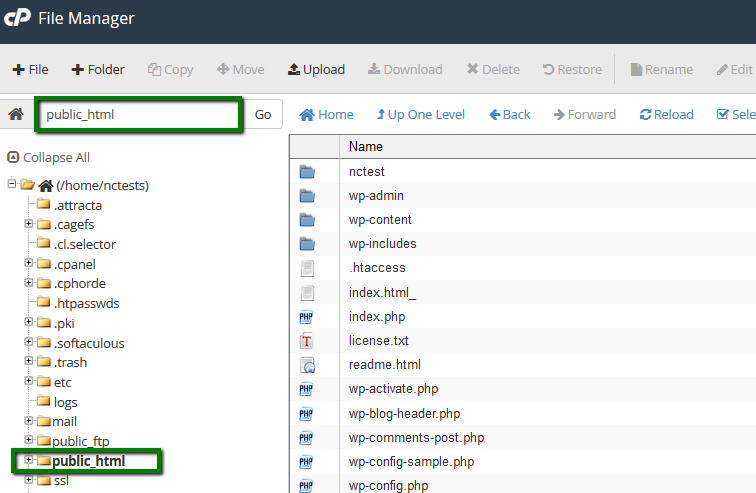
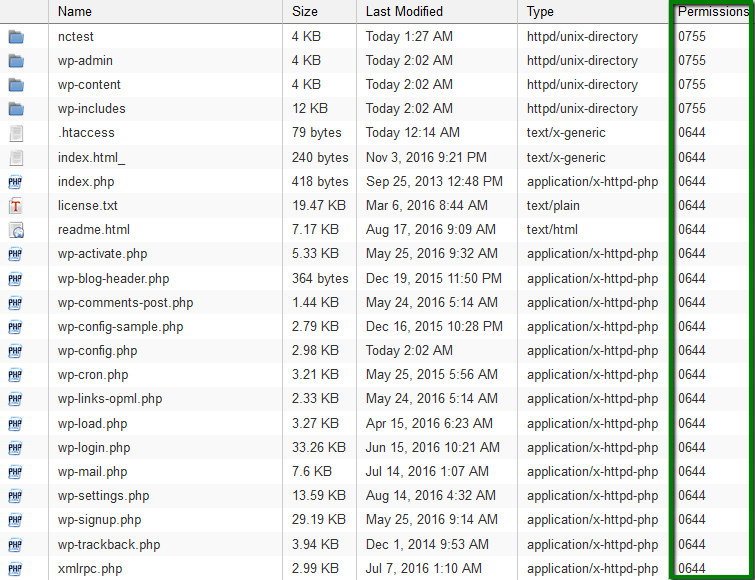
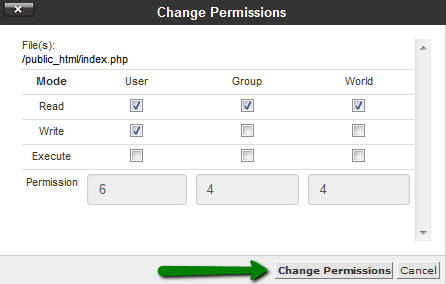
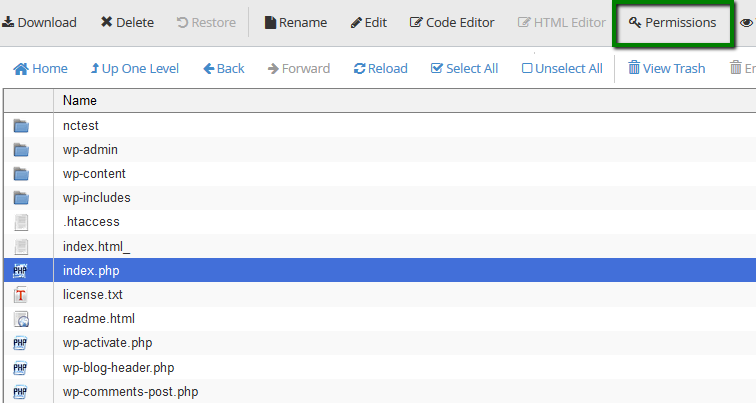
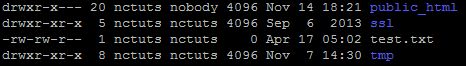
{"/api/v1/ncpl/simplekb/getarticle:\"{\\\"articleId\\\":400,\\\"categoryId\\\":205}\"":{"body":{"Id":400,"FriendlyId":"","ArticleTypeId":3,"Title":"File permissions","ArticleName":"File permissions","ArticleSummary":null,"PreponedSummary":false,"Approved":true,"Body":"RWFjaCBmaWxlIGFuZCBmb2xkZXIgbG9jYXRlZCBpbiB5b3VyIGFjY291bnQgaGFzIGNlcnRhaW4gcGVybWlzc2lvbnMgYXNzaWduZWQuIFRoZXkgZGVmaW5lIHdobyBpcyBhdXRob3JpemVkIHRvIHdyaXRlLCByZWFkIG9yIGV4ZWN1dGUgdGhpcyBmaWxlLjxiciAvPjxiciAvPk9uY2UgaXQgaXMgY3JlYXRlZCBpbiB5b3VyIGNQYW5lbCwgZGVmYXVsdCBwZXJtaXNzaW9ucyBhcmUgYXNzaWduZWQuIEluIG1vc3QgY2FzZXMsIHRoZXJlIGlzIG5vIG5lZWQgdG8gY2hhbmdlIHRoZW0sIGJ1dCBjZXJ0YWluIGluc3RhbGxhdGlvbnMgb3IgdXBkYXRlcyBtYXkgcmVxdWlyZSB0aGF0IGZpbGUgb3IgZm9sZGVyIHBlcm1pc3Npb25zIHNob3VsZCBiZSBjaGFuZ2VkLjxiciAvPjxiciAvPlRoZXJlIGFyZSB0aHJlZSB0eXBlcyBvZiBhY2Nlc3M6IDxiPjxiciAvPjwvYj48dWw+PGxpPjxiPnJlYWQ6PC9iPiB0aGUgZmlsZSBjYW4gb25seSBiZSAgcmVhZC48L2xpPjxsaT48Yj53cml0ZTo8L2I+IHRoZSBmaWxlIGNhbiBiZSBlZGl0ZWQuPC9saT48bGk+PGI+ZXhlY3V0ZTo8L2I+IHRoZSBmaWxlIGNhbiBiZSBleGVjdXRlZCBhcyBhIHByb2dyYW0uPC9saT48L3VsPlRoZXJlIGFyZSB0aHJlZSB0eXBlcyBvZiB1c2VyIGdyb3VwcywgdGhlc2UgYWNjZXNzIHR5cGVzIGNhbiBiZSBhcHBsaWVkIHRvOg0KDQo8YnIgLz48YnIgLz48dWw+PGxpPjxiPm93bmVyOjwvYj4gdGhlIG93bmVyIG9mIHRoZSBmaWxlPC9saT48bGk+PGI+Z3JvdXA6IDwvYj5vdGhlciBmaWxlcyB3aGljaCBhcmUgaW4gdGhlIHNhbWUgZm9sZGVyIG9yIGdyb3VwPC9saT48bGk+PGI+d29ybGQ6PC9iPiBhbnlvbmUgZWxzZTxiciAvPjwvbGk+PC91bD5UaGUgYWNjZXNzIGxldmVsIGlzIGRlZmluZWQgaW4gbnVtYmVyczoNCjxiciAvPjxiciAvPjx1bD48bGk+MCAtIG5vIGFjY2VzcyB0byB0aGUgZmlsZTwvbGk+PGxpPjEgLSBleGVjdXRlIG9ubHk8L2xpPjxsaT4yIC0gd3JpdGUgb25seTwvbGk+PGxpPjMgLSB3cml0ZSBhbmQgZXhlY3V0ZTwvbGk+PGxpPjQgLSByZWFkIG9ubHk8L2xpPjxsaT41IC0gcmVhZCBhbmQgZXhlY3V0ZTwvbGk+PGxpPjYgLSByZWFkIGFuZCB3cml0ZTwvbGk+PGxpPjcgLSByZWFkLCB3cml0ZSBhbmQgZXhlY3V0ZSAoZnVsbCBwZXJtaXNzaW9ucykNCg0KPC9saT48L3VsPlRoZSBmb2xsb3dpbmcgcGVybWlzc2lvbnMgc2hvdWxkIGJlIHNldCBpbiBvcmRlciBmb3IgeW91ciBmaWxlcyB0byBiZSBkaXNwbGF5ZWQgcHJvcGVybHkgaW4gdGhlIGJyb3dzZXI6IDxiciAvPjxiciAvPjx1bD48bGk+Rm9yIGFsbCBIVE1MIGFuZCBpbWFnZSBmaWxlcywgcGVybWlzc2lvbnMgc2hvdWxkIGJlIHNldCB0byA2NDQgKG9yIDA2NDQpLiBUaGV5IHdpbGwgYmUgcmVhZGFibGUgYnkgYWxsIHRoZSB1c2VyIGdyb3VwcyBidXQgb25seSB3cml0YWJsZSBieSB0aGUgdXNlci4gVGhlc2UgcGVybWlzc2lvbnMgYXJlIHNldCBhdXRvbWF0aWNhbGx5IHdoZW4gdGhlIGZpbGUgaXMgY3JlYXRlZC48L2xpPjxsaT5Gb3IgZm9sZGVycywgdGhlIHBlcm1pc3Npb25zIHNob3VsZCBiZSBzZXQgdG8gNzU1IChvciAwNzU1KS4gVGhlIGZvbGRlcnMgd2lsbCBiZSByZWFkYWJsZSBhbmQgZXhlY3V0ZWQgYnkgb3RoZXJzIGJ1dCBvbmx5IHdyaXRhYmxlIGJ5IHRoZSB1c2VyLiBUaGVzZSBwZXJtaXNzaW9ucyBhcmUgc2V0IGF1dG9tYXRpY2FsbHkgd2hlbiB0aGUgZm9sZGVyIGlzIGNyZWF0ZWQuPC9saT48bGk+Rm9yIGFsbCBDR0kgZmlsZXMsIHBlcm1pc3Npb25zIHNob3VsZCBiZSBzZXQgdG8gNzU1IChvciAwNzU1KS4gVGhlIGZpbGVzIHdpbGwgYmUgcmVhZGFibGUgYW5kIGV4ZWN1dGVkIGJ5IG90aGVycyBidXQgb25seSB3cml0YWJsZSBieSB0aGUgdXNlci4gVGhlc2UgcGVybWlzc2lvbnMgYXJlIE5PVCBzZXQgYXV0b21hdGljYWxseSBvbmNlIHRoZSBmaWxlIGlzIGNyZWF0ZWQsIHlvdSBzaG91bGQgYWRqdXN0IHRoZW0gbWFudWFsbHkuIDxiciAvPjwvbGk+PC91bD5JdCBpcyBwb3NzaWJsZSB0byB2aWV3IGZpbGUvZm9sZGVyIHBlcm1pc3Npb25zIGVpdGhlciB2aWEgRmlsZSBNYW5hZ2VyIGluIDxhIGhyZWY9IiNjcGFuZWwiPmNQYW5lbDwvYT4gb3IgdGhlIDxhIGhyZWY9IiNzc2giPlNTSCBjb21tYW5kIGxpbmU8L2E+LiANCg0KPGJyIC8+PGJyIC8+PGJyIC8+PGI+PGEgbmFtZT0iY3BhbmVsIj5jUGFuZWwgRmlsZSBNYW5hZ2VyPGJyIC8+PGJyIC8+PC9hPjwvYj48Yj5GaWxlIE1hbmFnZXI8L2I+IGNhbiBhbHNvIGJlIGFjY2Vzc2VkIHF1aWNrbHkgdmlhIDxhIGhyZWY9Imh0dHBzOi8vd3d3Lm5hbWVjaGVhcC5jb20vc3VwcG9ydC9rbm93bGVkZ2ViYXNlL2FydGljbGUuYXNweC8xMDEzMi8yNy93aGVyZS1jYW4taS1sb2ctaW50by1teS1jcGFuZWwtaG9zdGluZy1hY2NvdW50I2NQYW5lbCUyMFNob3J0Y3V0cyIgbGlua3RleHQ9ImNQYW5lbCBzaG9ydGN1dHMiIGxpbmt0eXBlPSJDdXN0b20iIHRhcmdldD0iX3BhcmVudCI+Y1BhbmVsIFNob3J0Y3V0czwvYT4gaW4gdGhlIE5hbWVjaGVhcCBhY2NvdW50LjxiciAvPjxiciAvPjxiPjxhIG5hbWU9InBhcGVyX2xhbnRlcm4iPmZvciBjUGFuZWwgcGFwZXJfbGFudGVybiB0aGVtZTo8L2E+PC9iPjxiciAvPjxiciAvPjEuIExvZyBpbnRvIHlvdXIgPGI+Y1BhbmVsPC9iPiwgbmF2aWdhdGUgdG8gdGhlIDxiPkZpbGVzPC9iPiBzZWN0aW9uIGFuZCBjbGljayB0aGUgPGI+RmlsZSBNYW5hZ2VyPC9iPiBpY29uOg0KPGJyIC8+PGJyIC8+PGltZyBjbGFzcz0ia2ItaW1hZ2UiIHNyYz0iaHR0cHM6Ly9OYW1lY2hlYXAuc2ltcGxla2IuY29tL1NpdGVDb250ZW50cy8yLTdDMjJENTIzNkE0NTQzRUI4MjdGM0JEODkzNkUxNTNFL21lZGlhL3BsX2ZpbGVfbWFuYWdlcl8xMy5wbmciIC8+PGJyIC8+PGJyIC8+Mi4gTW92ZSB0aGUgZG9jdW1lbnQgcm9vdCBvZiB5b3VyIGRvbWFpbiBuYW1lLg0KPGJyIC8+PGJyIC8+SWYgeW91IG5lZWQgdG8gY2hhbmdlIHBlcm1pc3Npb25zIGZvciB0aGUgbWFpbiBkb21haW4gbmFtZSwgbmF2aWdhdGUgdG8gdGhlIDxiPnB1YmxpY19odG1sPC9iPiBmb2xkZXIuIElmIHlvdSBuZWVkIHRvIGNoYW5nZSBwZXJtaXNzaW9ucyBmb3IgdGhlIGFkZG9uIGRvbWFpbiBuYW1lIGZpbGVzLCBtb3ZlIHRvIHRoZSA8Yj5wdWJsaWNfaHRtbC9hZGRvbmRvbWFpbi5jb208L2I+IGZvbGRlci4NCg0KPGJyIC8+PGJyIC8+V2UgaGF2ZSB0aGUgPGI+cHVibGljX2h0bWw8L2I+IGZvbGRlciBpbiBvdXIgY2FzZToNCg0KPGJyIC8+PGJyIC8+PGltZyBjbGFzcz0ia2ItaW1hZ2UiIHNyYz0iaHR0cHM6Ly9OYW1lY2hlYXAuc2ltcGxla2IuY29tL1NpdGVDb250ZW