk8c3Ryb25nPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQk8c3BhbiBzdHlsZT0iZm9udC13ZWlnaHQ6IG5vcm1hbDsgZm9udC1zaXplOiAxMXB0OyI+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJPGEgaHJlZj0iaHR0cHM6Ly93d3cubmFtZWNoZWFwLmNvbS9zdXBwb3J0L2tub3dsZWRnZWJhc2UvYXJ0aWNsZS5hc3B4LzM4NS8yMjM3L2hvdy1kby1pLXNldC11cC1hLXVybC1yZWRpcmVjdC1mb3ItYS1kb21haW4iIGxpbmt0ZXh0PSJVUkwgUmVkaXJlY3QiIGxpbmt0eXBlPSJDdXN0b20iIHRhcmdldD0iX2JsYW5rIj5VUkwgUmVkaXJlY3Q8L2E+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCTwvc3Bhbj4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCTwvc3Ryb25nPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJPHN0cm9uZz4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJPHNwYW4gc3R5bGU9ImZvbnQtc2l6ZTogMTFwdDsiPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQk8L3NwYW4+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQk8L3N0cm9uZz4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCTxzcGFuIHN0eWxlPSJmb250LXNpemU6IDExcHQ7Ij4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCTwvc3Bhbj4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQk8L3A+DQoJCQkJCQkJCTwvdGQ+DQoJCQkJCQkJCTx0ZCBzdHlsZT0iYm9yZGVyLXN0eWxlOiBub25lIHNvbGlkIHNvbGlkIG5vbmU7IGJvcmRlci1jb2xvcjogLW1vei11c2UtdGV4dC1jb2xvcjsgYm9yZGVyLXdpZHRoOiBtZWRpdW0gMXB0IDFwdCBtZWRpdW07IHBhZGRpbmc6IDBpbiA1LjRwdDsgYmFja2dyb3VuZDogcmdiKDI0NiwgMjQ2LCAyNTIpIG5vbmUgcmVwZWF0IHNjcm9sbCAwJSA1MCU7IHdpZHRoOiAyMjEuNHB0OyAtbW96LWJhY2tncm91bmQtY2xpcDogLW1vei1pbml0aWFsOyAtbW96LWJhY2tncm91bmQtb3JpZ2luOiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IC1tb3otYmFja2dyb3VuZC1pbmxpbmUtcG9saWN5OiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IiB3aWR0aD0iMjk1IiB2YWxpZ249InRvcCI+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJPHA+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQk8c3BhbiBzdHlsZT0iZm9udC1zaXplOiAxMXB0OyI+U3RhbmRhcmQgbWV0aG9kIGZvciBVUkwgRm9yd2FyZGluZy4gV2hlbiB3ZWIgdXNlcnMgdHlwZSBpbiB5b3VyIGRvbWFpbiBuYW1lLCB0aGV5IGFyZSByZWRpcmVjdGVkIHRvIHRoZSB3ZWIgc2VydmVyIHdoZXJlIHlvdXIgd2ViIHBhZ2VzIGFyZSBob3N0ZWQgb24uIDwvc3Bhbj4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQk8L3A+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJPHA+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQk8c3BhbiBzdHlsZT0iZm9udC1zaXplOiAxMXB0OyI+VGhlIG9ubHkgZHJhd2JhY2sgb2YgdGhpcyBvcHRpb24gaXMgdGhhdCB0aGUgVVJMIGRpc3BsYXllZCBieSB0aGUgYnJvd3NlciBpcyB0aGUgb25lIG9uIHRoZSBhY3R1YWwgd2ViIHBhZ2UsIG5vdCB5b3VyIGRvbWFpbiBuYW1lLiBZb3UgY2FuIG92ZXJjb21lIHRoaXMgZHJhd2JhY2sgYnkgdXNpbmcgdGhlIFVSTCBGcmFtZSBtZXRob2QgaW5zdGVhZC4gPC9zcGFuPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCTwvcD4NCgkJCQkJCQkJPC90ZD4NCgkJCQkJCTwvdHI+DQoJCQkJCQk8dHI+DQoJCQkJCQkJCTx0ZCBzdHlsZT0iYm9yZGVyLXN0eWxlOiBub25lIHNvbGlkIHNvbGlkOyBib3JkZXItY29sb3I6IC1tb3otdXNlLXRleHQtY29sb3I7IGJvcmRlci13aWR0aDogbWVkaXVtIDFwdCAxcHQ7IHBhZGRpbmc6IDBpbiA1LjRwdDsgYmFja2dyb3VuZDogcmdiKDIyMywgMjIzLCAyNDUpIG5vbmUgcmVwZWF0IHNjcm9sbCAwJSA1MCU7IHdpZHRoOiAyMjEuNHB0OyAtbW96LWJhY2tncm91bmQtY2xpcDogLW1vei1pbml0aWFsOyAtbW96LWJhY2tncm91bmQtb3JpZ2luOiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IC1tb3otYmFja2dyb3VuZC1pbmxpbmUtcG9saWN5OiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IiB3aWR0aD0iMjk1IiB2YWxpZ249InRvcCI+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJPHA+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQk8c3Ryb25nPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQk8c3BhbiBzdHlsZT0iZm9udC13ZWlnaHQ6IG5vcm1hbDsgZm9udC1zaXplOiAxMXB0OyI+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJPGEgaHJlZj0iaHR0cHM6Ly93d3cubmFtZWNoZWFwLmNvbS9zdXBwb3J0L2tub3dsZWRnZWJhc2UvYXJ0aWNsZS5hc3B4LzM4NS8yMjM3L2hvdy1kby1pLXNldC11cC1hLXVybC1yZWRpcmVjdC1mb3ItYS1kb21haW4iIGxpbmt0ZXh0PSJVUkwgRnJhbWUiIGxpbmt0eXBlPSJDdXN0b20iIHRhcmdldD0iX2JsYW5rIj5VUkwgRnJhbWU8L2E+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCTwvc3Bhbj4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCTwvc3Ryb25nPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJPHN0cm9uZz4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJPHNwYW4gc3R5bGU9ImZvbnQtc2l6ZTogMTFwdDsiPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQk8L3NwYW4+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQk8L3N0cm9uZz4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCTxzcGFuIHN0eWxlPSJmb250LXNpemU6IDExcHQ7Ij4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCTwvc3Bhbj4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQk8L3A+DQoJCQkJCQkJCTwvdGQ+DQoJCQkJCQkJCTx0ZCBzdHlsZT0iYm9yZGVyLXN0eWxlOiBub25lIHNvbGlkIHNvbGlkIG5vbmU7IGJvcmRlci1jb2xvcjogLW1vei11c2UtdGV4dC1jb2xvcjsgYm9yZGVyLXdpZHRoOiBtZWRpdW0gMXB0IDFwdCBtZWRpdW07IHBhZGRpbmc6IDBpbiA1LjRwdDsgYmFja2dyb3VuZDogcmdiKDIyMywgMjIzLCAyNDUpIG5vbmUgcmVwZWF0IHNjcm9sbCAwJSA1MCU7IHdpZHRoOiAyMjEuNHB0OyAtbW96LWJhY2tncm91bmQtY2xpcDogLW1vei1pbml0aWFsOyAtbW96LWJhY2tncm91bmQtb3JpZ2luOiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IC1tb3otYmFja2dyb3VuZC1pbmxpbmUtcG9saWN5OiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IiB3aWR0aD0iMjk1IiB2YWxpZ249InRvcCI+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJPHA+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQk8c3BhbiBzdHlsZT0iZm9udC1zaXplOiAxMXB0OyI+VGhlIFVSTCBGcmFtZSBpcyBzaW1pbGFyIHRvIFVSTCBSZWRpcmVjdCBleGNlcHQgdGhhdCBpbnN0ZWFkIG9mIHJlZGlyZWN0aW5nIHRoZSBjbGllbnQgdG8geW91ciB3ZWIgcGFnZSwgdGhlIHdlYiBwYWdlIGlzIGRpc3BsYXllZCBpbiBhIGZyYW1lIGZyb20gb3VyIHdlYiBzZXJ2ZXIuIDwvc3Bhbj4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQk8L3A+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJPHA+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQk8c3BhbiBzdHlsZT0iZm9udC1zaXplOiAxMXB0OyI+VXNpbmcgdGhpcyBvcHRpb24sIHRoZSBjbGllbnQncyBicm93c2VyIHdpbGwgZGlzcGxheSB5b3VyIGRvbWFpbiBuYW1lIChmb3IgZXhhbXBsZSwgd3d3Lm15ZG9tYWluLmNvbSkgd2hpbGUgdGhleSBhcmUgdXNpbmcgeW91ciBzaXRlIGFuZCBub3QgdGhlIGFjdHVhbCBVUkwgdG8geW91ciBwYWdlIChlLmcuLCA8YSBocmVmPSJodHRwOi8vaG9tZS5pbmZvc3BhY2UuY29tL3VzZXIzMyI+aG9tZS5pbmZvc3BhY2UuY29tL3VzZXIzMzwvYT4iKS48L3NwYW4+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJPC9wPg0KCQkJCQkJCQk8L3RkPg0KCQkJCQkJPC90