| Resource Type | Nebula/Level 1 Reseller | Galaxy Expert/Level 2 Reseller | Universe Pro/Level 3 Reseller | Level 4 Reseller | One Resold Account
|
|---|
| CPU Limit, % | 800 | 1600 | 2400 | 3200 | 20 |
| Physical Memory Limit, GB | 4 | 8 | 12 | 16 | 1 |
| maxEntryProc limit, N | 80 | 160 | 240 | 320 | 20 |
| IO, MB/s | 2048 | 4096 | 6144 | 8192 | 50 |
As you can see, more expensive packages come with more
resources and are designed for busier websites. You can upgrade your hosting account at any time to a
higher resource package if you run into any of the limits we have in place.
Just contact our team who will be happy to assist.
Checking your
current usage
It is possible to check your current resource Usage via cPanel account. Log into your hosting panel and navigate to
Stats widget on the left:
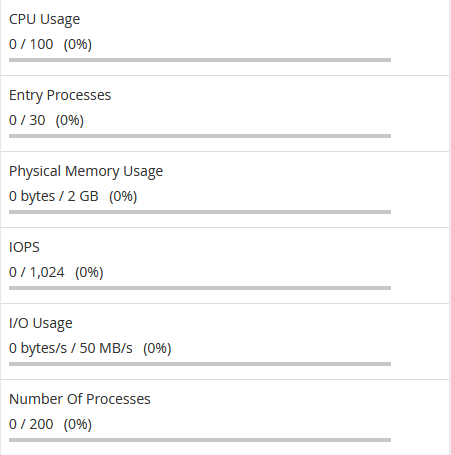
CPU Usage specifies how much of the allocated CPU resources you are currently using. The amount of CPU resources we provide to each account is the percentage of the server’s resources.
If CPU reaches 100% it means that your account is using all of the CPU resources allocated, and any new processes will be put to sleep until existing processes complete. This can cause your website to slow down dramatically and in extreme cases even time out.
Virtual Memory Usage corresponds to the amount of memory, processes can allocate within LVE. When the process tries to allocate memory, CloudLinux checks if the new total virtual memory used by all processes in LVE is within the limit set. If it is not, CloudLinux will prevent memory from being allocated and in most cases this causes the process to fail.
Physical Memory Usage (RAM) is the actual memory allocated for your account. Virtual memory is usually a file on a disk drive that the operating system uses to store information (swap-to-from) when the real memory becomes full, for instance, the page (swap) file on a Linux system. Therefore, if you try to publish a big post, it might take all physical memory to do so, but after some time it will be normalized.
If this value reaches the limit you may begin to experience PHP errors (if applicable) on your website, or in very extreme cases may see a CloudLinux error page. These errors are typically only brief and once the usage has reduced to below the limit, will automatically clear.
Entry Processes is the number of processes that enter your account. It is also known as "Apache concurrent connections". This value defines how many PHP or CGI scripts you can run at a single time. For example, every PHP page that is accessed by a user will usually generate a single entry process. Many people misinterpret this value as “number of visitors you can have on your website at once”. Whilst it is true that each visitor accessing a PHP page will spawn an entry process, these processes usually end so quickly that it is extremely unlikely that 10 will be spawned concurrently and at a single moment unless you had a significantly large number of simultaneous visitors on your website at once.
Number of Processes is the limit similar to the above but includes all processes generated by the account rather than the specific PHP, SSH, or cron jobs. This number is typically very low, even under high activity, as non-PHP tasks execute and complete even more quickly.
I/O Usage (input/output) represents how much I/O (or disk activity) your account is using. Any task which makes use of the servers disk drive (such as reading or writing to the server) will consume I/O. We limit the maximum disk speed of each account to ensure that no single account can saturate the disk drives which will reduce performance for everyone.
Reaching this limit will cause all processes to slow down (to within this limit) and take much longer to complete. Typically you won’t notice this setting ever increase unless you perform something disk intensive like generating a large backup of your account.