50cy8yLTdDMjJENTIzNkE0NTQzRUI4MjdGM0JEODkzNkUxNTNFL21lZGlhL3BsX2ZpbGVfbWFuYWdlcl8xOC5wbmciIC8+PGJyIC8+PGJyIC8+My4gWW91IHdpbGwgYmUgYWJsZSB0byBzZWUgY3VycmVudGx5IGFzc2lnbmVkIHBlcm1pc3Npb25zIGluIHRoZSByaWdodC1oYW5kIGNvbHVtbiBjYWxsZWQgPGI+UGVybWlzc2lvbnM8L2I+Og0KPGJyIC8+PGJyIC8+PGltZyBjbGFzcz0ia2ItaW1hZ2UiIHNyYz0iaHR0cHM6Ly9OYW1lY2hlYXAuc2ltcGxla2IuY29tL1NpdGVDb250ZW50cy8yLTdDMjJENTIzNkE0NTQzRUI4MjdGM0JEODkzNkUxNTNFL21lZGlhL3BsX2ZpbGVfbWFuYWdlcl8xOS5wbmciIC8+PGJyIC8+PGJyIC8+NC4gVG8gZWRpdCBjdXJyZW50IHBlcm1pc3Npb25zIGZvciBhIGNlcnRhaW4gZmlsZS9mb2xkZXIsIHJpZ2h0LWNsaWNrIG9uIGl0IGFuZCBjaG9vc2UgPGI+Q2hhbmdlIFBlcm1pc3Npb25zPC9iPi4gQSByZWxhdGVkIHdpbmRvdyB3aWxsIHBvcCB1cDoNCg0KPGJyIC8+PGJyIC8+PGltZyBjbGFzcz0ia2ItaW1hZ2UiIHNyYz0iaHR0cHM6Ly9OYW1lY2hlYXAuc2ltcGxla2IuY29tL1NpdGVDb250ZW50cy8yLTdDMjJENTIzNkE0NTQzRUI4MjdGM0JEODkzNkUxNTNFL21lZGlhL3BsX2ZpbGVfbWFuYWdlcl8yMC5wbmciIC8+PGJyIC8+PGJyIC8+NS4gU2V0IHJlcXVpcmVkIHBlcm1pc3Npb25zIGZvciBlYWNoIHVzZXIgZ3JvdXAgYW5kIHNhdmUgdGhlIGNoYW5nZXMuIEl0IGlzIGFsc28gcG9zc2libGUgdG8gdXNlIHRoZSBzYW1lIGJ1dHRvbiBpbiB0aGUgRmlsZSBNYW5hZ2VyIHVwcGVyLWJhciBtZW51LCB0aGUgPGI+UGVybWlzc2lvbnM8L2I+IG9wdGlvbjoNCg0KPGJyIC8+PGJyIC8+PGltZyBjbGFzcz0ia2ItaW1hZ2UiIHNyYz0iaHR0cHM6Ly9OYW1lY2hlYXAuc2ltcGxla2IuY29tL1NpdGVDb250ZW50cy8yLTdDMjJENTIzNkE0NTQzRUI4MjdGM0JEODkzNkUxNTNFL21lZGlhL3BsX2ZpbGVfbWFuYWdlcl8yMS5wbmciIC8+PGJyIC8+PGJyIC8+PGJyIC8+PGJyIC8+PGJyIC8+PGEgbmFtZT0ic3NoIj48Yj5TU0ggY29tbWFuZCBsaW5lPC9iPjwvYT48YnIgLz48YnIgLz4xLiBPbmNlIGxvZ2dlZCBpbnRvIHlvdXIgYWNjb3VudCB2aWEgPGEgaHJlZj0iaHR0cHM6Ly93d3cubmFtZWNoZWFwLmNvbS9zdXBwb3J0L2tub3dsZWRnZWJhc2UvYXJ0aWNsZS5hc3B4LzEwMTYvODkvaG93LXRvLWFjY2Vzcy1ob3N0aW5nLWFjY291bnQtdmlhLXNzaCI+U1NIPC9hPiwgcnVuIHRoZSBmb2xsb3dpbmcgY29tbWFuZCB0byBjaGVjayB0aGUgcGVybWlzc2lvbnMgYXNzaWduZWQgdG8gZmlsZXMgYW5kIGZvbGRlcnMgaW4gdGhlIGN1cnJlbnQgZGlyZWN0b3J5OiA8aT4gbHMgLWw8L2k+PGJyIC8+PGJyIC8+PGI+Tk9URTogPC9iPllvdSBjYW4gYWxzbyB1c2UgdGhlIDxpPmxzIC1hbGg8L2k+IGNvbW1hbmQgdG8gZ2V0IHRoZSBsaXN0IG9mIEFMTCB0aGUgZmlsZXMgd2l0aGluIHRoZSBkaXJlY3RvcnkgKGV2ZW4gaGlkZGVuIG9uZXMpIGluIGEgaHVtYW4gcmVhZGFibGUgZm9ybWF0IGFuZCB3aXRoIGFkZGl0aW9uYWwgZGV0YWlscy4gDQoNCjxiciAvPjxiciAvPjIuIFRvIGNoZWNrIHRoZSBwZXJtaXNzaW9ucyBhc3NpZ25lZCB0byBmaWxlcyBhbmQgZm9sZGVycyBpbiBhIGNlcnRhaW4gZGlyZWN0b3J5IChub3QgdGhlIG9uZSB5b3UgYXJlIGN1cnJlbnRseSBpbiksIGp1c3QgYWRkIHRoZSBmdWxsIHBhdGggYWZ0ZXIgdGhlIGNvbW1hbmQ6DQo8YnIgLz48YnIgLz48aT5scyAtbCAvaG9tZS8kVVNFUiQvZGVzdGluYXRpb25fZGlyZWN0b3J5DQo8L2k+PGJyIC8+PGJyIC8+d2hlcmUgJFVTRVIkIGlzIHlvdXIgY1BhbmVsIHVzZXJuYW1lIGFuZCBkZXN0aW5hdGlvbl9kaXJlY3RvcnkgaXMgdGhlIHBhdGggdG8gdGhlIGRpcmVjdG9yeSB5b3UgY2hlY2sgcGVybWlzc2lvbnMgaW4uIA0KDQpZb3Ugd2lsbCBnZXQgdGhlIGZvbGxvd2luZyBvdXRwdXQ6DQoNCg0KPGJyIC8+PGJyIC8+PGltZyBjbGFzcz0ia2ItaW1hZ2UiIHNyYz0iaHR0cHM6Ly9OYW1lY2hlYXAuc2ltcGxla2IuY29tL1NpdGVDb250ZW50cy8yLTdDMjJENTIzNkE0NTQzRUI4MjdGM0JEODkzNkUxNTNFL21lZGlhL2ZpbGVwZXJtczQucG5nIiB3aWR0aD0iNDQ1IiBoZWlnaHQ9IjYzIiAvPjxiciAvPjxiciAvPg0KCQkNCjMuIA0KSW4gdGhlIExpbnV4IHNoZWxsIGVudmlyb25tZW50IHBlcm1pc3Npb25zIGFyZSBleHByZXNzZWQgaW4gdGhlIGZvbGxvd2luZyB3YXk6DQo8YnIgLz48YnIgLz48aT5kcnd4ci14ci14DQo8L2k+PGJyIC8+PGJyIC8+VGhlIHZlcnkgZmlyc3QgY2hhcmFjdGVyIHN0YW5kcyBmb3IgdGhlIGZpbGUgdHlwZTogZCAtIGRpcmVjdG9yeS4gTmV4dCB0aHJlZSBsZXR0ZXJzIHJlcHJlc2VudCB0aGUgb3duZXIgcGVybWlzc2lvbnMgKHVzZXIgb25lcyk6DQo8YnIgLz48YnIgLz5yID0gcmVhZA0KPGJyIC8+dyA9IHdyaXRlDQo8YnIgLz54ID0gZXhlY3V0ZSA8YnIgLz4NCi0gPSBubyBwZXJtaXNzaW9uDQoNCjxiciAvPjxiciAvPk5vcm1hbGx5LCB0aGUgT3duZXIgaGFzIGFsbCB0aHJlZSBwZXJtaXNzaW9ucyByZXByZXNlbnRlZCBieSA8Yj5yd3g8L2I+LiA8YnIgLz48YnIgLz5UaGUgbmV4dCB0aHJlZSBjaGFyYWN0ZXJzIGRlZmluZSB0aGUgR3JvdXAgcGVybWlzc2lvbnMsIGFuZCB0aGUgbGFzdCBsZXR0ZXJzIHJlcHJlc2VudCBXb3JsZCBvbmVzLiBJbiBwbGFjZSBvZiDigJh34oCZIHRoZXJlIGlzIGEgaHlwaGVuLCB3aGljaCBtZWFucyB0aGF0IHdyaXRhYmxlIHBlcm1pc3Npb25zIGFyZSBub3QgYWxsb3dlZCBmb3IgR3JvdXAgYW5kIFdvcmxkLg0KDQogICAgPGJyIC8+PGJyIC8+PGI+Tk9URTogPC9iPkNoZWNraW5nIGFuZCB1bmRlcnN0YW5kaW5nIGZpbGUvZm9sZGVyIHBlcm1pc3Npb25zIHZpYSB0aGUgc2hlbGwgZW52aXJvbm1lbnQgaXMgbW9zdGx5IGZvciBhZHZhbmNlZCB1c2Vycy4gSWYgeW91IGhhdmUgbm8gb3RoZXIgaW50ZW50aW9uIHRoYW4gY2hlY2tpbmcvZWRpdGluZyBmaWxlIHBlcm1pc3Npb25zLCBpdCBpcyByZWNvbW1lbmRlZCB0byB1c2UgdGhlIEdVSSBjUGFuZWwgaW50ZXJmYWNlLiANCg0KPGJyIC8+PGJyIC8+PGJyIC8+VGhhdCdzIGl0ITxiciAvPjxiciAvPg0KwqDCoMKgwqDCoMKgwqDCoMKgwqDCoMKgwqDCoCA8YnIgLz7CoMKgwqDCoMKgwqDCoMKgwqDCoMKgwqDCoMKgwqDCoMKgwqDCoMKgwqAgTmVlZCBhbnkgaGVscD8gQ29udGFjdCBvdXIgPGEgaHJlZj0iaHR0cHM6Ly93d3cubmFtZWNoZWFwLmNvbS9oZWxwLWNlbnRlci8iPkhlbHBEZXNrPC9hPjxiciAvPjxiciAvPjxwPjwvcD48cD48L3A+","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"2024-11-11T13:34:26.0000000","LiveDateTime":"1754-02-02T00:00:00.0000000","CreatedDateTime":"2008-08-06T11:32:11.0000000","ApprovalDatetime":"2015-04-22T19:54:05.0000000","RequestCount":112565,"MarkedAsNew":false,"MarkedAsFeatured":false,"RatingValue":2,"CategoryPaths":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryPathDto","Level":1,"CategoryId":12,"CategoryName":"Hosting"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryPathDto","Level":2,"CategoryId":205,"CategoryName":"FTP