cj4NCgkJCQkJCTx0cj4NCgkJCQkJCQkJPHRkIHN0eWxlPSJib3JkZXItc3R5bGU6IG5vbmUgc29saWQgc29saWQ7IGJvcmRlci1jb2xvcjogLW1vei11c2UtdGV4dC1jb2xvcjsgYm9yZGVyLXdpZHRoOiBtZWRpdW0gMXB0IDFwdDsgcGFkZGluZzogMGluIDUuNHB0OyBiYWNrZ3JvdW5kOiByZ2IoMjQ2LCAyNDYsIDI1Mikgbm9uZSByZXBlYXQgc2Nyb2xsIDAlIDUwJTsgd2lkdGg6IDIyMS40cHQ7IC1tb3otYmFja2dyb3VuZC1jbGlwOiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IC1tb3otYmFja2dyb3VuZC1vcmlnaW46IC1tb3otaW5pdGlhbDsgLW1vei1iYWNrZ3JvdW5kLWlubGluZS1wb2xpY3k6IC1tb3otaW5pdGlhbDsiIHdpZHRoPSIyOTUiIHZhbGlnbj0idG9wIj4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQk8cD4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCTxzcGFuIHN0eWxlPSJmb250LXNpemU6IDExcHQ7Ij4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCTwvc3Bhbj4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCTxhIGhyZWY9Imh0dHBzOi8vd3d3Lm5hbWVjaGVhcC5jb20vc3VwcG9ydC9rbm93bGVkZ2ViYXNlL2FydGljbGUuYXNweC81OTcvMjIzNy9ob3ctY2FuLWktc2V0LXVwLWEtY2F0Y2hhbGwtd2lsZGNhcmQtc3ViZG9tYWluIiBsaW5rdGV4dD0iV2lsZGNhcmQgcmVjb3JkIiBsaW5rdHlwZT0iQ3VzdG9tIiB0YXJnZXQ9Il9ibGFuayI+V2lsZGNhcmQgcmVjb3JkPC9hPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJPHN0cm9uZz4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJPHNwYW4gc3R5bGU9ImZvbnQtd2VpZ2h0OiBub3JtYWw7IGZvbnQtc2l6ZTogMTFwdDsiPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQk8L3NwYW4+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQk8L3N0cm9uZz4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCTxzdHJvbmc+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCTxzcGFuIHN0eWxlPSJmb250LXNpemU6IDExcHQ7Ij4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJPC9zcGFuPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJPC9zdHJvbmc+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQk8c3BhbiBzdHlsZT0iZm9udC1zaXplOiAxMXB0OyI+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQk8L3NwYW4+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJPC9wPg0KCQkJCQkJCQk8L3RkPg0KCQkJCQkJCQk8dGQgc3R5bGU9ImJvcmRlci1zdHlsZTogbm9uZSBzb2xpZCBzb2xpZCBub25lOyBib3JkZXItY29sb3I6IC1tb3otdXNlLXRleHQtY29sb3I7IGJvcmRlci13aWR0aDogbWVkaXVtIDFwdCAxcHQgbWVkaXVtOyBwYWRkaW5nOiAwaW4gNS40cHQ7IGJhY2tncm91bmQ6IHJnYigyNDYsIDI0NiwgMjUyKSBub25lIHJlcGVhdCBzY3JvbGwgMCUgNTAlOyB3aWR0aDogMjIxLjRwdDsgLW1vei1iYWNrZ3JvdW5kLWNsaXA6IC1tb3otaW5pdGlhbDsgLW1vei1iYWNrZ3JvdW5kLW9yaWdpbjogLW1vei1pbml0aWFsOyAtbW96LWJhY2tncm91bmQtaW5saW5lLXBvbGljeTogLW1vei1pbml0aWFsOyIgd2lkdGg9IjI5NSIgdmFsaWduPSJ0b3AiPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCTxwPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJPHNwYW4gc3R5bGU9ImZvbnQtc2l6ZTogMTFwdDsiPldpbGRjYXJkIHJlY29yZCB3aGljaCBpcyB1c2VkIHRvIGluY2x1ZGUgYW55IHJlY29yZHMgb3Igc3ViZG9tYWlucyB0aGF0IHlvdSBoYXZlIG5vdCBzcGVjaWZpZWQgdG8gY2F0Y2ggYW55IHR5cG9zIG9yIG1pc3Rha2VzLiA8L3NwYW4+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJPC9wPg0KCQkJCQkJCQk8L3RkPg0KCQkJCQkJPC90cj4NCgkJCQkJCTx0cj4NCgkJCQkJCQkJPHRkIHN0eWxlPSJib3JkZXItc3R5bGU6IG5vbmUgc29saWQgc29saWQ7IGJvcmRlci1jb2xvcjogLW1vei11c2UtdGV4dC1jb2xvcjsgYm9yZGVyLXdpZHRoOiBtZWRpdW0gMXB0IDFwdDsgcGFkZGluZzogMGluIDUuNHB0OyBiYWNrZ3JvdW5kOiByZ2IoMjIzLCAyMjMsIDI0NSkgbm9uZSByZXBlYXQgc2Nyb2xsIDAlIDUwJTsgd2lkdGg6IDIyMS40cHQ7IC1tb3otYmFja2dyb3VuZC1jbGlwOiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IC1tb3otYmFja2dyb3VuZC1vcmlnaW46IC1tb3otaW5pdGlhbDsgLW1vei1iYWNrZ3JvdW5kLWlubGluZS1wb2xpY3k6IC1tb3otaW5pdGlhbDsiIHdpZHRoPSIyOTUiIHZhbGlnbj0idG9wIj4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQk8cD4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCTxzdHJvbmc+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCTxzcGFuIHN0eWxlPSJmb250LXdlaWdodDogbm9ybWFsOyBmb250LXNpemU6IDExcHQ7Ij4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQk8c3BhbiBzdHlsZT0iZm9udC1zaXplOiAxMXB0OyI+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQk8YSBocmVmPSJodHRwczovL3d3dy5uYW1lY2hlYXAuY29tL3N1cHBvcnQva25vd2xlZGdlYmFzZS9hcnRpY2xlLmFzcHgvMzE3LzIyMzcvaG93LWRvLWktYWRkLXR4dHNwZmRraW1kbWFyYy1yZWNvcmRzLWZvci1teS1kb21haW4iIGxpbmt0ZXh0PSJUWFQgcmVjb3JkIiBsaW5rdHlwZT0iQ3VzdG9tIiB0YXJnZXQ9Il9ibGFuayI+VFhUIHJlY29yZDwvYT4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQk8L3NwYW4+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCTwvc3Bhbj4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCTwvc3Ryb25nPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJPHN0cm9uZz4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJPHNwYW4gc3R5bGU9ImZvbnQtc2l6ZTogMTFwdDsiPg0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQk8L3NwYW4+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJCQk8L3N0cm9uZz4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCTxzcGFuIHN0eWxlPSJmb250LXNpemU6IDExcHQ7Ij4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQkJCTwvc3Bhbj4NCgkJCQkJCQkJCQk8L3A+DQoJCQkJCQkJCTwvdGQ+DQoJCQkJCQkJCTx0ZCBzdHlsZT0iYm9yZGVyLXN0eWxlOiBub25lIHNvbGlkIHNvbGlkIG5vbmU7IGJvcmRlci1jb2xvcjogLW1vei11c2UtdGV4dC1jb2xvcjsgYm9yZGVyLXdpZHRoOiBtZWRpdW0gMXB0IDFwdCBtZWRpdW07IHBhZGRpbmc6IDBpbiA1LjRwdDsgYmFja2dyb3VuZDogcmdiKDIyMywgMjIzLCAyNDUpIG5vbmUgcmVwZWF0IHNjcm9sbCAwJSA1MCU7IHdpZHRoOiAyMjEuNHB0OyAtbW96LWJhY2tncm91bmQtY2xpcDogLW1vei1pbml0aWFsOyAtbW96LWJhY2tncm91bmQtb3JpZ2luOiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IC1tb3otYmFja2dyb3VuZC1pbmxpbmUtcG9saWN5OiAtbW96LWluaXRpYWw7IiB3aWR0aD0iMjk1IiB2YWxpZ249InRvcCI+DQoJCQkJCQkJCQkJPHA+VFhUIHJlY29yZCBwcm92aWRlcyB0aGUgYWJpbGl0eSB0byBhc3NvY2lhdGUgc29tZSB0ZXh0IHdpdGggYSBob3N0IG9yIG90aGVyIG5hbWUuIFRoaXMgdHlwZSBvZiBETlMgcmVjb3JkIGlzIHVzdWFsbHkgdXNlZCBmb3IgU1BGIChTZW5kZXIgUG9saWN5IEZyYW1ld29yayksIERLSU0gKERvbWFpbktleXMgSWRlbnRpZmllZCBFLW1haWwpIGFuZCBETUFSQyAoRG9tYWluLWJhc2VkIE1lc3NhZ2UgQXV0aGVudGljYXRpb24sIFJlcG9ydGluZyBhbmQgQ29uZm9ybWFuY2UpIHB1cnBvc2VzLiA8c3BhbiBzdHlsZT0iZm9udC1zaXplOiAxMXB0OyI+PC9zcGFuPjwvcD4NCgkJCQkJCQkJPC90ZD4NCgkJCQkJCTwvdHI+DQoJCQkJPC90Ym9keT4NCgkJPC90YWJsZT4NCgkJPGRpdj4NCgkJCQk8YnIgLz4NCgkJPC9kaXY+DQoJCTxkaXY+DQoJCQkJPGI+Tk9URTwvYj46IFRoZSBtYXhpbXVtIGFtb3VudCBvZiB0aGUgcmVjb3JkcyB0aGF0IGNhbiBiZSBhZGRlZCBmb3IgYSBkb21haW4gcG9pbnRlZCB0byBGcmVlIEROUyBpcyAxNTAgcmVjb3JkcyAoaW5jbHVkaW5nIEEsIEFBQUEsIENOQU1FLCBNWCwgU1JWLCBUWFQsIE5TLCBVUkwpLjxiciAvPjwvZGl2Pg0KCQk8ZGl2Pg0KCQkJCTxiciAvPg0KCQk8L2Rpdj4NCgkJPGRpdj5UaGF0J3MgaXQhIA0KCQkJCQkJCQkJCQ0KCQkJCQkJCQkNCgkJCQkJCQ0KCQkJCQ0KCQkNCgkJDQoJCTwvZGl2Pg0KCQk8cD4NCgkJPC9wPg0KCQk8cCBhbGlnbj0iY2VudGVyIj5JZiB5b3UgaGF2ZSBhbnkgcXVlc3Rpb25zLCBmZWVsIGZyZWUgdG8gY29udGFjdCBvdXIgPGEgaHJlZj0iaHR0cHM6Ly93d3cubmFtZWNoZWFwLmNvbS8vc3VwcG9ydC9saXZlLWNoYXQvZG9tYWlucy5hc3B4IiB0YXJnZXQ9Il9ibGFuayI+U3VwcG9ydCBUZWFtPC9hPi48L3A+DQo=","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"2023-08-29T11:46:26.0000000","LiveDateTime":"1754-02-02T00:00:00.0000000","CreatedDateTime":"2009-01-12T09:18:34.0000000","ApprovalDatetime":"2009-02-16T14:12:25.0000000","RequestCount":93044,"MarkedAsNew":false,"MarkedAsFeatured":false,"RatingValue":3,"CategoryPaths":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryPathDto","Level":1,"CategoryId":34,"CategoryName":"Domains"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryPathDto","Level":2,"CategoryId":51,"CategoryName":"FreeDNS"}],"AssociatedCategories":[{"CategoryId":51,"CategoryName":"FreeDNS","CategoryDisplayName":"DomainsFreeDNS"}],"AssociatedTags":[{"TagId":24339,"Tag":" free dns"},{"TagId":81324,"Tag":"add record"},{"TagId":81325,"Tag":" create dns record with free d"}],"RelatedArticles":[{"ArticleId":537,"PreferedCategoryId":51,"ArticleTypeId":0,"ArticleName":"Can you make DNS active for me before verifying my host settings?","ArticleTypeName":null,"Title":"Can you make DNS active for me before verifying my host settings?","LiveDateTime":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"09/19/2018","MarkedAsNew":false,"MarkedAsFeatured":false},{"ArticleId":547,"PreferedCategoryId":51,"ArticleTypeId":0,"ArticleName":"Is there a limit on the number of times I can change host settings when I use FreeDNS?","ArticleTypeName":null,"Title":"Is there a limit on the number of times I can change host settings when I use FreeDNS?","LiveDateTime":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"04/25/2016","MarkedAsNew":false,"MarkedAsFeatured":false}],"AssociatedMedias":[],"PreferredCategoryId":0,"RootParentCategoryName":"","RootParentCategoryId":0},"status":200,"statusText":"OK"},"/api/v1/ncpl/simplekb/getcategorybycategoryid:\"{\\\"categoryId\\\":51}\"":{"body":{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryDto","Description":"VGhpcyB0b3BpYyBwcm92aWRlcyBoZWxwIHJlZ2FyZGluZyBvdXIgRnJlZSBETlMgb2ZmZXJpbmcuIFdlIG5vdyBwcm92aWRlIHlvdSB3aXRoIGFuIGFkdmFuY2VkIEROUyBvcHRpb24gZm9yIHlvdXIgZG9tYWluIGZyZWUgb2YgY29zdC4gSW5jbHVkZXMgVVJMIGZvcndhcmRpbmcsIEVtYWlsIGZvcndhcmRpbmcgYW5kIER5bmFtaWMgRE5TIGFzIHdlbGwuIDxiciAvPjxiciAvPg==","ParentCategoryId":34,"Parent_Category_Name":"Domains","FriendlyId":null,"ApprovedYN":true,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"CreatedDateTime":"01/10/2009 12:14:54","CurrentCategoryPaths":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryPathDto","Level":1,"CategoryId":34,"CategoryName":"Domains"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryPathDto","Level":2,"CategoryId":51,"CategoryName":"FreeDNS"}],"RelatedCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:RelatedCategoryDto","CategoryId":10,"CategoryName":"DNS Questions"}],"AssociatedArticles":[{"ArticleId":531,"Title":"What is FreeDNS?","ArticleName":"What is FreeDNS?","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"01/11/2021"},{"ArticleId":548,"Title":"Why is this free?","ArticleName":"Why is this free?","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"09/17/2018"},{"ArticleId":532,"Title":"How does FreeDNS work?","ArticleName":"How does FreeDNS work?","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"09/17/2018"},{"ArticleId":549,"Title":"How do I authorize FreeDNS?","ArticleName":"How do I authorize FreeDNS?","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"03/16/2023"},{"ArticleId":536,"Title":"How do I set my domain to use Namecheap's FreeDNS service","ArticleName":"How do I set my domain to use Namecheap's FreeDNS service","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"07/05/2025"},{"ArticleId":542,"Title":"How long will it take for Namecheap to verify my nameserver settings?","ArticleName":"How long will it take for Namecheap to verify my nameserver settings?","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"10/21/2024"},{"ArticleId":534,"Title":"What services do you provide with FreeDNS?","ArticleName":"What services do you provide with FreeDNS?","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"04/28/2016"},{"ArticleId":535,"Title":"What type of DNS records can I manage?","ArticleName":"What type of DNS records can I manage?","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"07/06/2022"},{"ArticleId":544,"Title":"How do I set up host records for a domain when I use FreeDNS?","ArticleName":"How do I set up host records for a domain when I use FreeDNS?","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"08/29/2023"},{"ArticleId":545,"Title":"How do I set up URL redirect when I use your FreeDNS service?","ArticleName":"How do I set up URL redirect when I use your FreeDNS service?","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"04/13/2020"},{"ArticleId":546,"Title":"How do I set up an email redirect when I use your FreeDNS service?","ArticleName":"How do I set up an email redirect when I use your FreeDNS service?","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"09/08/2017"},{"ArticleId":533,"Title":"How reliable are Namecheap's nameservers?","ArticleName":"How reliable are Namecheap's nameservers?","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"04/29/2016"},{"ArticleId":539,"Title":"Can I use Free DNS service as a backup to my current DNS?","ArticleName":"Can I use Free DNS service as a backup to my current DNS?","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"09/10/2018"},{"ArticleId":582,"Title":"How do I transfer a domain to Namecheap with minimal downtime?","ArticleName":"How do I transfer a domain to