Reasons for 'Resource Limit is Reached' errorsWhen your website is hitting one or more of its hosting account resource limits, it can result in 'Resource Limit Reached' errors or slow down the website. What error will appear depends on the resource limit the account is hitting.
The error 508 appears when entry processes hit the limit. If this limit is reached, mod_hostinglimits will not be able to place Apache process into LVE and will return error code 508. This way a very heavy site start returning 508 errors without affecting other users on the server.
However, if the site is limited by CPU or IO - the site will start responding slower.
If the site is limited by memory or number of processes limits - the user will see 500 or 503 errors that server cannot execute the script.
Everything you do on your website, from uploading files, installing plugins to having visitors, uses server resources.
Most common causes of the resource overusage are:
- increased legitimate website traffic: your website may suddenly receive a high amount of visitors and the error will be shown until the number of the visitors is reduced or the resource limits are increased;
- backend scripts or cron jobs: scripts running in the background, including automatic backups and demanding cron jobs can create significant load, which in addition to normal traffic can affect the website performance and cause the overusage;
- web crawlers or search engines indexing your website too often;
- badly written scripts: scripts and plugins that are outdated or incorrectly coded can malfunction and cause loops. Even a few concurrent requests to such scripts can push the website over its resource limits;
- DDOS: Denial of service attack overloads the server, making it unavailable for normal use.
It is possible to check resource usage of your account in more details through another menu:
Navigate to
Metrics section and click on
Resource Usage menu:
 NOTE:
NOTE: If your resource usage limits are being frequently hit, you will see a corresponding warning message under the Dashboard section of the Resource Usage menu with the reference to the exact limits:
Go to the Current Usage section of the menu and choose the desired period in
Timeframe drop-down:
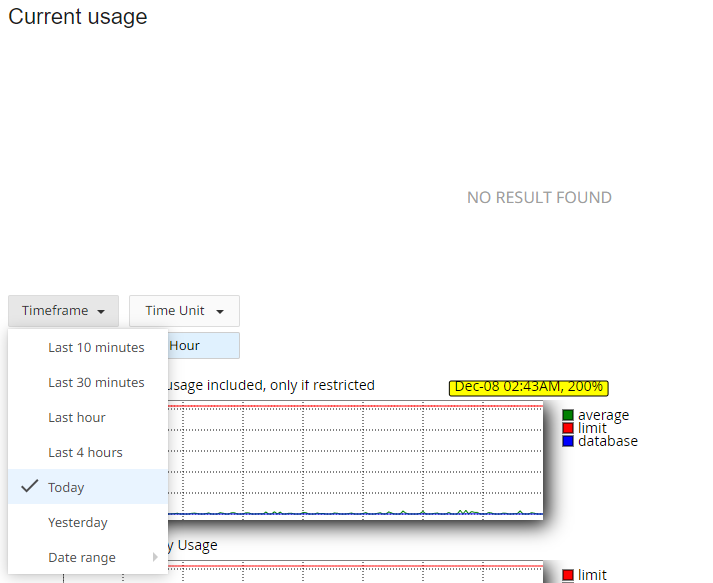
You will see diagrams and tables showing detailed statistics:
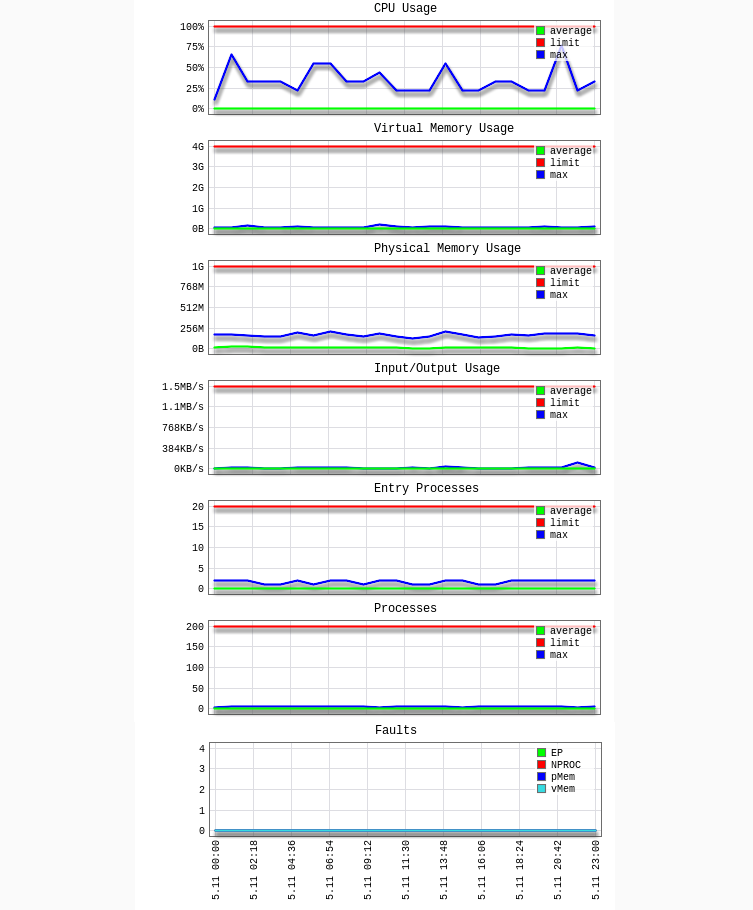
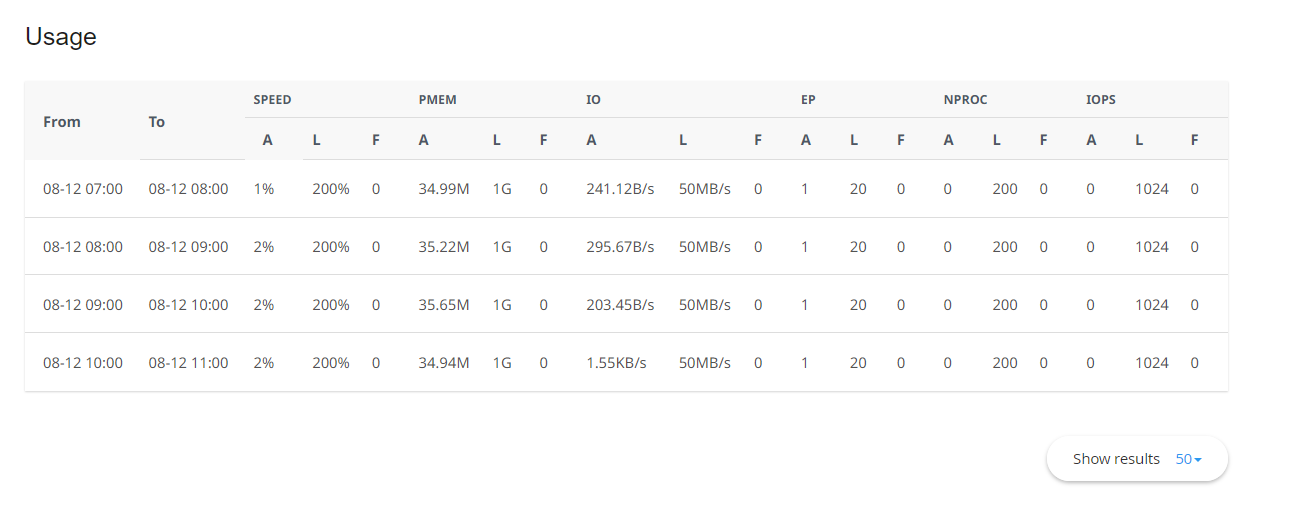 CPU
CPU – CPU limits
vMEM/vM – Virtual Memory limits
pMEM/pM – Physical Memory limits
EP – Entry Processes
nPROC/nP – Number of Processes
IO – Input/Output limits
a – average used
l – limit set for account
m – maximal used
f – failure
That's it!