questions"}],"AssociatedCategories":[{"CategoryId":205,"CategoryName":"FTP questions","CategoryDisplayName":"HostingFTP questions"}],"AssociatedTags":[{"TagId":48,"Tag":" web hosting"},{"TagId":17622,"Tag":" hosting"},{"TagId":20337,"Tag":" files"},{"TagId":20557,"Tag":" change"},{"TagId":25505,"Tag":" permissions"},{"TagId":25607,"Tag":" folders"},{"TagId":25609,"Tag":" check"}],"RelatedArticles":[{"ArticleId":182,"PreferedCategoryId":205,"ArticleTypeId":2,"ArticleName":"What permissions should be used for uploading files?","ArticleTypeName":"Regular","Title":"What permissions should be used for uploading files?","LiveDateTime":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"09/03/2017","MarkedAsNew":false,"MarkedAsFeatured":false},{"ArticleId":1034,"PreferedCategoryId":29,"ArticleTypeId":3,"ArticleName":"How to fix Error You do not have permission to access…","ArticleTypeName":"How_To","Title":"How to fix Error You do not have permission to access…","LiveDateTime":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"06/05/2024","MarkedAsNew":false,"MarkedAsFeatured":false}],"AssociatedMedias":[],"PreferredCategoryId":0,"RootParentCategoryName":"","RootParentCategoryId":0},"status":200,"statusText":"OK"},"/api/v1/ncpl/simplekb/getcategorybycategoryid:\"{\\\"categoryId\\\":205}\"":{"body":{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"Parent_Category_Name":"Hosting","FriendlyId":null,"ApprovedYN":true,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"CreatedDateTime":"02/01/2012 23:43:02","CurrentCategoryPaths":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryPathDto","Level":1,"CategoryId":12,"CategoryName":"Hosting"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryPathDto","Level":2,"CategoryId":205,"CategoryName":"FTP questions"}],"RelatedCategories":[],"AssociatedArticles":[{"ArticleId":9523,"Title":"How to create an FTP account","ArticleName":"How to create an FTP account","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"11/17/2025"},{"ArticleId":10042,"Title":"How to set up WinSCP","ArticleName":"How to set up WinSCP","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"12/10/2018"},{"ArticleId":10351,"Title":"Initial FTP configuration on VPS/Dedicated servers","ArticleName":"Initial FTP configuration on VPS/Dedicated servers","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"12/05/2022"},{"ArticleId":188,"Title":"How to access an account via FTP","ArticleName":"How to access an account via FTP","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"11/17/2025"},{"ArticleId":182,"Title":"What permissions should be used for uploading files?","ArticleName":"What permissions should be used for uploading files?","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"09/03/2017"},{"ArticleId":400,"Title":"File permissions","ArticleName":"File permissions","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"11/11/2024"},{"ArticleId":1279,"Title":"How to set up FileZilla","ArticleName":"How to set up FileZilla","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"11/17/2025"},{"ArticleId":9620,"Title":"How to set up Web Disk on Windows 7","ArticleName":"How to set up Web Disk on Windows 7","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"12/22/2021"},{"ArticleId":1282,"Title":"How to set up Cyberduck","ArticleName":"How to set up Cyberduck","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"12/09/2021"},{"ArticleId":9378,"Title":"How to set up iWeb","ArticleName":"How to set up iWeb","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"12/20/2021"},{"ArticleId":9547,"Title":"How to set up Adobe Muse","ArticleName":"How to set up Adobe Muse","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"12/20/2021"},{"ArticleId":1364,"Title":"How to set up Dreamweaver","ArticleName":"How to set up Dreamweaver","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"12/16/2021"},{"ArticleId":1281,"Title":"How to set up CoreFTP Client","ArticleName":"How to set up CoreFTP Client","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"12/28/2020"},{"ArticleId":9757,"Title":"How to set up CuteFTP","ArticleName":"How to set up CuteFTP","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"12/09/2021"},{"ArticleId":1283,"Title":"Table of the most frequent errors in FTP clients","ArticleName":"Table of the most frequent errors in FTP clients","LiveDateTime":"02/02/1754 00:00:00","NewTillDate":null,"FeaturedTillDate":null,"ModifiedDateTime":"08/17/2018"}],"AssociatedTags":[],"CategoryId":205,"CategoryName":"FTP questions"},"status":200,"statusText":"OK"},"/api/v1/ncpl/simplekb/getcategories:\"{\\\"parentCategoryId\\\":0,\\\"getTree\\\":true}\"":{"body":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2216,"CategoryName":"Spam Protection"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2217,"CategoryName":"Renewal"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2218,"CategoryName":"cPanel