Namecheap with minimal downtime?","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"01/28/2025"},{"ArticleId":537,"Title":"Can you make DNS active for me before verifying my host settings?","ArticleName":"Can you make DNS active for me before verifying my host settings?","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"09/19/2018"},{"ArticleId":543,"Title":"I forgot to point the host to Namecheap nameservers within the verification period. What do I do now?","ArticleName":"I forgot to point the host to Namecheap nameservers within the verification period. What do I do now?","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"04/25/2016"},{"ArticleId":547,"Title":"Is there a limit on the number of times I can change host settings when I use FreeDNS?","ArticleName":"Is there a limit on the number of times I can change host settings when I use FreeDNS?","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"04/25/2016"},{"ArticleId":33,"Title":"What is Dynamic DNS?","ArticleName":"What is Dynamic DNS?","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"10/23/2020"},{"ArticleId":551,"Title":"How do I set up Dynamic DNS if I’m using the FreeDNS service?","ArticleName":"How do I set up Dynamic DNS if I’m using the FreeDNS service?","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"04/13/2020"},{"ArticleId":28,"Title":"Do you provide any Dynamic DNS clients?","ArticleName":"Do you provide any Dynamic DNS clients?","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"09/22/2022"},{"ArticleId":295,"Title":"Can I use your Dynamic DNS client for a wildcard record?","ArticleName":"Can I use your Dynamic DNS client for a wildcard record?","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"03/15/2021"}],"AssociatedTags":[{"TagId":140,"Tag":"freedns"},{"TagId":25453,"Tag":"Namecheap"}],"CategoryId":51,"CategoryName":"FreeDNS"},"status":200,"statusText":"OK"},"/api/v1/ncpl/simplekb/getcategories:\"{\\\"parentCategoryId\\\":0,\\\"getTree\\\":true}\"":{"body":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2216,"CategoryName":"Spam Protection"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2217,"CategoryName":"Renewal"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2218,"CategoryName":"cPanel SSL Plugin"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2219,"CategoryName":"PHP Configuration"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2221,"CategoryName":"Multi-Domain SSL Certificates"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2222,"CategoryName":"Cancellation"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2223,"CategoryName":"Browser errors"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2224,"CategoryName":"Site Seal, Logo"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2225,"CategoryName":"SEO"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2226,"CategoryName":"Email Migration"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2211,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2227,"CategoryName":"SSL Resellers"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":true,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/cloud-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2228,"CategoryName":"Apps","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2228,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2251,"CategoryName":"Supersonic CDN"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2228,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2298,"CategoryName":"Site Maker"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2228,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":177,"CategoryName":"Google Workspace (formerly G Suite)"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2211,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2229,"CategoryName":"Hosting Resellers"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2232,"CategoryName":"DNSSEC"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2234,"CategoryName":"Google Workspace (formerly G Suite)"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2237,"CategoryName":"Host records setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2238,"CategoryName":"SSL installation errors"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/easywp-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2239,"CategoryName":"EasyWP","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2280,"CategoryName":"Getting Started"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2279,"CategoryName":"General Information"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2281,"CategoryName":"WordPress Migration"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2282,"CategoryName":"Plugins and Themes"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2284,"CategoryName":"WordPress Management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2285,"CategoryName":"SFTP and Database access"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2286,"CategoryName":"Domains questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2288,"CategoryName":"Billing questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2287,"CategoryName":"SSL questions"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2228,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2251,"CategoryName":"Supersonic CDN"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2252,"CategoryName":"InterWorx questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2253,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2254,"CategoryName":"Domains How-To"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2253,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2255,"CategoryName":"Hosting How-To"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2253,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2257,"CategoryName":"Sales & Payments How-To"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2253,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2258,"CategoryName":"cPanel Email How-To"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2260,"CategoryName":"Private Email Contacts and Calendars Setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2253,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2262,"CategoryName":"EasyWP How-To"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"https://download.namecheap.com/assets/img/domainvault-red@2x.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2289,"CategoryName":"Domain Vault","SubCategories":[]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2290,"CategoryName":"CSR code"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2291,"CategoryName":"Webuzo questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2292,"CategoryName":"Browser Extensions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2293,"CategoryName":"Automated SSL management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2228,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2298,"CategoryName":"Site Maker"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":27,"CategoryName":"Getting Started"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/support-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":5,"CategoryName":"General & Support","SubCategories":[]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2200,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":7,"CategoryName":"Billing FAQ"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2209,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":8,"CategoryName":"Transfer Information"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":22,"CategoryName":"Hosting Information"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":38,"CategoryName":"SSL General"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":9,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":45,"CategoryName":"Account Security"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":46,"CategoryName":"Domain Management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2211,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":63,"CategoryName":"Namecheap API"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2228,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":177,"CategoryName":"Google Workspace (formerly G Suite)"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2179,"CategoryName":"Private Email: General Information"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2274,"CategoryName":"General"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2280,"CategoryName":"Getting Started"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2279,"CategoryName":"General Information"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2215,"CategoryName":"Private Email: Mailbox Management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2211,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2196,"CategoryName":"WHMCS module for SSL"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/savings-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2200,"CategoryName":"Checkout & Billing","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2200,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":7,"CategoryName":"Billing FAQ"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2200,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2201,"CategoryName":"Domains Billing"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2200,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":21,"CategoryName":"Hosting Billing"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2200,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":71,"CategoryName":"SSL Certificates Billing"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2200,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2177,"CategoryName":"Private Email"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2200,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2201,"CategoryName":"Domains Billing"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":67,"CategoryName":"Activation"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2209,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":83,"CategoryName":"Transfer to Namecheap"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":9,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":43,"CategoryName":"Profile Management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":10,"CategoryName":"DNS Questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":29,"CategoryName":"cPanel questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2200,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":21,"CategoryName":"Hosting Billing"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":11,"CategoryName":"Dynamic DNS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":9,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":44,"CategoryName":"Account Access"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2209,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":84,"CategoryName":"Transfer to another provider"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":68,"CategoryName":"Validation"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2182,"CategoryName":"cPanel: Software Management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2214,"CategoryName":"Email Forwarding"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2270,"CategoryName":"Routers"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2281,"CategoryName":"WordPress Migration"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2282,"CategoryName":"Plugins and Themes"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2272,"CategoryName":"TV"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2187,"CategoryName":"cPanel: WordPress"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2209,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":219,"CategoryName":"Canceled