SSL Plugin"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2219,"CategoryName":"PHP Configuration"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2221,"CategoryName":"Multi-Domain SSL Certificates"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2222,"CategoryName":"Cancellation"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2223,"CategoryName":"Browser errors"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2224,"CategoryName":"Site Seal, Logo"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2225,"CategoryName":"SEO"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2226,"CategoryName":"Email Migration"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2211,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2227,"CategoryName":"SSL Resellers"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":true,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/cloud-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2228,"CategoryName":"Apps","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2228,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2251,"CategoryName":"Supersonic CDN"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2228,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2298,"CategoryName":"Site Maker"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2228,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":177,"CategoryName":"Google Workspace (formerly G Suite)"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2211,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2229,"CategoryName":"Hosting Resellers"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2232,"CategoryName":"DNSSEC"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2234,"CategoryName":"Google Workspace (formerly G Suite)"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2237,"CategoryName":"Host records setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2238,"CategoryName":"SSL installation errors"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/easywp-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2239,"CategoryName":"EasyWP","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2280,"CategoryName":"Getting Started"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2279,"CategoryName":"General Information"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2281,"CategoryName":"WordPress Migration"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2282,"CategoryName":"Plugins and Themes"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2284,"CategoryName":"WordPress Management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2285,"CategoryName":"SFTP and Database access"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2286,"CategoryName":"Domains questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2288,"CategoryName":"Billing questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2287,"CategoryName":"SSL questions"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2228,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2251,"CategoryName":"Supersonic CDN"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2252,"CategoryName":"InterWorx questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2253,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2254,"CategoryName":"Domains How-To"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2253,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2255,"CategoryName":"Hosting How-To"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2253,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2257,"CategoryName":"Sales & Payments How-To"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2253,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2258,"CategoryName":"cPanel Email How-To"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2260,"CategoryName":"Private Email Contacts and Calendars Setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2253,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2262,"CategoryName":"EasyWP How-To"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"https://download.namecheap.com/assets/img/domainvault-red@2x.