Transfers"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2200,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":71,"CategoryName":"SSL Certificates Billing"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2176,"CategoryName":"Private Email: DNS Settings"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":69,"CategoryName":"Installation"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/reseller-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":34,"CategoryName":"Domains","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2232,"CategoryName":"DNSSEC"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2234,"CategoryName":"Google Workspace (formerly G Suite)"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2237,"CategoryName":"Host records setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":46,"CategoryName":"Domain Management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":10,"CategoryName":"DNS Questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":11,"CategoryName":"Dynamic DNS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":35,"CategoryName":"Registrations"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2207,"CategoryName":"Renewal questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":36,"CategoryName":"Domains with extended attributes"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":51,"CategoryName":"FreeDNS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":15,"CategoryName":"Namecheap Market"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2208,"CategoryName":"3rd Party Services Setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2278,"CategoryName":"Handshake TLDs"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":35,"CategoryName":"Registrations"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":70,"CategoryName":"Reissuance"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/protection-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":37,"CategoryName":"Domain Privacy Protection","SubCategories":[]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2200,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2177,"CategoryName":"Private Email"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2178,"CategoryName":"Private Email: Webmail Features"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2207,"CategoryName":"Renewal questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2210,"CategoryName":"cPanel Add-ons"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2273,"CategoryName":"Gaming Consoles"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2284,"CategoryName":"WordPress Management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2285,"CategoryName":"SFTP and Database access"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2268,"CategoryName":"macOS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2175,"CategoryName":"Private Email: Client Setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/status-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2209,"CategoryName":"Domain Transfers","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2209,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":8,"CategoryName":"Transfer Information"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2209,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":83,"CategoryName":"Transfer to Namecheap"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2209,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":84,"CategoryName":"Transfer to another provider"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2209,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":219,"CategoryName":"Canceled Transfers"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":48,"CategoryName":"VPS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":36,"CategoryName":"Domains with extended attributes"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":true,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/server-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":12,"CategoryName":"Hosting","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2219,"CategoryName":"PHP Configuration"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2225,"CategoryName":"SEO"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2252,"CategoryName":"InterWorx questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2291,"CategoryName":"Webuzo questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":27,"CategoryName":"Getting Started"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":22,"CategoryName":"Hosting Information"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":29,"CategoryName":"cPanel questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2182,"CategoryName":"cPanel: Software Management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2187,"CategoryName":"cPanel: WordPress"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2210,"CategoryName":"cPanel Add-ons"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":48,"CategoryName":"VPS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2188,"CategoryName":"Dedicated Server"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":30,"CategoryName":"WHM questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":32,"CategoryName":"DNS settings"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":103,"CategoryName":"LVE (CloudLinux)"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":89,"CategoryName":"SSH Access"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":205,"CategoryName":"FTP questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2180,"CategoryName":"MySQL questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2199,"CategoryName":"Hosting Migration"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2194,"CategoryName":"Tips & Tricks"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":239,"CategoryName":"WHMCS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":33,"CategoryName":"SSL Installation"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2171,"CategoryName":"Private