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2289,"CategoryName":"Domain Vault","SubCategories":[]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2290,"CategoryName":"CSR code"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2291,"CategoryName":"Webuzo questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2292,"CategoryName":"Browser Extensions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2293,"CategoryName":"Automated SSL management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2228,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2298,"CategoryName":"Site Maker"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":27,"CategoryName":"Getting Started"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/support-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":5,"CategoryName":"General & Support","SubCategories":[]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2200,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":7,"CategoryName":"Billing FAQ"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2209,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":8,"CategoryName":"Transfer Information"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":22,"CategoryName":"Hosting Information"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":38,"CategoryName":"SSL General"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":9,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":45,"CategoryName":"Account Security"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":46,"CategoryName":"Domain Management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2211,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":63,"CategoryName":"Namecheap API"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2228,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":177,"CategoryName":"Google Workspace (formerly G Suite)"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2179,"CategoryName":"Private Email: General Information"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2274,"CategoryName":"General"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2280,"CategoryName":"Getting Started"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2279,"CategoryName":"General Information"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2215,"CategoryName":"Private Email: Mailbox Management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2211,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2196,"CategoryName":"WHMCS module for SSL"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/savings-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2200,"CategoryName":"Checkout & Billing","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2200,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":7,"CategoryName":"Billing FAQ"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2200,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2201,"CategoryName":"Domains Billing"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2200,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":21,"CategoryName":"Hosting Billing"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2200,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":71,"CategoryName":"SSL Certificates Billing"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2200,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2177,"CategoryName":"Private Email"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2200,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2201,"CategoryName":"Domains Billing"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":67,"CategoryName":"Activation"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2209,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":83,"CategoryName":"Transfer to Namecheap"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":9,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":43,"CategoryName":"Profile Management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":10,"CategoryName":"DNS Questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":29,"CategoryName":"cPanel questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2200,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":21,"CategoryName":"Hosting Billing"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":11,"CategoryName":"Dynamic DNS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":9,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":44,"CategoryName":"Account Access"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2209,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":84,"CategoryName":"Transfer to another provider"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":68,"CategoryName":"Validation"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2182,"CategoryName":"cPanel: Software Management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2214,"CategoryName":"Email Forwarding"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2270,"CategoryName":"Routers"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2281,"CategoryName":"WordPress Migration"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2282,"CategoryName":"Plugins and Themes"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2272,"CategoryName":"TV"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2187,"CategoryName":"cPanel: WordPress"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2209,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":219,"CategoryName":"Canceled