Email: Active Sync (Exchange) Setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2188,"CategoryName":"Dedicated Server"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2269,"CategoryName":"iOS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2286,"CategoryName":"Domains questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2288,"CategoryName":"Billing questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2271,"CategoryName":"Linux"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":30,"CategoryName":"WHM questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":31,"CategoryName":"cPanel Email FAQs"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":51,"CategoryName":"FreeDNS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/email-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":93,"CategoryName":"Email service","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2216,"CategoryName":"Spam Protection"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2226,"CategoryName":"Email Migration"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2260,"CategoryName":"Private Email Contacts and Calendars Setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2179,"CategoryName":"Private Email: General Information"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2215,"CategoryName":"Private Email: Mailbox Management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2214,"CategoryName":"Email Forwarding"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2176,"CategoryName":"Private Email: DNS Settings"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2178,"CategoryName":"Private Email: Webmail Features"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2175,"CategoryName":"Private Email: Client Setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2171,"CategoryName":"Private Email: Active Sync (Exchange) Setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":31,"CategoryName":"cPanel Email FAQs"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2186,"CategoryName":"cPanel Email: Client Setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2204,"CategoryName":"Private Email: Video Overview"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":32,"CategoryName":"DNS settings"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":15,"CategoryName":"Namecheap Market"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2186,"CategoryName":"cPanel Email: Client Setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2266,"CategoryName":"Windows"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2287,"CategoryName":"SSL questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2267,"CategoryName":"Android"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2208,"CategoryName":"3rd Party Services Setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2204,"CategoryName":"Private Email: Video Overview"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/security-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":14,"CategoryName":"SSL Certificates","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2217,"CategoryName":"Renewal"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2218,"CategoryName":"cPanel SSL Plugin"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2221,"CategoryName":"Multi-Domain SSL Certificates"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2222,"CategoryName":"Cancellation"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2223,"CategoryName":"Browser errors"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2224,"CategoryName":"Site Seal, Logo"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2238,"CategoryName":"SSL installation errors"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2290,"CategoryName":"CSR code"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2293,"CategoryName":"Automated SSL management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":38,"CategoryName":"SSL General"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":67,"CategoryName":"Activation"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":68,"CategoryName":"Validation"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":69,"CategoryName":"Installation"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":70,"CategoryName":"Reissuance"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":true,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/performance-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":9,"CategoryName":"My Account","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":9,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":45,"CategoryName":"Account Security"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":9,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":43,"CategoryName":"Profile Management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":9,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":44,"CategoryName":"Account Access"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2278,"CategoryName":"Handshake TLDs"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":103,"CategoryName":"LVE (CloudLinux)"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/affiliates-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":55,"CategoryName":"Affiliates","SubCategories":[]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":89,"CategoryName":"SSH Access"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/tools-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2211,"CategoryName":"API & Resellers","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2211,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2227,"CategoryName":"SSL Resellers"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2211,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2229,"CategoryName":"Hosting Resellers"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2211,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":63,"CategoryName":"Namecheap