Transfers"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2200,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":71,"CategoryName":"SSL Certificates Billing"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2176,"CategoryName":"Private Email: DNS Settings"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":69,"CategoryName":"Installation"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/reseller-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":34,"CategoryName":"Domains","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2232,"CategoryName":"DNSSEC"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2234,"CategoryName":"Google Workspace (formerly G Suite)"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2237,"CategoryName":"Host records setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":46,"CategoryName":"Domain Management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":10,"CategoryName":"DNS Questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":11,"CategoryName":"Dynamic DNS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":35,"CategoryName":"Registrations"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2207,"CategoryName":"Renewal questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":36,"CategoryName":"Domains with extended attributes"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":51,"CategoryName":"FreeDNS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":15,"CategoryName":"Namecheap Market"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2208,"CategoryName":"3rd Party Services Setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2278,"CategoryName":"Handshake TLDs"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":35,"CategoryName":"Registrations"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":70,"CategoryName":"Reissuance"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/protection-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":37,"CategoryName":"Domain Privacy Protection","SubCategories":[]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2200,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2177,"CategoryName":"Private Email"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2178,"CategoryName":"Private Email: Webmail Features"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2207,"CategoryName":"Renewal questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2210,"CategoryName":"cPanel Add-ons"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2273,"CategoryName":"Gaming Consoles"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2284,"CategoryName":"WordPress Management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2285,"CategoryName":"SFTP and Database access"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2268,"CategoryName":"macOS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2175,"CategoryName":"Private Email: Client Setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/status-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2209,"CategoryName":"Domain Transfers","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2209,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":8,"CategoryName":"Transfer Information"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2209,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":83,"CategoryName":"Transfer to Namecheap"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2209,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":84,"CategoryName":"Transfer to another provider"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2209,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":219,"CategoryName":"Canceled Transfers"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":48,"CategoryName":"VPS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":36,"CategoryName":"Domains with extended attributes"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":true,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/server-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":12,"CategoryName":"Hosting","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2219,"CategoryName":"PHP Configuration"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2225,"CategoryName":"SEO"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2252,"CategoryName":"InterWorx questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2291,"CategoryName":"Webuzo questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":27,"CategoryName":"Getting Started"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":22,"CategoryName":"Hosting Information"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":29,"CategoryName":"cPanel questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2182,"CategoryName":"cPanel: Software Management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2187,"CategoryName":"cPanel: WordPress"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2210,"CategoryName":"cPanel Add-ons"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":48,"CategoryName":"VPS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2188,"CategoryName":"Dedicated Server"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":30,"CategoryName":"WHM questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":32,"CategoryName":"DNS settings"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":103,"CategoryName":"LVE (CloudLinux)"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":89,"CategoryName":"SSH Access"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":205,"CategoryName":"FTP questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2180,"CategoryName":"MySQL questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2199,"CategoryName":"Hosting Migration"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2194,"CategoryName":"Tips & Tricks"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":239,"CategoryName":"WHMCS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":33,"CategoryName":"SSL Installation"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2171,"CategoryName":"Private Email: Active Sync (Exchange) Setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2188,"CategoryName":"Dedicated Server"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2269,"CategoryName":"iOS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2286,"CategoryName":"Domains questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2288,"CategoryName":"Billing questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2271,"CategoryName":"Linux"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":30,"CategoryName":"WHM questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":31,"CategoryName":"cPanel Email FAQs"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":51,"CategoryName":"FreeDNS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/email-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":93,"CategoryName":"Email service","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2216,"CategoryName":"Spam Protection"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2226,"CategoryName":"Email Migration"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2260,"CategoryName":"Private Email Contacts and Calendars Setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2179,"CategoryName":"Private Email: General Information"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2215,"CategoryName":"Private Email: Mailbox Management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2214,"CategoryName":"Email Forwarding"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2176,"CategoryName":"Private Email: DNS Settings"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2178,"CategoryName":"Private Email: Webmail Features"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2175,"CategoryName":"Private Email: Client Setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2171,"CategoryName":"Private Email: Active Sync (Exchange) Setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":31,"CategoryName":"cPanel Email FAQs"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2186,"CategoryName":"cPanel Email: Client Setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2204,"CategoryName":"Private Email: Video Overview"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":32,"CategoryName":"DNS settings"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":15,"CategoryName":"Namecheap Market"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2186,"CategoryName":"cPanel Email: Client Setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2266,"CategoryName":"Windows"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2239,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2287,"CategoryName":"SSL questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2267,"CategoryName":"Android"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2208,"CategoryName":"3rd Party Services Setup"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":93,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2204,"CategoryName":"Private Email: Video Overview"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/security-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":14,"CategoryName":"SSL Certificates","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2217,"CategoryName":"Renewal"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2218,"CategoryName":"cPanel SSL Plugin"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2221,"CategoryName":"Multi-Domain SSL Certificates"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2222,"CategoryName":"Cancellation"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2223,"CategoryName":"Browser errors"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2224,"CategoryName":"Site Seal, Logo"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2238,"CategoryName":"SSL