API"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2211,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2196,"CategoryName":"WHMCS module for SSL"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/timer-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2212,"CategoryName":"Legacy Products","SubCategories":[]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":205,"CategoryName":"FTP questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2180,"CategoryName":"MySQL questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2199,"CategoryName":"Hosting Migration"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/premiumdns-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2231,"CategoryName":"PremiumDNS","SubCategories":[]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2194,"CategoryName":"Tips & Tricks"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"https://static.nc-img.com/live-resource/icons/knowledgebase/fastVPN_icon-150px.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2265,"CategoryName":"FastVPN","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2292,"CategoryName":"Browser Extensions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2274,"CategoryName":"General"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2270,"CategoryName":"Routers"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2272,"CategoryName":"TV"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2273,"CategoryName":"Gaming Consoles"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2268,"CategoryName":"macOS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2269,"CategoryName":"iOS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2271,"CategoryName":"Linux"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2266,"CategoryName":"Windows"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2267,"CategoryName":"Android"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":239,"CategoryName":"WHMCS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":33,"CategoryName":"SSL Installation"}],"status":200,"statusText":"OK"}}To set up your host records for a domain that uses FreeDNS, follow the instructions given below:
1. Sign into your Namecheap account (The Sign In option is available in the header of the page).
2. Mouse over the Account option in the upper right corner of the page and choose Domain List or choose Domain List from the left sidebar: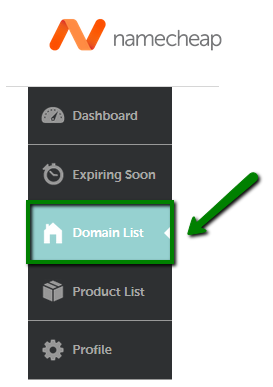
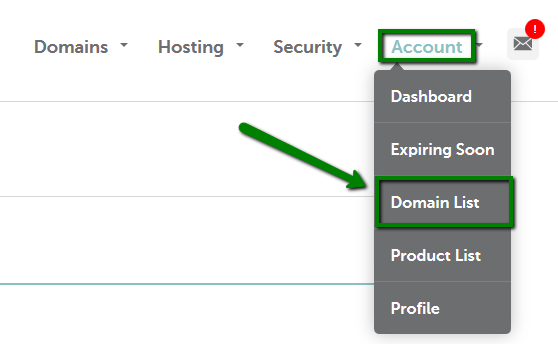
3. Select All Products from the list at the right side of the page: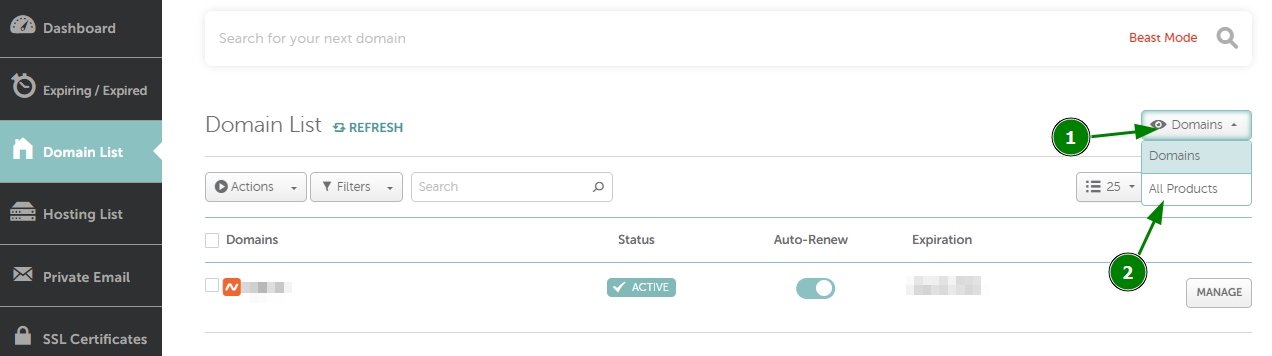
4. Click on the Manage option in front of the domain name:
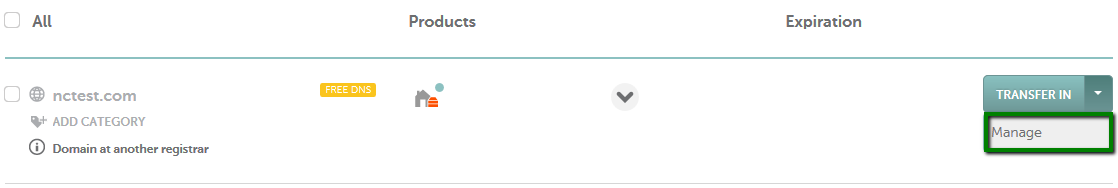
5. Select Advanced DNS at the top of the page. Here you can add domain's host records (including A, CNAME, TXT, SRV, etc.), set up mail settings or enable/disable the Dynamic DNS feature:
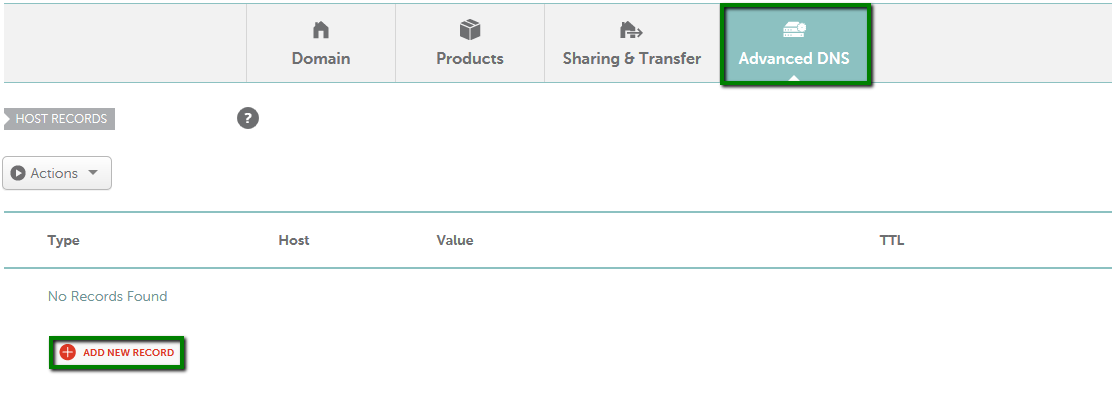
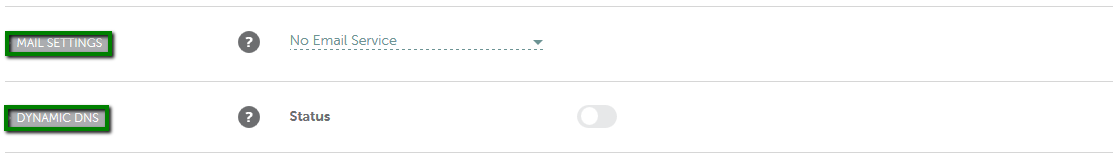
Here is a brief description of all record types that can be added on our DNS servers:
|
Address Record Type
|
Description |
|
Allows you to associate a host with an IPv4 address. The IP address that you use does not have to be on your network. For example: You can have the host record for www pointed to 207.46.130.14 (Microsoft website's address). |
|
|
Allows you to associate a host with an IPv6 address. The IP address that you use does not have to be on your network.
For example:
You can have the host record for www pointed to 2001:0db8:11a3:09d7:1f34:8a2e:07a0:765d |
|
|
Allows you to specify the address of your mail server. When you use a mail record, you must use an IP address in the address field. Note to professional users: Creating a mail record creates both the MX and A records in DNS. Also, when using multiple mail servers, a preference value of 10 is used on all entries. |
|
|
C an be either a host name under your domain name (for example, "mail3") or the name of a mail server (for example, "mail.yahoo.com."). NOTE: When using a mail server name, it should end with a period ("."). (If you forget the period and we recognize the TLD, we will automatically insert one). |
|
|
Associates a host name with another host. The host that you wish to point to does not have to be on your network. For example: You can have the host record for www point to www.microsoft.com. You can also simply use the "@" sign to represent your domain. |
|
|
NS |
Primarily used if you want to break your domain into subdomains. Subdomains indicate you are delegating a portion of a domain name to a different group of nameservers, thus, creating NS records to point the hostname (name of the subdomain) to different nameservers. |
|
Standard method for URL Forwarding. When web users type in your domain name, they are redirected to the web server where your web pages are hosted on. The only drawback of this option is that the URL displayed by the browser is the one on the actual web page, not your domain name. You can overcome this drawback by using the URL Frame method instead. |
|
|
The URL Frame is similar to URL Redirect except that instead of redirecting the client to your web page, the web page is displayed in a frame from our web server. Using this option, the client's browser will display your domain name (for example, www.mydomain.com) while they are using your site and not the actual URL to your page (e.g., home.infospace.com/user33"). |
|
|
Wildcard record which is used to include any records or subdomains that you have not specified to catch any typos or mistakes. |
|
|
TXT record provides the ability to associate some text with a host or other name. This type of DNS record is usually used for SPF (Sender Policy Framework), DKIM (DomainKeys Identified E-mail) and DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting and Conformance) purposes. |
If you have any questions, feel free to contact our Support Team.
Need help? We're always here for you.