installation errors"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2290,"CategoryName":"CSR code"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2293,"CategoryName":"Automated SSL management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":38,"CategoryName":"SSL General"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":67,"CategoryName":"Activation"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":68,"CategoryName":"Validation"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":69,"CategoryName":"Installation"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":14,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":70,"CategoryName":"Reissuance"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":true,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/performance-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":9,"CategoryName":"My Account","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":9,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":45,"CategoryName":"Account Security"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":9,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":43,"CategoryName":"Profile Management"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":9,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":44,"CategoryName":"Account Access"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":34,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2278,"CategoryName":"Handshake TLDs"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":103,"CategoryName":"LVE (CloudLinux)"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/affiliates-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":55,"CategoryName":"Affiliates","SubCategories":[]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":89,"CategoryName":"SSH Access"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/tools-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2211,"CategoryName":"API & Resellers","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2211,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2227,"CategoryName":"SSL Resellers"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2211,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2229,"CategoryName":"Hosting Resellers"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2211,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":63,"CategoryName":"Namecheap API"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2211,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2196,"CategoryName":"WHMCS module for SSL"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/timer-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2212,"CategoryName":"Legacy Products","SubCategories":[]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":205,"CategoryName":"FTP questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2180,"CategoryName":"MySQL questions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2199,"CategoryName":"Hosting Migration"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"/assets/img/pictograms/150/premiumdns-red.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2231,"CategoryName":"PremiumDNS","SubCategories":[]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2194,"CategoryName":"Tips & Tricks"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":0,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"https://static.nc-img.com/live-resource/icons/knowledgebase/fastVPN_icon-150px.png","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2265,"CategoryName":"FastVPN","SubCategories":[{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2292,"CategoryName":"Browser Extensions"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2274,"CategoryName":"General"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2270,"CategoryName":"Routers"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2272,"CategoryName":"TV"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2273,"CategoryName":"Gaming Consoles"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2268,"CategoryName":"macOS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2269,"CategoryName":"iOS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2271,"CategoryName":"Linux"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2266,"CategoryName":"Windows"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":2265,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":2267,"CategoryName":"Android"}]},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":239,"CategoryName":"WHMCS"},{"__type":"Nc:SimpleKB:Abstractions:Dtos:CategoryItemDto","ParentCategoryId":12,"TreatAsTopicYN":false,"Description":"","ImageUrl":"","ShortDesc":"","CategoryId":33,"CategoryName":"SSL Installation"}],"status":200,"statusText":"OK"}}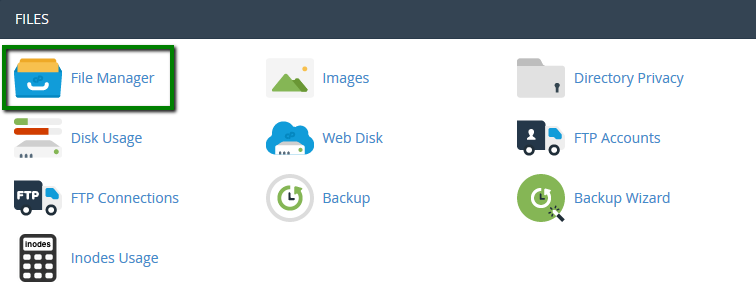
Need help? We're always here for you.